Page Summary
-
To utilize data-driven styling for datasets, obtain an API key, enable necessary APIs (Maps JavaScript API and Maps Datasets API), and create a map ID associated with a vector-based map style.
-
Initialization involves providing the map ID during map instantiation and loading the Maps JavaScript API with the
v=betaparameter in the script tag. -
For troubleshooting, optionally use the
mapcapabilities_changedlistener to verify map capabilities, such as a valid map ID linked to a vector map, ensuring data-driven styling functionality. -
After setup, proceed to create and upload a dataset to leverage data-driven styling within your maps.
Follow these steps to get set up with the data-driven styling for datasets.
Get an API key and enable APIs
Before using the data-driven styling for datasets, you need: Google Cloud project with a billing account, and both the Maps JavaScript API and the Maps Datasets API enabled. To learn more, see Set up your Google Cloud project .
Enable the Maps JavaScript API
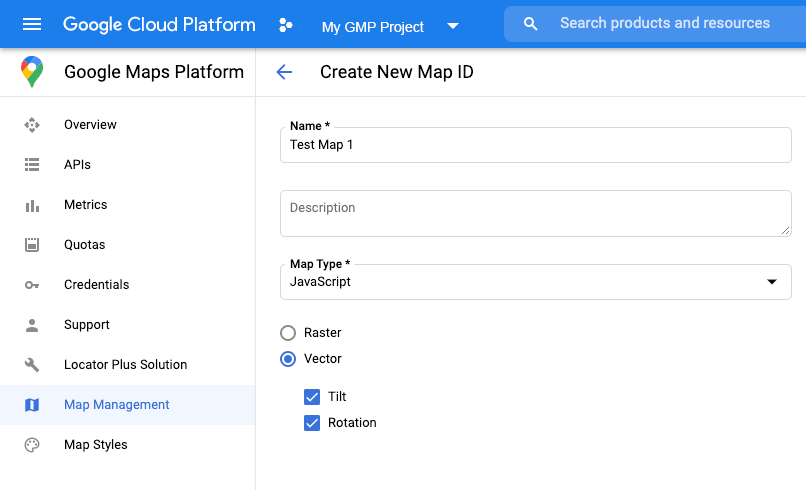
Create a map ID
To create a new map ID , follow the steps in Cloud customization . Set the Map type to JavaScript, and select the Vectoroption.
Provide a map ID using the mapId
property when you instantiate the map .
The map ID must correspond to the map style that is associated with the dataset
to display.
const position = new google . maps . LatLng ( 40.75 , - 74.05 ); const map = new google . maps . Map ( document . getElementById ( 'map' ), { zoom : 11 , center : position , mapId : 'YOUR_MAP_ID' , });
Create a new map style
To create a new map style, follow the instructions in Create and use map styles to create the style, and associate the style with the map ID you just created .
Update your map initialization code
To use the data-driven styling for datasets, first load the
Maps JavaScript API, by adding the inline bootstrap loader to
your application code, as shown here
(use v=beta
in your API script
tag):
< script > ( g =>{ var h , a , k , p = "The Google Maps JavaScript API" , c = "google" , l = "importLibrary" , q = "__ib__" , m = document , b = window ; b = b [ c ] || ( b [ c ] = {}); var d = b . maps || ( b . maps = {}), r = new Set , e = new URLSearchParams , u = ()=> h || ( h = new Promise ( async ( f , n )=>{ await ( a = m . createElement ( "script" )); e . set ( "libraries" ,[... r ] + "" ); for ( k in g ) e . set ( k . replace ( /[A-Z]/g , t => "_" + t [ 0 ]. toLowerCase ()), g [ k ]); e . set ( "callback" , c + ".maps." + q ); a . src = `https://maps. ${ c } apis.com/maps/api/js?` + e ; d [ q ] = f ; a . onerror = ()=> h = n ( Error ( p + " could not load." )); a . nonce = m . querySelector ( "script[nonce]" ) ? . nonce || "" ; m . head . append ( a )})); d [ l ] ? console . warn ( p + " only loads once. Ignoring:" , g ) : d [ l ] = ( f ,... n )=> r . add ( f ) && u (). then (()=> d [ l ]( f ,... n ))})({ key : " YOUR_API_KEY " , v : "weekly" , // Use the 'v' parameter to indicate the version to use (weekly, beta, alpha, etc.). // Add other bootstrap parameters as needed, using camel case. }); < /script >
Check map capabilities (optional)
Data-driven styling for datasets requires a map ID. If the map ID is missing,
or an invalid map ID is passed, data features cannot load. As a
troubleshooting step, you can add a mapcapabilities_changed
listener to
subscribe to map capability changes. This will indicate whether the following
conditions have been met:
- A valid map ID is in use.
- The map ID is associated with a vector map.
Using Map Capabilities is optional, and recommended only for testing and troubleshooting purposes, or for runtime fallback purposes.
// Optional: subscribe to map capability changes. map . addListener ( 'mapcapabilities_changed' , () => { const mapCapabilities = map . getMapCapabilities (); if ( ! mapCapabilities . isDataDrivenStylingAvailable ) { // Data-driven styling is *not* available, add a fallback. // Existing feature layers are also unavailable. } });


