AI-generated Key Takeaways
-
Google Ads has two account types: manager accounts and advertiser accounts, which can be linked in a directed acyclic graph structure with advertiser accounts at the leaf level.
-
Users can be granted direct access to an advertiser account or indirect access through a linked manager account.
-
When making API calls, the
login-customer-idheader specifies the root account to determine authorization and access levels, and can be omitted if the user has direct access to the target account. -
User roles in Google Ads are followed by the API and are inherited through the account hierarchy, with the
login-customer-idresolving conflicting roles.
There are two types of Google Ads accounts: Google Ads manager accounts and Google Ads advertiser accounts (also known as customer or client accounts). Manager accounts can manage other Google Ads manager accounts or Google Ads advertiser accounts. You can link an advertiser account to a manager account and then manage the advertiser account through the manager account. The overall linked structure is a directed acyclic graph with advertiser accounts at the leaf level.
You can give individual users or service accounts access to Google Ads accounts. There are two ways to give users access to an advertiser account:
- Grant the user direct access to the advertiser account by inviting them to that account.
- Grant the user indirect access to the advertiser account by inviting them to a manager account linked to that account. The user gains access to the advertiser account since the manager account has access to all the accounts linked under it.
You can also assign user roles when you invite a user to manage an account.
Consider the following account hierarchy. Assume that all the users have Standard Access.
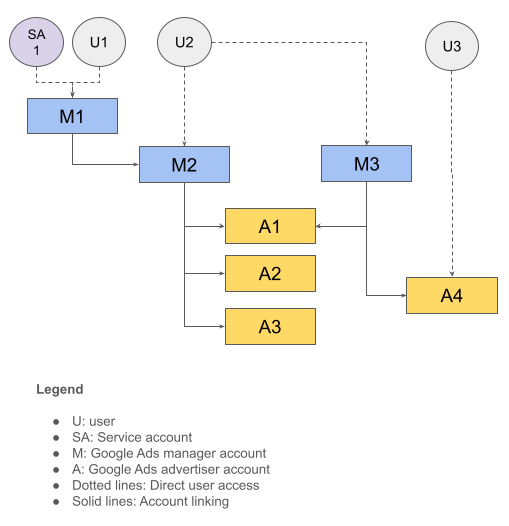
The following table summarizes this account structure.
| User | Has direct access to | Has indirect access to |
|---|---|---|
|
U1, SA1
|
M1 | M2, A1, A2, A3 |
|
U2
|
M2, M3 | A1, A2, A3, A4 |
|
U3
|
A4 |
Login customer ID
A user may have access to multiple account hierarchies. When making an API call
in such cases, you need to specify the root account to be used to correctly
determine the authorization and account access levels. This is done by
specifying a login-customer-id
header as part of the API request.
The following table uses the account hierarchy from the previous example to show what login customer IDs you can use, and the corresponding list of accounts that you can make calls to.
| User | Login Customer ID to use | Accounts to make API calls to |
|---|---|---|
|
U1, SA1
|
M1 | M1, M2, A1, A2, A3 |
|
U2
|
M2 | M2, A1, A2, A3 |
|
U2
|
M3 | M3, A1, A4 |
|
U3
|
A4 | A4 |
You can skip providing the login-customer-id
header if the user has direct
access to the Google Ads account that you are making calls to. For example, you
don't need to specify login-customer-id
header when using U3
credentials to
make a call to A4
, since the Google Ads servers can correctly determine the access
level from the customer ID ( A4
).
If you are using one of our client libraries, then use the following settings to
specify login-customer-id
header.
Java
Add the following setting to your ads.properties
file.
api.googleads.loginCustomerId
=
INSERT_LOGIN_CUSTOMER_ID_HERE
C#
Add the following setting when you initialize the GoogleAdsConfig
object
and use it to create a GoogleAdsClient
object.
GoogleAdsConfig
config
=
new
GoogleAdsConfig
()
{
...
LoginCustomerId
=
******
};
GoogleAdsClient
client
=
new
GoogleAdsClient
(
config
);
PHP
Add the following setting to your google_ads_php.ini
file.
[GOOGLE_ADS]
loginCustomerId
=
"INSERT_LOGIN_CUSTOMER_ID_HERE"
Python
Add the following setting to your google-ads.yaml
file.
login_customer_id
:
INSERT_LOGIN_CUSTOMER_ID_HERE
Ruby
Add the following setting to your google_ads_config.rb
file.
Google
::
Ads
::
GoogleAds
::
Config
.
new
do
|
c
|
c
.
login_customer_id
=
'INSERT_LOGIN_CUSTOMER_ID_HERE'
end
Create a GoogleAdsClient
instance by passing the path to where you keep
this file.
client
=
Google
::
Ads
::
GoogleAds
::
GoogleAdsClient
.
new
(
'path/to/google_ads_config.rb'
)
Perl
Add the following setting to your googleads.properties
file.
loginCustomerId
=
INSERT_LOGIN_CUSTOMER_ID_HERE
curl
Specify the following command line argument when running the curl
command.
-H "login-customer-id: LOGIN_CUSTOMER_ID"
You can use the CustomerService.ListAccessibleCustomers
method to
retrieve the list of accounts that a user has direct access to. These accounts
can be used as valid values for the login-customer-id
header.
Java
private void runExample ( GoogleAdsClient client ) { // Optional: Change credentials to use a different refresh token, to retrieve customers // available for a specific user. // // UserCredentials credentials = // UserCredentials.newBuilder() // .setClientId("INSERT_OAUTH_CLIENT_ID") // .setClientSecret("INSERT_OAUTH_CLIENT_SECRET") // .setRefreshToken("INSERT_REFRESH_TOKEN") // .build(); // // client = client.toBuilder().setCredentials(credentials).build(); try ( CustomerServiceClient customerService = client . getLatestVersion (). createCustomerServiceClient ()) { ListAccessibleCustomersResponse response = customerService . listAccessibleCustomers ( ListAccessibleCustomersRequest . newBuilder (). build ()); System . out . printf ( "Total results: %d%n" , response . getResourceNamesCount ()); for ( String customerResourceName : response . getResourceNamesList ()) { System . out . printf ( "Customer resource name: %s%n" , customerResourceName ); } } }
C#
public void Run ( GoogleAdsClient client ) { // Get the CustomerService. CustomerServiceClient customerService = client . GetService ( Services . V22 . CustomerService ); try { // Retrieve the list of customer resources. string [] customerResourceNames = customerService . ListAccessibleCustomers (); // Display the result. foreach ( string customerResourceName in customerResourceNames ) { Console . WriteLine ( $"Found customer with resource name = '{customerResourceName}'." ); } } catch ( GoogleAdsException e ) { Console . WriteLine ( "Failure:" ); Console . WriteLine ( $"Message: {e.Message}" ); Console . WriteLine ( $"Failure: {e.Failure}" ); Console . WriteLine ( $"Request ID: {e.RequestId}" ); throw ; } }
PHP
public static function runExample(GoogleAdsClient $googleAdsClient) { $customerServiceClient = $googleAdsClient->getCustomerServiceClient(); // Issues a request for listing all accessible customers. $accessibleCustomers = $customerServiceClient->listAccessibleCustomers(new ListAccessibleCustomersRequest()); print 'Total results: ' . count($accessibleCustomers->getResourceNames()) . PHP_EOL; // Iterates over all accessible customers' resource names and prints them. foreach ($accessibleCustomers->getResourceNames() as $resourceName) { /** @var string $resourceName */ printf("Customer resource name: '%s'%s", $resourceName, PHP_EOL); } }


