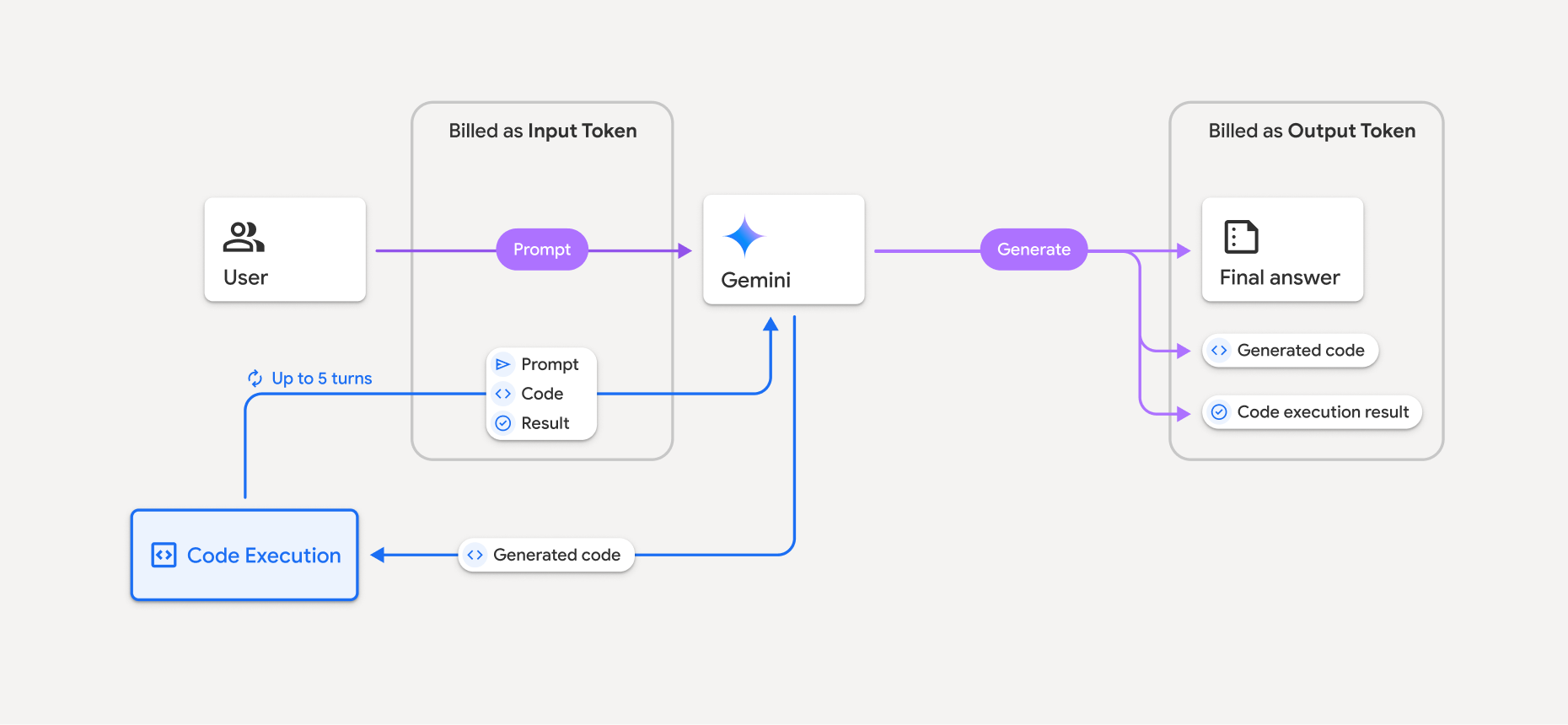
Code execution is a tool that enables the model to generate and run Python code. The model can learn iteratively from the code execution results until it arrives at a final output.
You can use code execution to build features that benefit from code-based reasoning and that generate text output. For example, you could use code execution to solve equations or process text. You can also use the libraries included in the code execution environment to perform more specialized tasks.
Just like with all tools that you provide to the model, the model decides when to use code execution.
Comparison of code execution versus function calling
Code execution and function calling are similar features. In general, you should prefer to use code execution if the model can handle your use case. Code execution is also simpler to use because you just enable it.
Here are some additional differences between code execution and function calling:
| Code execution | Function calling |
|---|---|
| Use code execution if you want the model to write and run Python code for you and return the result. | Use function calling if you already have your own functions that you want to run locally. |
| Code execution lets the model run code in the API backend in a fixed, isolated environment. | Function calling lets you run the functions that the model requests, in whatever environment you want. |
| Code execution resolves in a single request. Although you can optionally use code execution with the chat capability, there's no requirement. | Function calling requires an additional request to send back the output from each function call. Thus, you're required to use the chat capability. |
Supported models
-
gemini-3-pro-preview -
gemini-3-flash-preview -
gemini-2.5-pro -
gemini-2.5-flash -
gemini-2.5-flash-lite -
gemini-2.0-flash-001(and its auto-updated aliasgemini-2.0-flash)
Use code execution
You can use code execution with both text-only and multimodal input, but the response will always be text or code only.
Before you begin
Click your Gemini API provider to view provider-specific content and code on this page.
If you haven't already, complete the getting started guide
, which describes how to
set up your Firebase project, connect your app to Firebase, add the SDK,
initialize the backend service for your chosen Gemini API
provider, and
create a GenerativeModel
instance.
For testing and iterating on your prompts, we recommend using Google AI Studio .
Enable code execution
In that section, you'll also click a button for your chosen Gemini API provider so that you see provider-specific content on this page.
When you create the GenerativeModel
instance, provide CodeExecution
as a
tool that the model can use to generate its response. This allows the model to
generate and run Python code.
Swift
import
FirebaseAILogic
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
let
ai
=
FirebaseAI
.
firebaseAI
(
backend
:
.
googleAI
())
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
let
model
=
ai
.
generativeModel
(
modelName
:
" GEMINI_MODEL_NAME
"
,
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools
:
[.
codeExecution
()]
)
let
prompt
=
"""
What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers?
Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.
"""
let
response
=
try
await
model
.
generateContent
(
prompt
)
guard
let
candidate
=
response
.
candidates
.
first
else
{
print
(
"No candidates in response."
)
return
}
for
part
in
candidate
.
content
.
parts
{
if
let
textPart
=
part
as
?
TextPart
{
print
(
"Text =
\(
textPart
.
text
)
"
)
}
else
if
let
executableCode
=
part
as
?
ExecutableCodePart
{
print
(
"Code =
\(
executableCode
.
code
)
, Language =
\(
executableCode
.
language
)
"
)
}
else
if
let
executionResult
=
part
as
?
CodeExecutionResultPart
{
print
(
"Outcome =
\(
executionResult
.
outcome
)
, Result =
\(
executionResult
.
output
??
"no output"
)
"
)
}
}
Kotlin
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
val
model
=
Firebase
.
ai
(
backend
=
GenerativeBackend
.
googleAI
()).
generativeModel
(
modelName
=
" GEMINI_MODEL_NAME
"
,
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools
=
listOf
(
Tool
.
codeExecution
())
)
val
prompt
=
"What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? "
+
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
val
response
=
model
.
generateContent
(
prompt
)
response
.
candidates
.
first
().
content
.
parts
.
forEach
{
if
(
it
is
TextPart
)
{
println
(
"Text =
${
it
.
text
}
"
)
}
if
(
it
is
ExecutableCodePart
)
{
println
(
"Code =
${
it
.
code
}
, Language =
${
it
.
language
}
"
)
}
if
(
it
is
CodeExecutionResultPart
)
{
println
(
"Outcome =
${
it
.
outcome
}
, Result =
${
it
.
output
}
"
)
}
}
Java
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
GenerativeModel
ai
=
FirebaseAI
.
getInstance
(
GenerativeBackend
.
googleAI
())
.
generativeModel
(
" GEMINI_MODEL_NAME
"
,
null
,
null
,
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
List
.
of
(
Tool
.
codeExecution
()));
// Use the GenerativeModelFutures Java compatibility layer which offers
// support for ListenableFuture and Publisher APIs
GenerativeModelFutures
model
=
GenerativeModelFutures
.
from
(
ai
);
String
text
=
"What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? "
+
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
;
Content
prompt
=
new
Content
.
Builder
()
.
addText
(
text
)
.
build
();
ListenableFuture
response
=
model
.
generateContent
(
prompt
);
Futures
.
addCallback
(
response
,
new
FutureCallback
()
{
@Override
public
void
onSuccess
(
GenerateContentResponse
response
)
{
// Access the first candidate's content parts
List
parts
=
response
.
getCandidates
().
get
(
0
).
getContent
().
getParts
();
for
(
Part
part
:
parts
)
{
if
(
part
instanceof
TextPart
)
{
TextPart
textPart
=
(
TextPart
)
part
;
System
.
out
.
println
(
"Text = "
+
textPart
.
getText
());
}
else
if
(
part
instanceof
ExecutableCodePart
)
{
ExecutableCodePart
codePart
=
(
ExecutableCodePart
)
part
;
System
.
out
.
println
(
"Code = "
+
codePart
.
getCode
()
+
", Language = "
+
codePart
.
getLanguage
());
}
else
if
(
part
instanceof
CodeExecutionResultPart
)
{
CodeExecutionResultPart
resultPart
=
(
CodeExecutionResultPart
)
part
;
System
.
out
.
println
(
"Outcome = "
+
resultPart
.
getOutcome
()
+
", Result = "
+
resultPart
.
getOutput
());
}
}
}
@Override
public
void
onFailure
(
Throwable
t
)
{
t
.
printStackTrace
();
}
},
executor
);
Web
import
{
initializeApp
}
from
"firebase/app"
;
import
{
getAI
,
getGenerativeModel
,
GoogleAIBackend
}
from
"firebase/ai"
;
// TODO(developer) Replace the following with your app's Firebase configuration
// See: https://firebase.google.com/docs/web/learn-more#config-object
const
firebaseConfig
=
{
// ...
};
// Initialize FirebaseApp
const
firebaseApp
=
initializeApp
(
firebaseConfig
);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
const
ai
=
getAI
(
firebaseApp
,
{
backend
:
new
GoogleAIBackend
()
});
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
const
model
=
getGenerativeModel
(
ai
,
{
model
:
" GEMINI_MODEL_NAME
"
,
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools
:
[{
codeExecution
:
{}
}]
}
);
const
prompt
=
"What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? "
+
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
const
result
=
await
model
.
generateContent
(
prompt
);
const
response
=
await
result
.
response
;
const
parts
=
response
.
candidates
?
.[
0
].
content
.
parts
;
if
(
parts
)
{
parts
.
forEach
((
part
)
=>
{
if
(
part
.
text
)
{
console
.
log
(
`Text:
${
part
.
text
}
`
);
}
else
if
(
part
.
executableCode
)
{
console
.
log
(
`Code:
${
part
.
executableCode
.
code
}
, Language:
${
part
.
executableCode
.
language
}
`
);
}
else
if
(
part
.
codeExecutionResult
)
{
console
.
log
(
`Outcome:
${
part
.
codeExecutionResult
.
outcome
}
, Result:
${
part
.
codeExecutionResult
.
output
}
`
);
}
});
}
Dart
import
'package:firebase_core/firebase_core.dart'
;
import
'package:firebase_ai/firebase_ai.dart'
;
import
'firebase_options.dart'
;
// Initialize FirebaseApp
await
Firebase
.
initializeApp
(
options:
DefaultFirebaseOptions
.
currentPlatform
,
);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
final
model
=
FirebaseAI
.
googleAI
().
generativeModel
(
model:
' GEMINI_MODEL_NAME
'
,
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools:
[
Tool
.
codeExecution
(),
],
);
const
prompt
=
'What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? '
'Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.'
;
final
response
=
await
model
.
generateContent
([
Content
.
text
(
prompt
)]);
final
buffer
=
StringBuffer
();
for
(
final
part
in
response
.
candidates
.
first
.
content
.
parts
)
{
if
(
part
is
TextPart
)
{
buffer
.
writeln
(
part
.
text
);
}
else
if
(
part
is
ExecutableCodePart
)
{
buffer
.
writeln
(
'Executable Code:'
);
buffer
.
writeln
(
'Language:
${
part
.
language
}
'
);
buffer
.
writeln
(
'Code:'
);
buffer
.
writeln
(
part
.
code
);
}
else
if
(
part
is
CodeExecutionResultPart
)
{
buffer
.
writeln
(
'Code Execution Result:'
);
buffer
.
writeln
(
'Outcome:
${
part
.
outcome
}
'
);
buffer
.
writeln
(
'Output:'
);
buffer
.
writeln
(
part
.
output
);
}
}
Unity
using
Firebase
;
using
Firebase.AI
;
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
var
ai
=
FirebaseAI
.
GetInstance
(
FirebaseAI
.
Backend
.
GoogleAI
());
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
var
model
=
ai
.
GetGenerativeModel
(
modelName
:
" GEMINI_MODEL_NAME
"
,
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools
:
new
Tool
[]
{
new
Tool
(
new
CodeExecution
())
}
);
var
prompt
=
"What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? "
+
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
;
var
response
=
await
model
.
GenerateContentAsync
(
prompt
);
foreach
(
var
part
in
response
.
Candidates
.
First
().
Content
.
Parts
)
{
if
(
part
is
ModelContent
.
TextPart
tp
)
{
UnityEngine
.
Debug
.
Log
(
$"Text = {tp.Text}"
);
}
else
if
(
part
is
ModelContent
.
ExecutableCodePart
esp
)
{
UnityEngine
.
Debug
.
Log
(
$"Code = {esp.Code}, Language = {esp.Language}"
);
}
else
if
(
part
is
ModelContent
.
CodeExecutionResultPart
cerp
)
{
UnityEngine
.
Debug
.
Log
(
$"Outcome = {cerp.Outcome}, Output = {cerp.Output}"
);
}
}
Learn how to choose a model appropriate for your use case and app.
View example output
The output might look something like the following, which has been formatted for readability:
Okay, I need to calculate the sum of the first 50 prime numbers. Here's how I'll
approach this:
1. **Generate Prime Numbers:** I'll use an iterative method to find prime
numbers. I'll start with 2 and check if each subsequent number is divisible
by any number between 2 and its square root. If not, it's a prime.
2. **Store Primes:** I'll store the prime numbers in a list until I have 50 of
them.
3. **Calculate the Sum:** Finally, I'll sum the prime numbers in the list.
Here's the Python code to do this:
def is_prime(n):
"""Efficiently checks if a number is prime."""
if n <= 1:
return False
if n <= 3:
return True
if n % 2 == 0 or n % 3 == 0:
return False
i = 5
while i * i <= n:
if n % i == 0 or n % (i + 2) == 0:
return False
i += 6
return True
primes = []
num = 2
while len(primes) < 50:
if is_prime(num):
primes.append(num)
num += 1
sum_of_primes = sum(primes)
print(f'{primes=}')
print(f'{sum_of_primes=}')
primes=[2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67,
71, 73, 79, 83, 89, 97, 101, 103, 107, 109, 113, 127, 131, 137, 139, 149, 151,
157, 163, 167, 173, 179, 181, 191, 193, 197, 199, 211, 223, 227, 229]
sum_of_primes=5117
The sum of the first 50 prime numbers is 5117.
This output combines several content parts that the model returns when using code execution:
-
text: Inline text generated by the model -
executableCode: Code generated by the model that is meant to be executed -
codeExecutionResult: Result of the executed code
The naming conventions for these parts vary by programming language.