This document should be your primary guide for usage of the AMAPI SDK for the purposes of receiving device trust signals.
The AMAPI SDK enables your application (which we may sometimes refer to as a "Companion" app) to access device trust signals from the ADP (Android Device Policy) app. Your app can then use these signals to compute the device's trust state and enact business logic as chosen.
Prerequisites
- Access to the device trust signals is restricted to prevent unauthorized usage. For information on how to apply, go to the device trust signals access page.
- Android Enterprise recommends integrating the Play Integrity suite of APIs into your client application and referring to the result prior to reading and relying on the device trust signals. Devices that fail Play Integrity API checks shouldn't be trusted, nor any signals derived from the device used to make trust posture determinations. You can refer to Play Integrity's documentation for more details.
Integrate with the AMAPI SDK in your application
To access the device trust signals your application has to integrate with the AMAPI SDK. You can find more information about this library and how to add it to your application in the AMAPI SDK integration guide .
Add required permissions
A few of the signals returned from the Device Trust from Android Enterprise API requires that the app declares the same permission that would be required to access this information in the first place, in particular:
| Signal | Required permission |
|---|---|
| Network State | ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE
|
| Screen lock complexity | REQUEST_PASSWORD_COMPLEXITY
|
If these permissions are not included in the app's AndroidManifest.xml
, the
Device Trust from Android Enterprise API will return PERMISSION_ISSUE
in the
metadata of the related signal:
internalDeviceSettings=DeviceSettings{
screenLockComplexity=COMPLEXITY_UNSPECIFIED,
internalScreenLockComplexityMetadata=Metadata{
dataIssues=[
DataIssue{
issueType=PERMISSION_ISSUE,
issueLevel=WARNING,
issueDetails=IssueDetailsCase{none}
}
]
},
For additional details see the list of the available device trust signals .
Steps to access the device trust signals
Applications that want to access the device trust signals are required to verify that the client environment is up to date and update it if necessary.
The steps to access the device trust signals are:
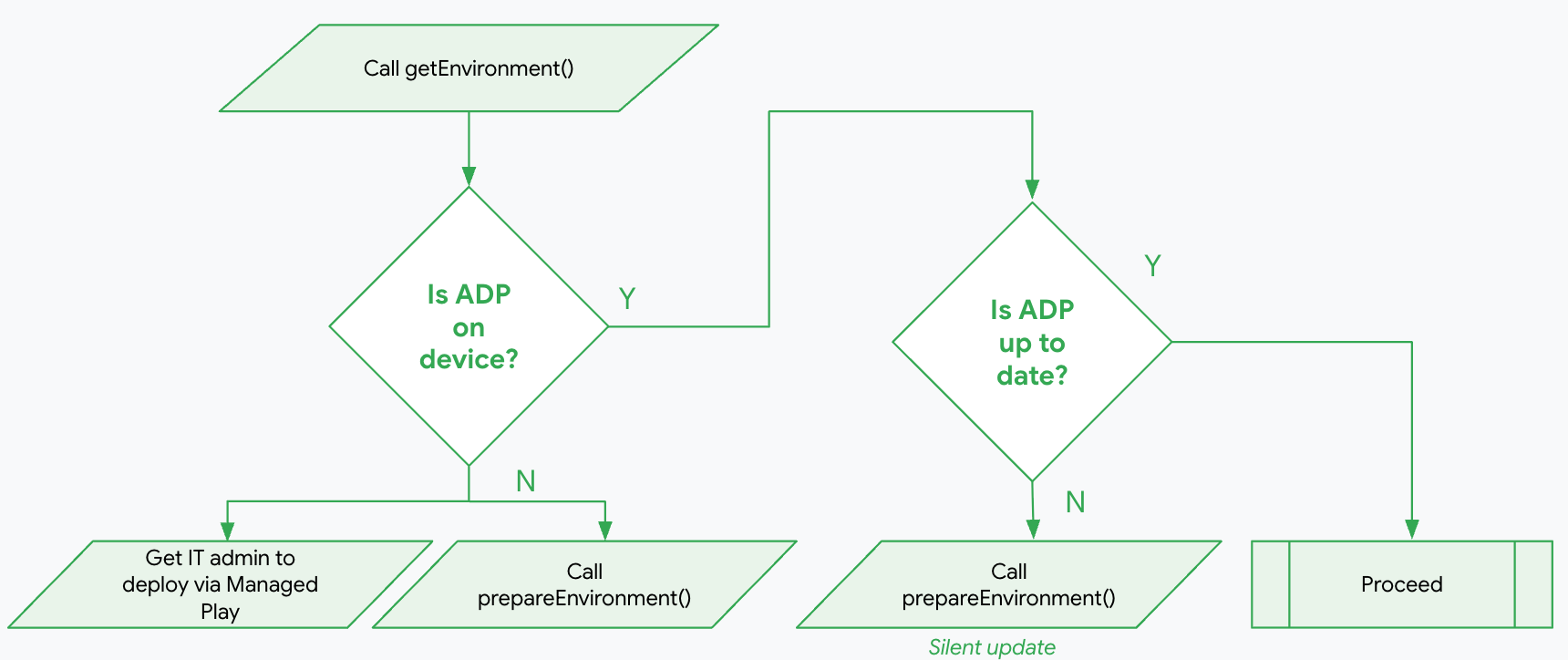
Verify the client environment
The following code example shows how to use getEnvironment
to read the
current state of the ADP app. Your application can then create a deviceClient
to access the device trust signals if the environment is ready
and up to date (see Access device trust signals
).
Kotlin
import com.google.android.managementapi.common.model.Role import com.google.android.managementapi.device.DeviceClient import com.google.android.managementapi.device.DeviceClientFactory import com.google.android.managementapi.device.model.GetDeviceRequest import com.google.android.managementapi.environment.EnvironmentClient import com.google.android.managementapi.environment.EnvironmentClientFactory import com.google.android.managementapi.environment.model.Environment.AndroidDevicePolicyEnvironment.State.INSTALLED import com.google.android.managementapi.environment.model.Environment.AndroidDevicePolicyEnvironment.State.NOT_INSTALLED import com.google.android.managementapi.environment.model.Environment.AndroidDevicePolicyEnvironment.State.READY import com.google.android.managementapi.environment.model.Environment.AndroidDevicePolicyEnvironment.Version.UP_TO_DATE import com.google.android.managementapi.environment.model.GetEnvironmentRequest import com.google.android.managementapi.environment.model.PrepareEnvironmentRequest try { val context = applicationContext val roles = listOf ( Role . builder (). setRoleType ( Role . RoleType . IDENTITY_PROVIDER ). build ()) val request = GetEnvironmentRequest . builder (). setRoles ( roles ). build () val environmentClient = EnvironmentClientFactory . create ( context ) val environmentResponse = environmentClient . getEnvironment ( request ) if ( environmentResponse . hasAndroidDevicePolicyEnvironment ()) { val adpEnvironment = environmentResponse . androidDevicePolicyEnvironment if ( adpEnvironment . state == READY && adpEnvironment . version == UP_TO_DATE ) { // AMAPI Environment State OK, Version OK. Requesting Device signals.. checkDevice ( deviceClient = DeviceClientFactory . create ( context )) } else if ( adpEnvironment . state == INSTALLED ) { // prepareEnvironment should be called, calling // prepareEnvironment won't show the UI prepareEnvironment ( context , environmentClient ) } else if ( adpEnvironment . state == NOT_INSTALLED ) { // prepareEnvironment should be called, calling // prepareEnvironment will show the UI prepareEnvironment ( context , environmentClient ) } } } catch ( e : Exception ) { Log . e ( TAG , "Exception" , e ) }
Java
import static com.google.android.managementapi.environment.model.Environment.AndroidDevicePolicyEnvironment.State.INSTALLED ; import static com.google.android.managementapi.environment.model.Environment.AndroidDevicePolicyEnvironment.State.NOT_INSTALLED ; import static com.google.android.managementapi.environment.model.Environment.AndroidDevicePolicyEnvironment.State.READY ; import static com.google.android.managementapi.environment.model.Environment.AndroidDevicePolicyEnvironment.Version.UP_TO_DATE ; import com.google.android.managementapi.common.model.Role ; import com.google.android.managementapi.device.DeviceClient ; import com.google.android.managementapi.device.DeviceClientFactory ; import com.google.android.managementapi.device.model.Device ; import com.google.android.managementapi.device.model.GetDeviceRequest ; import com.google.android.managementapi.environment.EnvironmentClient ; import com.google.android.managementapi.environment.EnvironmentClientFactory ; import com.google.android.managementapi.environment.model.Environment ; import com.google.android.managementapi.environment.model.Environment.AndroidDevicePolicyEnvironment ; import com.google.android.managementapi.environment.model.GetEnvironmentRequest ; import com.google.android.managementapi.environment.model.PrepareEnvironmentRequest ; import com.google.android.managementapi.environment.model.PrepareEnvironmentResponse ; try { Context context = getApplicationContext (); ImmutableListroles = new ImmutableList . Builder () . add ( Role . builder () . setRoleType ( Role . RoleType . IDENTITY_PROVIDER ) . build ()) . build (); EnvironmentClient environmentClient = EnvironmentClientFactory . create ( context ); GetEnvironmentRequest request = GetEnvironmentRequest . builder () . setRoles ( roles ) . build (); ListenableFuture getEnvironmentFuture = environmentClient . getEnvironmentAsync ( request ); Futures . addCallback ( getEnvironmentFuture , new FutureCallback <> () { @Override public void onSuccess ( Environment environment ) { AndroidDevicePolicyEnvironment adpEnvironment = environment . getAndroidDevicePolicyEnvironment (); AndroidDevicePolicyEnvironment . State state = adpEnvironment . getState (); AndroidDevicePolicyEnvironment . Version version = adpEnvironment . getVersion (); if ( state == READY && version == UP_TO_DATE ) { // AMAPI Environment State OK, Version OK. Requesting Device signals.. DeviceClient deviceClient = DeviceClientFactory . create ( context ); checkDevice ( deviceClient ); } else if ( state == INSTALLED ) { // prepareEnvironment should be called, calling // prepareEnvironment won't show the UI prepareEnvironment ( context , environmentClient ); } else if ( state == NOT_INSTALLED ) { // prepareEnvironment should be called, calling // prepareEnvironment will show the UI prepareEnvironment ( context , environmentClient ); } } @Override public void onFailure ( Throwable t ) { Log . d ( TAG , t . toString ()); } }, MoreExecutors . directExecutor ()); } catch ( Exception e ) { Log . d ( TAG , e . toString ()); }
If the ADP app is installed but not up to date, your application should call prepareEnvironment
to silently update the ADP app without user intervention.
If the ADP app is not installed, your application can call prepareEnvironment
to prompt the user to install the ADP app. See Prepare the client environment
.
Prepare the client environment
-
If the ADP app is already installed, the API will silently update it with no user intervention.
-
If the ADP app is not installed, the API will prompt the user to accept the installation of the ADP app.
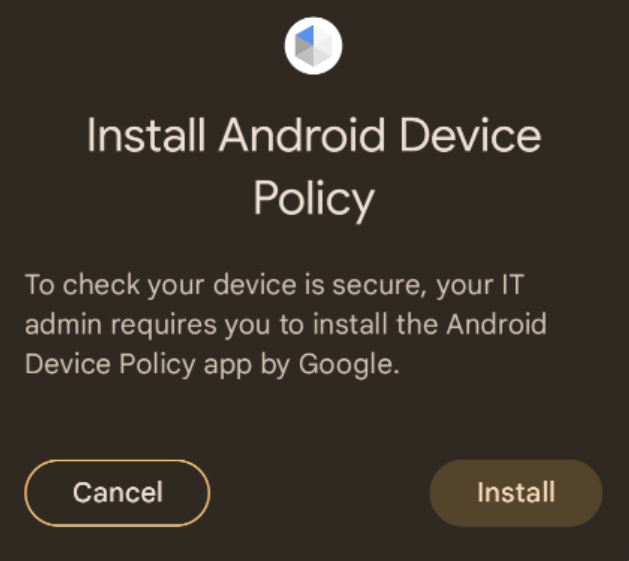
It is possible to register a callback to monitor the user choice. See Track user interaction during the ADP app installation for additional details.
We recommend that the prepareEnvironment
call is done from a foreground
process, during the onboarding UX flow to avoid surprising the user with the Install Android Device Policy
modal dialog.
If calling from a foreground process is not possible, because this is a Web flow
and the Android component has no UI, calling from background is permitted with
the requirement that this happens during the onboarding UX flow.
Once the environment is correctly set up, it is possible to access the device trust Signals. See Access device trust signals .
Kotlin
try { val myNotificationReceiverService = ComponentName ( context , MyNotificationReceiverService :: class . java ) val roles = listOf ( Role . builder (). setRoleType ( Role . RoleType . IDENTITY_PROVIDER ). build ()) val request = PrepareEnvironmentRequest . builder (). setRoles ( roles ). build () val response = environmentClient . prepareEnvironment ( request , myNotificationReceiverService ) val environment = response . environment val adpEnvironment = environment . androidDevicePolicyEnvironment val state = adpEnvironment . state val version = adpEnvironment . version if ( state == READY && version == UP_TO_DATE ) { // Environment is prepared, access device posture signals using // DeviceClient. checkDevice ( deviceClient = DeviceClientFactory . create ( context )) } else { // The prepareEnvironment call failed to prepare Log . w ( TAG , "AMAPI environment was not ready: " + state + " - " + version ) } } catch ( e : java . lang . Exception ) { Log . d ( TAG , e . toString ()) }
Java
try { ComponentName myNotificationReceiverService = new ComponentName ( context , MyNotificationReceiverService . class ); ImmutableListroles = new ImmutableList . Builder () . add ( Role . builder () . setRoleType ( Role . RoleType . IDENTITY_PROVIDER ) . build ()) . build (); PrepareEnvironmentRequest request = PrepareEnvironmentRequest . builder () . setRoles ( roles ) . build (); ListenableFuture environmentFuture = environmentClient . prepareEnvironmentAsync ( request , myNotificationReceiverService ); Futures . addCallback ( environmentFuture , new FutureCallback <> () { @Override public void onSuccess ( PrepareEnvironmentResponse response ) { Environment environment = response . getEnvironment (); AndroidDevicePolicyEnvironment adpEnvironment = environment . getAndroidDevicePolicyEnvironment (); AndroidDevicePolicyEnvironment . State state = adpEnvironment . getState (); AndroidDevicePolicyEnvironment . Version version = adpEnvironment . getVersion (); if ( state == READY && version == UP_TO_DATE ) { // AMAPI Environment State OK, Version OK. Requesting Device signals.. DeviceClient deviceClient = DeviceClientFactory . create ( context ); checkDevice ( deviceClient ); } else { // The prepareEnvironment call failed to prepare Log . w ( TAG , "AMAPI environment was not ready: " + adpEnvironment . getState () + " - " + adpEnvironment . getVersion () ); } } @Override public void onFailure ( @NonNull Throwable t ) { // Handle the error Log . d ( TAG , "AMAPI response did not contain an ADP environment" ); } }, MoreExecutors . directExecutor ()); } catch ( Exception e ) { Log . d ( TAG , e . toString ()); }
Access device trust signals
To Access the device trust signals you are interested in, you can use the deviceClient
instance seen in the previous step to request the Device
object.
Kotlin
try { kotlin . runCatching { deviceClient . getDeviceAwait ( GetDeviceRequest . getDefaultInstance ()) }. onFailure { t -> Log . d ( TAG , t . toString ()) }. onSuccess { device -> // Access device posture signals available in device val deviceString = device . toString () Log . d ( TAG , deviceString ) } } catch ( e : java . lang . Exception ) { Log . d ( TAG , e . toString ()) }
Java
try { ListenableFuturedeviceFuture = deviceClient . getDevice ( GetDeviceRequest . getDefaultInstance ()); Futures . addCallback ( deviceFuture , new FutureCallback () { @Override public void onSuccess ( Device device ) { // Access device posture signals available in device String deviceString = device . toString (); Log . d ( TAG , deviceString ); } @Override public void onFailure ( Throwable t ) { Log . d ( TAG , Log . d ( TAG , t . toString ()); } }, MoreExecutors . directExecutor ()); } catch ( Exception e ) { Log . d ( TAG , e . toString ()); }
Track user interaction during ADP app installation
If the device needs to install the ADP app during the prepareEnvironment
your
application can track the user interaction implementing a NotificationReceiverService
to receive notifications overriding getPrepareEnvironmentListener
:
Kotlin
import android.util.Log import com.google.android.managementapi.environment.EnvironmentListener import com.google.android.managementapi.environment.model.EnvironmentEvent.EventCase.Kind.ANDROID_DEVICE_POLICY_INSTALL_CONSENT_ACCEPTED import com.google.android.managementapi.environment.model.EnvironmentEvent import com.google.android.managementapi.notification.NotificationReceiverService class MyNotificationReceiverService : NotificationReceiverService () { override fun getPrepareEnvironmentListener (): EnvironmentListener { return MyEnvironmentListener () } } class MyEnvironmentListener : EnvironmentListener { override fun onEnvironmentEvent ( event : EnvironmentEvent ) { if ( event . event . kind == ANDROID_DEVICE_POLICY_INSTALL_CONSENT_ACCEPTED ) { Log . d ( TAG , "User provided install consent" ) } else { Log . d ( TAG , "User rejected install consent" ) } } companion object { private val TAG : String = MyEnvironmentListener :: class . java . simpleName } }
Java
import static com.google.android.managementapi.environment.model.EnvironmentEvent.EventCase.Kind.ANDROID_DEVICE_POLICY_INSTALL_CONSENT_ACCEPTED ; import android.util.Log ; import androidx.annotation.NonNull ; import com.google.android.managementapi.environment.EnvironmentListener ; import com.google.android.managementapi.environment.model.EnvironmentEvent ; import com.google.android.managementapi.notification.NotificationReceiverService ; class MyNotificationReceiverService extends NotificationReceiverService { @NonNull @Override protected EnvironmentListener getPrepareEnvironmentListener () { return new MyEnvironmentListener (); } } class MyEnvironmentListener implements EnvironmentListener { final private String TAG = MyEnvironmentListener . class . getSimpleName (); @Override public void onEnvironmentEvent ( EnvironmentEvent event ) { if ( event . getEvent (). getKind () == ANDROID_DEVICE_POLICY_INSTALL_CONSENT_ACCEPTED ) { Log . d ( TAG , "User provided install consent" ); } else { Log . d ( TAG , "User rejected install consent" ); } } }
Known issues
There are no known issues at the moment.


