The autocomplete service in the Places SDK for iOS returns place predictions in response to user search queries. As the user types, the autocomplete service returns suggestions for places such as businesses, addresses, plus codes and points of interest.
You can add autocomplete to your app in the following ways:
- Add an autocomplete UI control to save development time and ensure a consistent user experience.
- Get place predictions programmatically to create a customized user experience.
Adding an autocomplete UI control
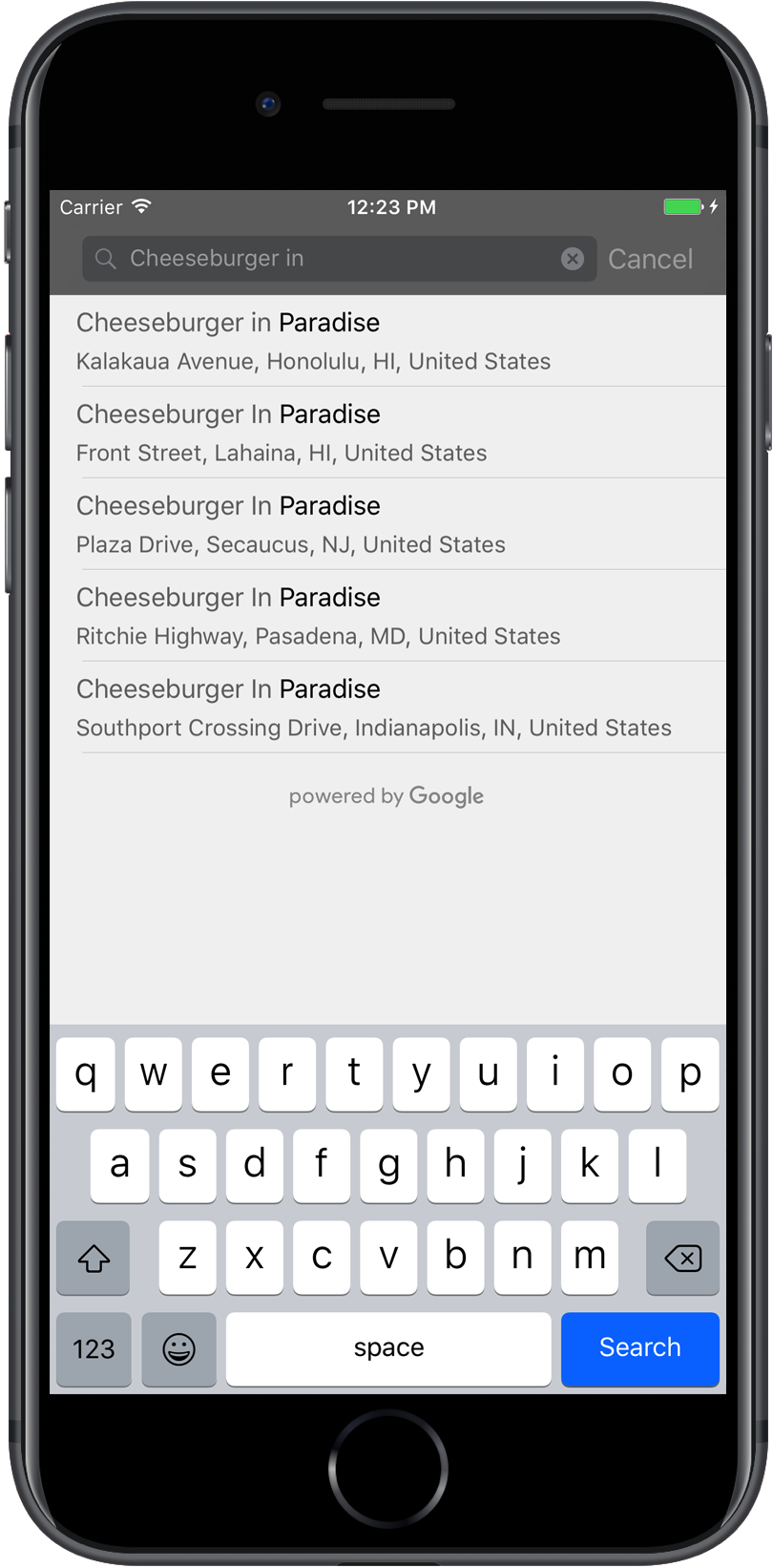
The autocomplete UI control is a search dialog with built-in autocomplete
functionality. As a user enters search terms, the control presents a list of
predicted places to choose from. When the user makes a selection, a GMSPlace
instance is returned, which your app can then use to get details about the
selected place.
You can add the autocomplete UI control to your app in the following ways:
Adding a full-screen control
Use the full-screen control when you want a modal context, where the
autocomplete UI temporarily replaces the UI of your app until the user has made
their selection. This functionality is provided by the GMSAutocompleteViewController
class. When the user selects a place, your app receives a callback.
To add a full-screen control to your app:
- Create a UI element in your main app to launch the autocomplete UI control,
for example a touch handler on a
UIButton. - Implement the
GMSAutocompleteViewControllerDelegateprotocol in the parent view controller. - Create an instance of
GMSAutocompleteViewControllerand assign the parent view controller as the delegate property. - Create a
GMSPlaceFieldto define the place data types to return. - Add a
GMSAutocompleteFilterto constrain the query to a particular type of place . - Present the
GMSAutocompleteViewControllerusing[self presentViewController...]. - Handle the user's selection in the
didAutocompleteWithPlacedelegate method. - Dismiss the controller in the
didAutocompleteWithPlace,didFailAutocompleteWithError, andwasCancelleddelegate methods.
The following example demonstrates one possible way to launch GMSAutocompleteViewController
in response to the user tapping on a button.
Swift
import UIKit import GooglePlaces class ViewController : UIViewController { override func viewDidLoad () { makeButton () } // Present the Autocomplete view controller when the button is pressed. @objc func autocompleteClicked ( _ sender : UIButton ) { let autocompleteController = GMSAutocompleteViewController () autocompleteController . delegate = self // Specify the place data types to return. let fields : GMSPlaceField = GMSPlaceField ( rawValue : UInt ( GMSPlaceField . name . rawValue ) | UInt ( GMSPlaceField . placeID . rawValue )) ! autocompleteController . placeFields = fields // Specify a filter. let filter = GMSAutocompleteFilter () filter . types = [. address ] autocompleteController . autocompleteFilter = filter // Display the autocomplete view controller. present ( autocompleteController , animated : true , completion : nil ) } // Add a button to the view. func makeButton () { let btnLaunchAc = UIButton ( frame : CGRect ( x : 5 , y : 150 , width : 300 , height : 35 )) btnLaunchAc . backgroundColor = . blue btnLaunchAc . setTitle ( "Launch autocomplete" , for : . normal ) btnLaunchAc . addTarget ( self , action : #selector ( autocompleteClicked ), for : . touchUpInside ) self . view . addSubview ( btnLaunchAc ) } } extension ViewController : GMSAutocompleteViewControllerDelegate { // Handle the user's selection. func viewController ( _ viewController : GMSAutocompleteViewController , didAutocompleteWith place : GMSPlace ) { print ( "Place name: \( place . name ) " ) print ( "Place ID: \( place . placeID ) " ) print ( "Place attributions: \( place . attributions ) " ) dismiss ( animated : true , completion : nil ) } func viewController ( _ viewController : GMSAutocompleteViewController , didFailAutocompleteWithError error : Error ) { // TODO: handle the error. print ( "Error: " , error . localizedDescription ) } // User canceled the operation. func wasCancelled ( _ viewController : GMSAutocompleteViewController ) { dismiss ( animated : true , completion : nil ) } // Turn the network activity indicator on and off again. func didRequestAutocompletePredictions ( _ viewController : GMSAutocompleteViewController ) { UIApplication . shared . isNetworkActivityIndicatorVisible = true } func didUpdateAutocompletePredictions ( _ viewController : GMSAutocompleteViewController ) { UIApplication . shared . isNetworkActivityIndicatorVisible = false } }
Objective-C
#import "ViewController.h" @import GooglePlaces ; @interface ViewController () < GMSAutocompleteViewControllerDelegate > @end @implementation ViewController { GMSAutocompleteFilter * _filter ; } - ( void ) viewDidLoad { [ super viewDidLoad ]; [ self makeButton ]; } // Present the autocomplete view controller when the button is pressed. - ( void ) autocompleteClicked { GMSAutocompleteViewController * acController = [[ GMSAutocompleteViewController alloc ] init ]; acController . delegate = self ; // Specify the place data types to return. GMSPlaceField fields = ( GMSPlaceFieldName | GMSPlaceFieldPlaceID ); acController . placeFields = fields ; // Specify a filter. _filter = [[ GMSAutocompleteFilter alloc ] init ]; _filter . types = @[ kGMSPlaceTypeBank ] ; acController . autocompleteFilter = _filter ; // Display the autocomplete view controller. [ self presentViewController : acController animated : YES completion : nil ]; } // Add a button to the view. - ( void ) makeButton { UIButton * btnLaunchAc = [ UIButton buttonWithType : UIButtonTypeCustom ]; [ btnLaunchAc addTarget : self action : @selector ( autocompleteClicked ) forControlEvents : UIControlEventTouchUpInside ]; [ btnLaunchAc setTitle : @"Launch autocomplete" forState : UIControlStateNormal ]; btnLaunchAc . frame = CGRectMake ( 5.0 , 150.0 , 300.0 , 35.0 ); btnLaunchAc . backgroundColor = [ UIColor blueColor ]; [ self . view addSubview : btnLaunchAc ]; } // Handle the user's selection. - ( void ) viewController: ( GMSAutocompleteViewController * ) viewController didAutocompleteWithPlace :( GMSPlace * ) place { [ self dismissViewControllerAnimated : YES completion : nil ]; // Do something with the selected place. NSLog ( @"Place name %@" , place . name ); NSLog ( @"Place ID %@" , place . placeID ); NSLog ( @"Place attributions %@" , place . attributions . string ); } - ( void ) viewController: ( GMSAutocompleteViewController * ) viewController didFailAutocompleteWithError :( NSError * ) error { [ self dismissViewControllerAnimated : YES completion : nil ]; // TODO: handle the error. NSLog ( @"Error: %@" , [ error description ]); } // User canceled the operation. - ( void ) wasCancelled: ( GMSAutocompleteViewController * ) viewController { [ self dismissViewControllerAnimated : YES completion : nil ]; } // Turn the network activity indicator on and off again. - ( void ) didRequestAutocompletePredictions: ( GMSAutocompleteViewController * ) viewController { [ UIApplication sharedApplication ]. networkActivityIndicatorVisible = YES ; } - ( void ) didUpdateAutocompletePredictions: ( GMSAutocompleteViewController * ) viewController { [ UIApplication sharedApplication ]. networkActivityIndicatorVisible = NO ; } @end
Adding a results controller
Use a results controller when you want more control over the text input UI. The results controller dynamically toggles the visibility of the results list based on input UI focus.
To add a results controller to your app:
- Create a
GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController.- Implement the
GMSAutocompleteResultsViewControllerDelegateprotocol in the parent view controller and assign the parent view controller as the delegate property.
- Implement the
- Create a
UISearchControllerobject, passing in theGMSAutocompleteResultsViewControlleras the results controller argument. - Set the
GMSAutocompleteResultsViewControlleras thesearchResultsUpdaterproperty of theUISearchController. - Add the
searchBarfor theUISearchControllerto your app's UI. - Handle the user's selection in the
didAutocompleteWithPlacedelegate method.
There are several ways to place the search bar of a UISearchController
into
your app's UI:
- Add a search bar to the navigation bar
- Add a search bar to the top of a view
- Add a search bar using popover results
Adding a search bar to the navigation bar
The following code example demonstrates adding a results controller, adding the searchBar
to the navigation bar, and handling the user's selection:
Swift
class ViewController : UIViewController { var resultsViewController : GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController ? var searchController : UISearchController ? var resultView : UITextView ? override func viewDidLoad () { super . viewDidLoad () resultsViewController = GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController () resultsViewController ?. delegate = self searchController = UISearchController ( searchResultsController : resultsViewController ) searchController ?. searchResultsUpdater = resultsViewController // Put the search bar in the navigation bar. searchController ?. searchBar . sizeToFit () navigationItem . titleView = searchController ?. searchBar // When UISearchController presents the results view, present it in // this view controller, not one further up the chain. definesPresentationContext = true // Prevent the navigation bar from being hidden when searching. searchController ?. hidesNavigationBarDuringPresentation = false } } // Handle the user's selection. extension ViewController : GMSAutocompleteResultsViewControllerDelegate { func resultsController ( _ resultsController : GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController , didAutocompleteWith place : GMSPlace ) { searchController ?. isActive = false // Do something with the selected place. print ( "Place name: \( place . name ) " ) print ( "Place address: \( place . formattedAddress ) " ) print ( "Place attributions: \( place . attributions ) " ) } func resultsController ( _ resultsController : GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController , didFailAutocompleteWithError error : Error ){ // TODO: handle the error. print ( "Error: " , error . localizedDescription ) } // Turn the network activity indicator on and off again. func didRequestAutocompletePredictions ( _ viewController : GMSAutocompleteViewController ) { UIApplication . shared . isNetworkActivityIndicatorVisible = true } func didUpdateAutocompletePredictions ( _ viewController : GMSAutocompleteViewController ) { UIApplication . shared . isNetworkActivityIndicatorVisible = false } }
Objective-C
- ( void ) viewDidLoad { _resultsViewController = [[ GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController alloc ] init ]; _resultsViewController . delegate = self ; _searchController = [[ UISearchController alloc ] initWithSearchResultsController : _resultsViewController ]; _searchController . searchResultsUpdater = _resultsViewController ; // Put the search bar in the navigation bar. [ _searchController . searchBar sizeToFit ]; self . navigationItem . titleView = _searchController . searchBar ; // When UISearchController presents the results view, present it in // this view controller, not one further up the chain. self . definesPresentationContext = YES ; // Prevent the navigation bar from being hidden when searching. _searchController . hidesNavigationBarDuringPresentation = NO ; } // Handle the user's selection. - ( void ) resultsController: ( GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController * ) resultsController didAutocompleteWithPlace :( GMSPlace * ) place { _searchController . active = NO ; // Do something with the selected place. NSLog ( @"Place name %@" , place . name ); NSLog ( @"Place address %@" , place . formattedAddress ); NSLog ( @"Place attributions %@" , place . attributions . string ); } - ( void ) resultsController: ( GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController * ) resultsController didFailAutocompleteWithError :( NSError * ) error { [ self dismissViewControllerAnimated : YES completion : nil ]; // TODO: handle the error. NSLog ( @"Error: %@" , [ error description ]); } // Turn the network activity indicator on and off again. - ( void ) didRequestAutocompletePredictionsForResultsController: ( GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController * ) resultsController { [ UIApplication sharedApplication ]. networkActivityIndicatorVisible = YES ; } - ( void ) didUpdateAutocompletePredictionsForResultsController: ( GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController * ) resultsController { [ UIApplication sharedApplication ]. networkActivityIndicatorVisible = NO ; }
Adding a search bar to the top of a view
The following code example shows adding the searchBar
to the top of a view.
Swift
import UIKit import GooglePlaces class ViewController : UIViewController { var resultsViewController : GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController ? var searchController : UISearchController ? var resultView : UITextView ? override func viewDidLoad () { super . viewDidLoad () resultsViewController = GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController () resultsViewController ?. delegate = self searchController = UISearchController ( searchResultsController : resultsViewController ) searchController ?. searchResultsUpdater = resultsViewController let subView = UIView ( frame : CGRect ( x : 0 , y : 65.0 , width : 350.0 , height : 45.0 )) subView . addSubview (( searchController ?. searchBar ) ! ) view . addSubview ( subView ) searchController ?. searchBar . sizeToFit () searchController ?. hidesNavigationBarDuringPresentation = false // When UISearchController presents the results view, present it in // this view controller, not one further up the chain. definesPresentationContext = true } } // Handle the user's selection. extension ViewController : GMSAutocompleteResultsViewControllerDelegate { func resultsController ( _ resultsController : GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController , didAutocompleteWith place : GMSPlace ) { searchController ?. isActive = false // Do something with the selected place. print ( "Place name: \( place . name ) " ) print ( "Place address: \( place . formattedAddress ) " ) print ( "Place attributions: \( place . attributions ) " ) } func resultsController ( _ resultsController : GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController , didFailAutocompleteWithError error : Error ){ // TODO: handle the error. print ( "Error: " , error . localizedDescription ) } // Turn the network activity indicator on and off again. func didRequestAutocompletePredictions ( forResultsController resultsController : GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController ) { UIApplication . shared . isNetworkActivityIndicatorVisible = true } func didUpdateAutocompletePredictions ( forResultsController resultsController : GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController ) { UIApplication . shared . isNetworkActivityIndicatorVisible = false } }
Objective-C
- ( void ) viewDidLoad { [ super viewDidLoad ]; _resultsViewController = [[ GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController alloc ] init ]; _resultsViewController . delegate = self ; _searchController = [[ UISearchController alloc ] initWithSearchResultsController : _resultsViewController ]; _searchController . searchResultsUpdater = _resultsViewController ; UIView * subView = [[ UIView alloc ] initWithFrame : CGRectMake ( 0 , 65.0 , 250 , 50 )]; [ subView addSubview : _searchController . searchBar ]; [ _searchController . searchBar sizeToFit ]; [ self . view addSubview : subView ]; // When UISearchController presents the results view, present it in // this view controller, not one further up the chain. self . definesPresentationContext = YES ; } // Handle the user's selection. - ( void ) resultsController: ( GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController * ) resultsController didAutocompleteWithPlace :( GMSPlace * ) place { [ self dismissViewControllerAnimated : YES completion : nil ]; // Do something with the selected place. NSLog ( @"Place name %@" , place . name ); NSLog ( @"Place address %@" , place . formattedAddress ); NSLog ( @"Place attributions %@" , place . attributions . string ); } - ( void ) resultsController: ( GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController * ) resultsController didFailAutocompleteWithError :( NSError * ) error { [ self dismissViewControllerAnimated : YES completion : nil ]; // TODO: handle the error. NSLog ( @"Error: %@" , [ error description ]); } // Turn the network activity indicator on and off again. - ( void ) didRequestAutocompletePredictionsForResultsController: ( GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController * ) resultsController { [ UIApplication sharedApplication ]. networkActivityIndicatorVisible = YES ; } - ( void ) didUpdateAutocompletePredictionsForResultsController: ( GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController * ) resultsController { [ UIApplication sharedApplication ]. networkActivityIndicatorVisible = NO ; }
By default, UISearchController
hides the navigation bar when presenting (this can be disabled). In cases where
the navigation bar is visible and opaque, UISearchController
does not set the
placement correctly.
Use the following code as a workaround:
Swift
navigationController ?. navigationBar . translucent = false searchController ?. hidesNavigationBarDuringPresentation = false // This makes the view area include the nav bar even though it is opaque. // Adjust the view placement down. self . extendedLayoutIncludesOpaqueBars = true self . edgesForExtendedLayout = . top
Objective-C
self . navigationController . navigationBar . translucent = NO ; _searchController . hidesNavigationBarDuringPresentation = NO ; // This makes the view area include the nav bar even though it is opaque. // Adjust the view placement down. self . extendedLayoutIncludesOpaqueBars = YES ; self . edgesForExtendedLayout = UIRectEdgeTop ;
Adding a search bar using popover results
The following code example shows placing a search bar on the right side of the navigation bar, and displaying results in a popover.
Swift
import UIKit import GooglePlaces class ViewController : UIViewController { var resultsViewController : GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController ? var searchController : UISearchController ? var resultView : UITextView ? override func viewDidLoad () { super . viewDidLoad () resultsViewController = GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController () resultsViewController ?. delegate = self searchController = UISearchController ( searchResultsController : resultsViewController ) searchController ?. searchResultsUpdater = resultsViewController // Add the search bar to the right of the nav bar, // use a popover to display the results. // Set an explicit size as we don't want to use the entire nav bar. searchController ?. searchBar . frame = ( CGRect ( x : 0 , y : 0 , width : 250.0 , height : 44.0 )) navigationItem . rightBarButtonItem = UIBarButtonItem ( customView : ( searchController ?. searchBar ) ! ) // When UISearchController presents the results view, present it in // this view controller, not one further up the chain. definesPresentationContext = true // Keep the navigation bar visible. searchController ?. hidesNavigationBarDuringPresentation = false searchController ?. modalPresentationStyle = . popover } } // Handle the user's selection. extension ViewController : GMSAutocompleteResultsViewControllerDelegate { func resultsController ( _ resultsController : GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController , didAutocompleteWith place : GMSPlace ) { searchController ?. isActive = false // Do something with the selected place. print ( "Place name: \( place . name ) " ) print ( "Place address: \( place . formattedAddress ) " ) print ( "Place attributions: \( place . attributions ) " ) } func resultsController ( _ resultsController : GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController , didFailAutocompleteWithError error : Error ){ // TODO: handle the error. print ( "Error: " , error . localizedDescription ) } // Turn the network activity indicator on and off again. func didRequestAutocompletePredictions ( forResultsController resultsController : GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController ) { UIApplication . shared . isNetworkActivityIndicatorVisible = true } func didUpdateAutocompletePredictions ( forResultsController resultsController : GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController ) { UIApplication . shared . isNetworkActivityIndicatorVisible = false } }
Objective-C
- ( void ) viewDidLoad { [ super viewDidLoad ]; _resultsViewController = [[ GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController alloc ] init ]; _resultsViewController . delegate = self ; _searchController = [[ UISearchController alloc ] initWithSearchResultsController : _resultsViewController ]; _searchController . searchResultsUpdater = _resultsViewController ; // Add the search bar to the right of the nav bar, // use a popover to display the results. // Set an explicit size as we don't want to use the entire nav bar. _searchController . searchBar . frame = CGRectMake ( 0 , 0 , 250.0f , 44.0f ); self . navigationItem . rightBarButtonItem = [[ UIBarButtonItem alloc ] initWithCustomView : _searchController . searchBar ]; // When UISearchController presents the results view, present it in // this view controller, not one further up the chain. self . definesPresentationContext = YES ; // Keep the navigation bar visible. _searchController . hidesNavigationBarDuringPresentation = NO ; _searchController . modalPresentationStyle = UIModalPresentationPopover ; } // Handle the user's selection. - ( void ) resultsController: ( GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController * ) resultsController didAutocompleteWithPlace :( GMSPlace * ) place { [ self dismissViewControllerAnimated : YES completion : nil ]; NSLog ( @"Place name %@" , place . name ); NSLog ( @"Place address %@" , place . formattedAddress ); NSLog ( @"Place attributions %@" , place . attributions . string ); } - ( void ) resultsController: ( GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController * ) resultsController didFailAutocompleteWithError :( NSError * ) error { [ self dismissViewControllerAnimated : YES completion : nil ]; // TODO: handle the error. NSLog ( @"Error: %@" , [ error description ]); } // Turn the network activity indicator on and off again. - ( void ) didRequestAutocompletePredictionsForResultsController: ( GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController * ) resultsController { [ UIApplication sharedApplication ]. networkActivityIndicatorVisible = YES ; } - ( void ) didUpdateAutocompletePredictionsForResultsController: ( GMSAutocompleteResultsViewController * ) resultsController { [ UIApplication sharedApplication ]. networkActivityIndicatorVisible = NO ; }
Using a table data source
If your app has a custom search text UI, you can use the GMSAutocompleteTableDataSource
class to drive the table view displaying the results on the view controller.
To use GMSAutocompleteTableDataSource
as the data source and delegate of the UITableView
in a view controller:
- Implement the
GMSAutocompleteTableDataSourceDelegateandUISearchBarDelegateprotocols in the view controller. - Create a
GMSAutocompleteTableDataSourceinstance and assign the view controller as the delegate property. - Set the
GMSAutocompleteTableDataSourceas the datasource and delegate properties of theUITableViewinstance on the view controller. - In the handler for the search text input, call
sourceTextHasChangedon theGMSAutocompleteTableDataSource.- Handle the user's selection in the
didAutocompleteWithPlacedelegate method.
- Handle the user's selection in the
- Dismiss the controller in the
didAutocompleteWithPlace,didFailAutocompleteWithError,wasCancelleddelegate methods.
The following code example demonstrates using the GMSAutocompleteTableDataSource
class to drive the table view of a UIViewController
when the UISearchBar
is
added separately.
Swift
// Copyright 2020 Google LLC // // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); // you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. // You may obtain a copy of the License at // // http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 // // Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software // distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, // WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. // See the License for the specific language governing permissions and // limitations under the License. import GooglePlaces import UIKit class PlaceAutocompleteViewController : UIViewController { private var tableView : UITableView ! private var tableDataSource : GMSAutocompleteTableDataSource ! override func viewDidLoad () { super . viewDidLoad () let searchBar = UISearchBar ( frame : CGRect ( x : 0 , y : 20 , width : self . view . frame . size . width , height : 44.0 )) searchBar . delegate = self view . addSubview ( searchBar ) tableDataSource = GMSAutocompleteTableDataSource () tableDataSource . delegate = self tableView = UITableView ( frame : CGRect ( x : 0 , y : 64 , width : self . view . frame . size . width , height : self . view . frame . size . height - 44 )) tableView . delegate = tableDataSource tableView . dataSource = tableDataSource view . addSubview ( tableView ) } } extension PlaceAutocompleteViewController : UISearchBarDelegate { func searchBar ( _ searchBar : UISearchBar , textDidChange searchText : String ) { // Update the GMSAutocompleteTableDataSource with the search text. tableDataSource . sourceTextHasChanged ( searchText ) } } extension PlaceAutocompleteViewController : GMSAutocompleteTableDataSourceDelegate { func didUpdateAutocompletePredictions ( for tableDataSource : GMSAutocompleteTableDataSource ) { // Turn the network activity indicator off. UIApplication . shared . isNetworkActivityIndicatorVisible = false // Reload table data. tableView . reloadData () } func didRequestAutocompletePredictions ( for tableDataSource : GMSAutocompleteTableDataSource ) { // Turn the network activity indicator on. UIApplication . shared . isNetworkActivityIndicatorVisible = true // Reload table data. tableView . reloadData () } func tableDataSource ( _ tableDataSource : GMSAutocompleteTableDataSource , didAutocompleteWith place : GMSPlace ) { // Do something with the selected place. print ( "Place name: \( place . name ) " ) print ( "Place address: \( place . formattedAddress ) " ) print ( "Place attributions: \( place . attributions ) " ) } func tableDataSource ( _ tableDataSource : GMSAutocompleteTableDataSource , didFailAutocompleteWithError error : Error ) { // Handle the error. print ( "Error: \( error . localizedDescription ) " ) } func tableDataSource ( _ tableDataSource : GMSAutocompleteTableDataSource , didSelect prediction : GMSAutocompletePrediction ) - > Bool { return true } }
Objective-C
// Copyright 2020 Google LLC // // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); // you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. // You may obtain a copy of the License at // // http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 // // Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software // distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, // WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. // See the License for the specific language governing permissions and // limitations under the License. #import "PlaceAutocompleteViewController.h" @import GooglePlaces ; @import UIKit ; @interface PlaceAutocompleteViewController () < GMSAutocompleteTableDataSourceDelegate , UISearchBarDelegate > @end @implementation PlaceAutocompleteViewController { UITableView * tableView ; GMSAutocompleteTableDataSource * tableDataSource ; } - ( void ) viewDidLoad { [ super viewDidLoad ]; UISearchBar * searchBar = [[ UISearchBar alloc ] initWithFrame : CGRectMake ( 0 , 20 , self . view . frame . size . width , 44 )]; searchBar . delegate = self ; [ self . view addSubview : searchBar ]; tableDataSource = [[ GMSAutocompleteTableDataSource alloc ] init ]; tableDataSource . delegate = self ; tableView = [[ UITableView alloc ] initWithFrame : CGRectMake ( 0 , 64 , self . view . frame . size . width , self . view . frame . size . height - 44 )]; tableView . delegate = tableDataSource ; tableView . dataSource = tableDataSource ; [ self . view addSubview : tableView ]; } #pragma mark - GMSAutocompleteTableDataSourceDelegate - ( void ) didUpdateAutocompletePredictionsForTableDataSource: ( GMSAutocompleteTableDataSource * ) tableDataSource { // Turn the network activity indicator off. UIApplication . sharedApplication . networkActivityIndicatorVisible = NO ; // Reload table data. [ tableView reloadData ]; } - ( void ) didRequestAutocompletePredictionsForTableDataSource: ( GMSAutocompleteTableDataSource * ) tableDataSource { // Turn the network activity indicator on. UIApplication . sharedApplication . networkActivityIndicatorVisible = YES ; // Reload table data. [ tableView reloadData ]; } - ( void ) tableDataSource: ( GMSAutocompleteTableDataSource * ) tableDataSource didAutocompleteWithPlace: ( GMSPlace * ) place { // Do something with the selected place. NSLog ( @"Place name: %@" , place . name ); NSLog ( @"Place address: %@" , place . formattedAddress ); NSLog ( @"Place attributions: %@" , place . attributions ); } - ( void ) tableDataSource: ( GMSAutocompleteTableDataSource * ) tableDataSource didFailAutocompleteWithError: ( NSError * ) error { // Handle the error NSLog ( @"Error %@" , error . description ); } - ( BOOL ) tableDataSource: ( GMSAutocompleteTableDataSource * ) tableDataSource didSelectPrediction: ( GMSAutocompletePrediction * ) prediction { return YES ; } #pragma mark - UISearchBarDelegate - ( void ) searchBar: ( UISearchBar * ) searchBar textDidChange: ( NSString * ) searchText { // Update the GMSAutocompleteTableDataSource with the search text. [ tableDataSource sourceTextHasChanged : searchText ]; } @end
Customizing text and background colors
You can set the colors of all text and backgrounds in the autocomplete UI control, to make the widget match the visual appearance of your app more closely. There are two ways to set the UI control colors:
- By using the built-in iOS UIAppearance protocol to globally style UI controls where possible. These settings apply to many, but not all, of the UI control elements.
- By using the SDK methods on the widget classes to set properties which are not supported by the UIAppearance protocol .
Typically, your app will use some combination of the UIAppearance protocol and the SDK methods. The following diagram shows which elements can be styled:
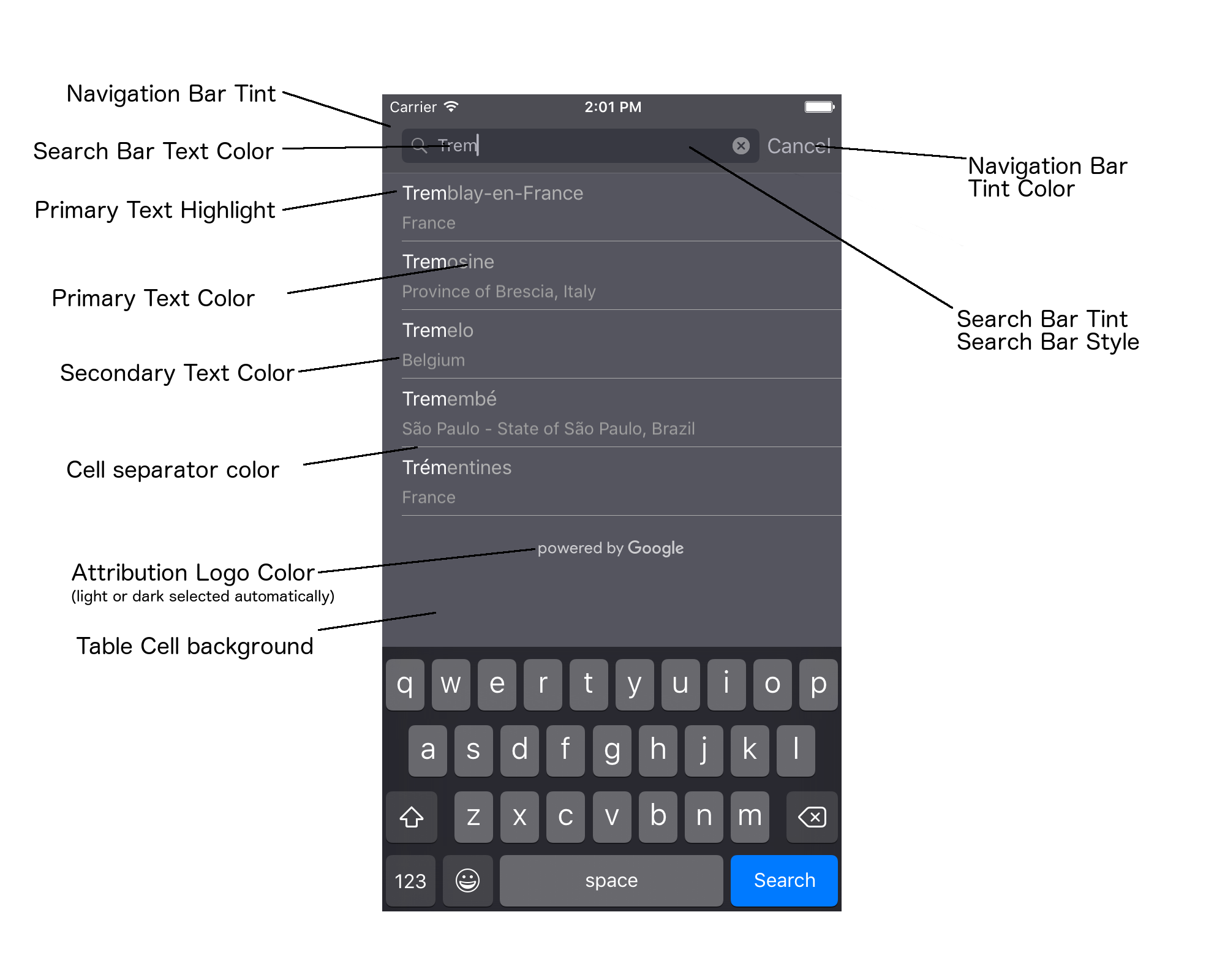
The following table lists all of the UI elements, and indicates how each one should be styled (UIAppearance protocol or SDK method).
| UI Element | Method | How to style |
|---|---|---|
|
Navigation Bar tint (background)
|
UIAppearance protocol | Call setBarTintColor
on UINavigationBar
proxy. |
|
Navigation Bar tint color (search bar text caret and Cancel button)
|
UIAppearance protocol | Call setTintColor
on UINavigationBar
proxy. |
|
Search Bar text color
|
UIAppearance protocol | Set NSForegroundColorAttributeName
in searchBarTextAttributes
. |
|
Search bar tint color
|
N/A | The search bar is translucent, and will display as a shaded version of the Navigation Bar. |
|
Search bar placeholder text color (default search text)
|
UIAppearance protocol | Set NSForegroundColorAttributeName
in placeholderAttributes
. |
|
Primary text (also applied to error and message text)
|
SDK method | Call primaryTextColor
. |
|
Primary text highlight
|
SDK method | Call primaryTextHighlightColor
. |
|
Secondary text
|
SDK method | Call secondaryTextColor
. |
|
Error and message text
|
SDK method | Call primaryTextColor
. |
|
Table cell background
|
SDK method | Call tableCellBackgroundColor
. |
|
Table cell separator color
|
SDK method | Call tableCellSeparatorColor
. |
|
"Try Again" button
|
SDK method | Call tintColor
. |
|
Activity indicator (progress spinner)
|
UIAppearance protocol | Call setColor
on UIActivityIndicatorView
proxy. |
|
"Powered by Google" logo, Sad cloud image
|
N/A | White or gray version is automatically selected based on background contrast. |
|
Magnifying glass and clear text icons in Search Bar text field
|
N/A | To style, replace the default images with images of the desired color. |
Using the UIAppearance protocol
You can use the UIAppearance
protocol
to get the appearance proxy for a given UI element, which you can then use to
set the color for the UI element. When a modification is made, all instances of
a given UI element are affected. For example, the following example globally
changes the text color of UITextField
classes to green when they are contained
in a UISearchBar
:
[[UITextField appearanceWhenContainedIn:[UISearchBar class], nil] setDefaultTextAttributes : @{NSForegroundColorAttributeName:[UIColor greenColor]}] ;
For more information about defining color values, consult the UIColor Class Reference .
The following code snippets show all of the proxy commands you need to use to
style everything in the full-screen autocomplete UI control. Add this code to
the didFinishLaunchingWithOptions
method in Appdelegate.m:
// Define some colors. UIColor * darkGray = [ UIColor darkGrayColor ]; UIColor * lightGray = [ UIColor lightGrayColor ]; // Navigation bar background. [[ UINavigationBar appearance ] setBarTintColor : darkGray ]; [[ UINavigationBar appearance ] setTintColor : lightGray ]; // Color of typed text in the search bar. NSDictionary * searchBarTextAttributes = @{ NSForegroundColorAttributeName : lightGray , NSFontAttributeName : [ UIFont systemFontOfSize : [ UIFont systemFontSize ]] } ; [ UITextField appearanceWhenContainedInInstancesOfClasses : @[ [ UISearchBar class ] ] ] . defaultTextAttributes = searchBarTextAttributes ; // Color of the placeholder text in the search bar prior to text entry. NSDictionary * placeholderAttributes = @{ NSForegroundColorAttributeName : lightGray , NSFontAttributeName : [ UIFont systemFontOfSize : [ UIFont systemFontSize ]] } ; // Color of the default search text. // NOTE: In a production scenario, "Search" would be a localized string. NSAttributedString * attributedPlaceholder = [[ NSAttributedString alloc ] initWithString : @"Search" attributes : placeholderAttributes ]; [ UITextField appearanceWhenContainedInInstancesOfClasses : @[ [ UISearchBar class ] ] ] . attributedPlaceholder = attributedPlaceholder ; // Color of the in-progress spinner. [[ UIActivityIndicatorView appearance ] setColor : lightGray ]; // To style the two image icons in the search bar (the magnifying glass // icon and the 'clear text' icon), replace them with different images. [[ UISearchBar appearance ] setImage : [ UIImage imageNamed : @"custom_clear_x_high" ] forSearchBarIcon : UISearchBarIconClear state : UIControlStateHighlighted ]; [[ UISearchBar appearance ] setImage : [ UIImage imageNamed : @"custom_clear_x" ] forSearchBarIcon : UISearchBarIconClear state : UIControlStateNormal ]; [[ UISearchBar appearance ] setImage : [ UIImage imageNamed : @"custom_search" ] forSearchBarIcon : UISearchBarIconSearch state : UIControlStateNormal ]; // Color of selected table cells. UIView * selectedBackgroundView = [[ UIView alloc ] init ]; selectedBackgroundView . backgroundColor = [ UIColor lightGrayColor ]; [ UITableViewCell appearanceWhenContainedIn : [ GMSAutocompleteViewController class ], nil ] . selectedBackgroundView = selectedBackgroundView ;
Setting UI control style properties
A subset of UI control elements have properties that are not affected by the
UIAppearance protocol, and so must be set directly. The following code example
shows defining foreground and background colors, and applying them to a UI
control instance named acController
. Add this code to the onLaunchClicked
method in ViewController.m:
UIColor * darkGray = [ UIColor darkGrayColor ]; UIColor * lightGray = [ UIColor lightGrayColor ]; acController . secondaryTextColor = [ UIColor colorWithWhite : 1.0f alpha : 0.5f ]; acController . primaryTextColor = lightGray ; acController . primaryTextHighlightColor = [ UIColor grayColor ]; acController . tableCellBackgroundColor = darkGray ; acController . tableCellSeparatorColor = lightGray ; acController . tintColor = lightGray ;
Getting place predictions programmatically
You can create a custom search UI as an alternative to the UI provided by the autocomplete widget. To do this, your app must get place predictions programmatically. Your app can get a list of predicted place names and/or addresses in one of the following ways:
Calling GMSPlacesClient findAutocompletePredictionsFromQuery:
To get a list of predicted place names and/or addresses, first instantiate
GMSPlacesClient
,
then call the GMSPlacesClient
findAutocompletePredictionsFromQuery:
method with the following parameters:
- An
autocompleteQuerystring containing the text typed by the user. - A
GMSAutocompleteSessionToken, which is used to identify each individual session. Your app should pass the same token for each autocomplete request call, then pass that token, along with a Place ID, in the subsequent call tofetchPlacefromPlaceID:to retrieve Place Details for the place that was selected by the user. - A
GMSAutocompleteFilterto:- Bias or restrict the results to a specific region.
- Restrict the results to a specific type of place .
- A
GMSPlaceLocationBias/Restriction object biasing the results to a specific area specified by latitude and longitude bounds.
- A callback method to handle the returned predictions.
The code examples below show a call to findAutocompletePredictionsFromQuery:
.
Swift
/** * Create a new session token. Be sure to use the same token for calling * findAutocompletePredictions, as well as the subsequent place details request. * This ensures that the user's query and selection are billed as a single session. */ let token = GMSAutocompleteSessionToken . init () // Create a type filter. let filter = GMSAutocompleteFilter () filter . types = [. bank ] filter . locationBias = GMSPlaceRectangularLocationOption ( northEastBounds , southWestBounds ); placesClient ?. findAutocompletePredictions ( fromQuery : "cheesebu" , filter : filter , sessionToken : token , callback : { ( results , error ) in if let error = error { print ( "Autocomplete error: \( error ) " ) return } if let results = results { for result in results { print ( "Result \( result . attributedFullText ) with placeID \( result . placeID ) " ) } } })
Objective-C
/** * Create a new session token. Be sure to use the same token for calling * findAutocompletePredictionsFromQuery:, as well as the subsequent place details request. * This ensures that the user's query and selection are billed as a single session. */ GMSAutocompleteSessionToken * token = [[ GMSAutocompleteSessionToken alloc ] init ]; // Create a type filter. GMSAutocompleteFilter * _filter = [[ GMSAutocompleteFilter alloc ] init ]; _filter . types = @[ kGMSPlaceTypeBank ] ; [ _placesClient findAutocompletePredictionsFromQuery : @"cheesebu" filter : _filter sessionToken : token callback :^ ( NSArray<GMSAutocompletePrediction * > * _Nullable results , NSError * _Nullable error ) { if ( error != nil ) { NSLog ( @"An error occurred %@" , [ error localizedDescription ]); return ; } if ( results != nil ) { for ( GMSAutocompletePrediction * result in results ) { NSLog ( @"Result %@ with PlaceID %@" , result . attributedFullText , result . placeID ); } } }];
The API invokes the specified callback method, passing in an array of GMSAutocompletePrediction
objects.
Each GMSAutocompletePrediction
object contains the following information:
-
attributedFullText– The full text of the prediction, in the form of anNSAttributedString. For example, 'Sydney Opera House, Sydney, New South Wales, Australia'. Every text range that matches the user input has an attribute,kGMSAutocompleteMatchAttribute. You can use this attribute to highlight the matching text in the user's query, for example, as shown below. -
placeID– The place ID of the predicted place. A place ID is a textual identifier that uniquely identifies a place. For more information about place IDs, see the Place ID overview . -
distanceMeters– The straight-line distance from the specifiedoriginto the destination. If theoriginproperty is not set, no distance value will be returned.
The following code example illustrates how to highlight in bold text the parts
of the result that match text in the user's query, using enumerateAttribute
:
Swift
let regularFont = UIFont . systemFont ( ofSize : UIFont . labelFontSize ) let boldFont = UIFont . boldSystemFont ( ofSize : UIFont . labelFontSize ) let bolded = prediction . attributedFullText . mutableCopy () as ! NSMutableAttributedString bolded . enumerateAttribute ( kGMSAutocompleteMatchAttribute , in : NSMakeRange ( 0 , bolded . length ), options : []) { ( value , range : NSRange , stop : UnsafeMutablePointer<ObjCBool> ) - > Void in let font = ( value == nil ) ? regularFont : boldFont bolded . addAttribute ( NSFontAttributeName , value : font , range : range ) } label . attributedText = bolded
Objective-C
UIFont * regularFont = [ UIFont systemFontOfSize : [ UIFont labelFontSize ]]; UIFont * boldFont = [ UIFont boldSystemFontOfSize : [ UIFont labelFontSize ]]; NSMutableAttributedString * bolded = [ prediction . attributedFullText mutableCopy ]; [ bolded enumerateAttribute : kGMSAutocompleteMatchAttribute inRange : NSMakeRange ( 0 , bolded . length ) options : 0 usingBlock : ^ ( id value , NSRange range , BOOL * stop ) { UIFont * font = ( value == nil ) ? regularFont : boldFont ; [ bolded addAttribute : NSFontAttributeName value : font range : range ]; }]; label . attributedText = bolded ;
Using the fetcher
If you want to build your own autocomplete control from scratch, you can use GMSAutocompleteFetcher
, which
wraps the autocompleteQuery
method on GMSPlacesClient
. The fetcher
throttles requests, returning only results for the most recently entered search
text. It provides no UI elements.
To implement GMSAutocompleteFetcher
,
take the following steps:
- Implement the
GMSAutocompleteFetcherDelegateprotocol. - Create a
GMSAutocompleteFetcherobject. - Call
sourceTextHasChangedon the fetcher as the user types. - Handle predictions and errors using the
didAutcompleteWithPredictionsanddidFailAutocompleteWithErrorprotocol methods.
The following code example demonstrates using the fetcher to take user input and
display place matches in a text view. Functionality for selecting a place has
been omitted. FetcherSampleViewController
derives from UIViewController
in
FetcherSampleViewController.h.
Swift
import UIKit import GooglePlaces class ViewController : UIViewController { var textField : UITextField ? var resultText : UITextView ? var fetcher : GMSAutocompleteFetcher ? override func viewDidLoad () { super . viewDidLoad () view . backgroundColor = . white edgesForExtendedLayout = [] // Set bounds to inner-west Sydney Australia. let neBoundsCorner = CLLocationCoordinate2D ( latitude : - 33.843366 , longitude : 151.134002 ) let swBoundsCorner = CLLocationCoordinate2D ( latitude : - 33.875725 , longitude : 151.200349 ) // Set up the autocomplete filter. let filter = GMSAutocompleteFilter () filter . locationRestriction = GMSPlaceRectangularLocationOption ( neBoundsCorner , swBoundsCorner ) // Create a new session token. let token : GMSAutocompleteSessionToken = GMSAutocompleteSessionToken . init () // Create the fetcher. fetcher = GMSAutocompleteFetcher ( bounds : nil , filter : filter ) fetcher ?. delegate = self fetcher ?. provide ( token ) textField = UITextField ( frame : CGRect ( x : 5.0 , y : 10.0 , width : view . bounds . size . width - 5.0 , height : 64.0 )) textField ?. autoresizingMask = . flexibleWidth textField ?. addTarget ( self , action : #selector ( textFieldDidChange ( textField :)), for : . editingChanged ) let placeholder = NSAttributedString ( string : "Type a query..." ) textField ?. attributedPlaceholder = placeholder resultText = UITextView ( frame : CGRect ( x : 0 , y : 65.0 , width : view . bounds . size . width , height : view . bounds . size . height - 65.0 )) resultText ?. backgroundColor = UIColor ( white : 0.95 , alpha : 1.0 ) resultText ?. text = "No Results" resultText ?. isEditable = false self . view . addSubview ( textField !) self . view . addSubview ( resultText !) } @objc func textFieldDidChange ( textField : UITextField ) { fetcher ?. sourceTextHasChanged ( textField . text !) } } extension ViewController : GMSAutocompleteFetcherDelegate { func didAutocomplete ( with predictions : [ GMSAutocompletePrediction ]) { let resultsStr = NSMutableString () for prediction in predictions { resultsStr . appendFormat ( " \n Primary text: %@ \n " , prediction . attributedPrimaryText ) resultsStr . appendFormat ( "Place ID: %@ \n " , prediction . placeID ) } resultText ?. text = resultsStr as String } func didFailAutocompleteWithError ( _ error : Error ) { resultText ?. text = error . localizedDescription } }
Objective-C
#import "FetcherSampleViewController.h" #import <GooglePlaces/GooglePlaces.h> @interface FetcherSampleViewController () < GMSAutocompleteFetcherDelegate > @end @implementation FetcherSampleViewController { UITextField * _textField ; UITextView * _resultText ; GMSAutocompleteFetcher * _fetcher ; } - ( void ) viewDidLoad { [ super viewDidLoad ]; self . view . backgroundColor = [ UIColor whiteColor ]; self . edgesForExtendedLayout = UIRectEdgeNone ; // Set bounds to inner-west Sydney Australia. CLLocationCoordinate2D neBoundsCorner = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake ( -33.843366 , 151.134002 ); CLLocationCoordinate2D swBoundsCorner = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake ( -33.875725 , 151.200349 ); GMSAutocompleteFilter * autocompleteFilter = [[ GMSAutocompleteFilter alloc ] init ]; autocompleteFilter . locationRestriction = GMSPlaceRectangularLocationOption ( neBoundsCorner , swBoundsCorner ); // Create the fetcher. _fetcher = [[ GMSAutocompleteFetcher alloc ] initWithBounds : nil filter : filter ]; _fetcher . delegate = self ; // Set up the UITextField and UITextView. _textField = [[ UITextField alloc ] initWithFrame : CGRectMake ( 5.0f , 0 , self . view . bounds . size . width - 5.0f , 44.0f )]; _textField . autoresizingMask = UIViewAutoresizingFlexibleWidth ; [ _textField addTarget : self action : @selector ( textFieldDidChange : ) forControlEvents : UIControlEventEditingChanged ]; _resultText = [[ UITextView alloc ] initWithFrame : CGRectMake ( 0 , 45.0f , self . view . bounds . size . width , self . view . bounds . size . height - 45.0f )]; _resultText . backgroundColor = [ UIColor colorWithWhite : 0.95f alpha : 1.0f ]; _resultText . text = @"No Results" ; _resultText . editable = NO ; [ self . view addSubview : _textField ]; [ self . view addSubview : _resultText ]; } - ( void ) textFieldDidChange: ( UITextField * ) textField { NSLog ( @"%@" , textField . text ); [ _fetcher sourceTextHasChanged : textField . text ]; } #pragma mark - GMSAutocompleteFetcherDelegate - ( void ) didAutocompleteWithPredictions: ( NSArray * ) predictions { NSMutableString * resultsStr = [ NSMutableString string ]; for ( GMSAutocompletePrediction * prediction in predictions ) { [ resultsStr appendFormat : @"%@ \n " , [ prediction . attributedPrimaryText string ]]; } _resultText . text = resultsStr ; } - ( void ) didFailAutocompleteWithError: ( NSError * ) error { _resultText . text = [ NSString stringWithFormat : @"%@" , error . localizedDescription ]; } @end
Session tokens
Session tokens group the query and selection phases of a user autocomplete search into a discrete session for billing purposes. The session begins when the user starts typing a query, and concludes when they select a place. Each session can have multiple queries, followed by one place selection. Once a session has concluded, the token is no longer valid; your app must generate a fresh token for each session. We recommend using session tokens for all programmatic autocomplete sessions (when you use the full-screen controller, or the results controller, the API takes care of this automatically).
The Places SDK for iOS uses a GMSAutocompleteSessionToken
to identify each session. Your app should pass a new session token upon
beginning each new session, then pass that same token, along with a Place ID, in
the subsequent call to fetchPlacefromPlaceID:
to retrieve Place Details for the place that was selected by the user.
Learn more about session tokens .
Use the following code to generate a new session token:
let token: GMSAutocompleteSessionToken = GMSAutocompleteSessionToken.init()
Usage limits
- Use of the
GMSPlacesClient findAutocompletePredictionsFromQuerymethod is subject to tiered query limits. See the documentation on usage limits .
Displaying attributions in your app
- If your app uses the autocomplete service programmatically, your UI must either display a 'Powered by Google' attribution, or appear within a Google-branded map.
- If your app uses the autocomplete UI control no additional action is required (the required attribution is displayed by default).
- If you retrieve and display additional place information after getting a place by ID , you must display third-party attributions too.
For more details, see the documentation on attributions .
Controlling the network activity indicator
To control the network activity indicator in the applications status bar you must implement the appropriate optional delegate methods for the autocomplete class you are using and turn the network indicator on and off yourself.
- For
GMSAutocompleteViewControlleryou must implement the delegate methodsdidRequestAutocompletePredictions:anddidUpdateAutocompletePredictions:. - For
GMSAutocompleteResultsViewControlleryou must implement the delegate methodsdidRequestAutocompletePredictionsForResultsController:anddidUpdateAutocompletePredictionsForResultsController:. - For
GMSAutocompleteTableDataSourceyou must implement the delegate methodsdidRequestAutocompletePredictionsForTableDataSource:anddidUpdateAutocompletePredictionsForTableDataSource:.
By implementing these methods and setting [UIApplication
sharedApplication].networkActivityIndicatorVisible
to YES
and NO
respectively the status bar will correctly match the autocomplete UI.
Constrain autocomplete results
You can set the autocomplete UI control to constrain results to a specific geographic region, and/or filter the results to one or more place types, or to a specific country or countries. To constrain results, you can do the following:
- To prefer
(bias) results within the defined region, set
locationBiason theGMSAutocompleteFilter(some results from outside the defined region may still be returned). IflocationRestrictionis also set,locationBiaswill be ignored. -
To only show (restrict) results within the defined region, set
locationRestrictionon theGMSAutocompleteFilter(only results within the defined region will be returned).- Note:This restriction is only applied to entire routes, synthetic results located outside the rectangular bounds may be returned based on a route that overlaps with the location restrict.
-
To return only results that conform to a particular place type, set
typeson theGMSAutocompleteFilter, (for example, specifying TypeFilter.ADDRESS will cause the widget to return only results with a precise address). -
To return only results within up to five specified countries, set
countrieson theGMSAutocompleteFilter.
Bias results to a specific region
To prefer
(bias) results within the defined region, set locationBias
on the GMSAutocompleteFilter
, as shown here:
northEast
=
CLLocationCoordinate2DMake
(
39.0
,
-95.0
);
southWest
=
CLLocationCoordinate2DMake
(
37.5
,
-100.0
);
GMSAutocompleteFilter
*
filter
=
[[
GMSAutocompleteFilter
alloc
]
init
];
filter
.
locationBias
=
GMSPlaceRectangularLocationOption
(
northEast
,
southWest
);
Restrict results to a specific region
To only show
(restrict) results within the defined region, set locationRestriction
on the GMSAutocompleteFilter
, as shown here:
northEast
=
CLLocationCoordinate2DMake
(
39.0
,
-95.0
);
southWest
=
CLLocationCoordinate2DMake
(
37.5
,
-100.0
);
GMSAutocompleteFilter
*
filter
=
[[
GMSAutocompleteFilter
alloc
]
init
];
filter
.
locationRestriction
=
GMSPlaceRectangularLocationOption
(
northEast
,
southWest
);
Filter results by country
To filter results within up to five specified countries, set countries
on the GMSAutocompleteFilter
, as shown here:
GMSAutocompleteFilter
*
filter
=
[[
GMSAutocompleteFilter
alloc
]
init
];
filter
.
countries
=
@[
@"au"
,
@"nz"
]
;
Filter results by place type or type collection
Restrict results to be of a certain type or type collection by setting the types
property of GMSAutoCompleteFilter
.
Use this property to specify filters listed in Tables 1, 2, and 3 on Place
Types
. If nothing is specified, all types are returned.
To specify a type or type collection filter:
-
Use the
typesproperty to specify up to five type values from Table 1 and Table 2 shown on Place Types . The type values are defined by the constants inGMSPlaceType. -
Use the
typesproperty to specify a type collection from Table 3 shown on Place Types . The type collection values are defined by the constants inGMSPlaceType.Only a single type from Table 3 is allowed in the request. If you specify a value from Table 3, you cannot specify a value from Table 1 or Table 2. If you do, then an error occurs.
For example, to return only results that conform to a particular place type, set types
on the GMSAutocompleteFilter
. The following example shows setting the
filter to return only results with a precise address:
GMSAutocompleteFilter
*
filter
=
[[
GMSAutocompleteFilter
alloc
]
init
];
filter
.
types
=
@[
kGMSPlaceTypeAirport
,
kGMSPlaceTypeAmusementPark
]
;
Place Autocomplete (Legacy) optimization
This section describes best practices to help you make the most of the Place Autocomplete (Legacy) service.
Here are some general guidelines:
- The quickest way to develop a working user interface is to use the Maps JavaScript API Place Autocomplete (Legacy) widget , Places SDK for Android Place Autocomplete (Legacy) widget , or Places SDK for iOS Place Autocomplete (Legacy) UI control .
- Understand essential Place Autocomplete (Legacy) data fields from the start.
- Location biasing and location restriction fields are optional but can have a significant impact on autocomplete performance.
- Use error handling to make sure your app degrades gracefully if the API returns an error.
- Make sure your app handles when there is no selection and offers users a way to continue.
Cost optimization best practices
Basic cost optimization
To optimize the cost of using the Place Autocomplete (Legacy) service, use field masks in Place Details (Legacy) and Place Autocomplete (Legacy) widgets to return only the Place Autocomplete (Legacy) data fields you need.
Advanced cost optimization
Consider programmatic implementation of Place Autocomplete (Legacy) in order to access SKU: Autocomplete - Per Request pricing and request Geocoding API results about the selected place instead of Place Details (Legacy). Per-request pricing paired with Geocoding API is more cost-effective than per-session (session-based) pricing if both of the following conditions are met:
- If you only need the latitude/longitude or address of the user's selected place, the Geocoding API delivers this information for less than a Place Details (Legacy) call.
- If users select an autocomplete prediction within an average of four Place Autocomplete (Legacy) predictions requests or fewer, per-request pricing may be more cost-effective than per-session pricing.
Does your application require any information other than the address and latitude/longitude of the selected prediction?
Yes, needs more details
Use session-based Place Autocomplete (Legacy) with Place Details (Legacy).
Since your application requires Place Details (Legacy), such as the place name, business status,
or opening hours, your implementation of Place Autocomplete (Legacy) should use a session token
( programmatically
or built into the JavaScript
, Android
,
or iOS
widgets) per session
plus applicable Places Data SKUs
,
depending on which place data fields you request. 1
Widget implementation
Session management is automatically built into the JavaScript
, Android
,
or iOS
widgets. This includes both the Place Autocomplete (Legacy) requests and the Place Details (Legacy) request
on the selected prediction. Be sure to specify the fields
parameter in order to
ensure you are only requesting the
Place Autocomplete (Legacy) data fields
you need.
Programmatic implementation
Use a session token
with your Place Autocomplete (Legacy) requests. When requesting Place Details (Legacy) about the selected prediction, include the following parameters:
- The place ID from the Place Autocomplete (Legacy) response
- The session token used in the Place Autocomplete (Legacy) request
- The
fieldsparameter specifying the Place Autocomplete (Legacy) data fields you need
No, needs only address and location
Geocoding API could be a more cost-effective option than Place Details (Legacy) for your application, depending on the performance of your Place Autocomplete (Legacy) usage. Every application's Place Autocomplete (Legacy) efficiency varies depending on what users are entering, where the application is being used, and whether performance optimization best practices have been implemented.
In order to answer the following question, analyze how many characters a user types on average before selecting a Place Autocomplete (Legacy) prediction in your application.
Do your users select a Place Autocomplete (Legacy) prediction in four or fewer requests, on average?
Yes
Implement Place Autocomplete (Legacy) programmatically without session tokens and call Geocoding API on the selected place prediction.
Geocoding API delivers addresses and latitude/longitude coordinates.
Making four Autocomplete - Per Request
requests plus a Geocoding API
call about the selected place prediction is less than the per-session Place Autocomplete (Legacy)
cost per session. 1
Consider employing performance best practices to help your users get the prediction they're looking for in even fewer characters.
No
Use session-based Place Autocomplete (Legacy) with Place Details (Legacy).
Since the average number of requests you expect to make before a user selects a
Place Autocomplete (Legacy) prediction exceeds the cost of per-session pricing, your implementation
of Place Autocomplete (Legacy) should use a session token for both the Place Autocomplete (Legacy) requests
and the associated Place Details (Legacy) request per session
. 1
Widget implementation
Session management is automatically built into the JavaScript
, Android
,
or iOS
widgets. This includes both the Place Autocomplete (Legacy) requests and the Place Details (Legacy)
request on the selected prediction. Be sure to specify the fields
parameter
in order to ensure you are only requesting the fields you need.
Programmatic implementation
Use a session token
with your Place Autocomplete (Legacy) requests.
When requesting Place Details (Legacy) about the selected prediction,
include the following parameters:
- The place ID from the Place Autocomplete (Legacy) response
- The session token used in the Place Autocomplete (Legacy) request
- The
fieldsparameter specifying Basic Data fields such as address and geometry
Consider delaying Place Autocomplete (Legacy) requests
You can employ strategies such as delaying a Place Autocomplete (Legacy) request until the user has typed in the first three or four characters so that your application makes fewer requests. For example, making Place Autocomplete (Legacy) requests for each character after
the user has typed the third character means that if the user types seven characters then selects a prediction for which you make one Geocoding API request, the total cost would be for 4 Place Autocomplete (Legacy) Per Request + Geocoding. 1
If delaying requests can get your average programmatic request below four, you can follow the guidance for performant Place Autocomplete (Legacy) with Geocoding API implementation. Note that delaying requests can be perceived as latency by the user who might be expecting to see predictions with every new keystroke.
Consider employing performance best practices to help your users get the prediction they're looking for in fewer characters.
-
For costs, see Google Maps Platform pricing lists .
Performance best practices
The following guidelines describe ways to optimize Place Autocomplete (Legacy) performance:
- Add country restrictions, location biasing , and (for programmatic implementations) language preference to your Place Autocomplete (Legacy) implementation. Language preference is not needed with widgets since they pick language preferences from the user's browser or mobile device.
- If Place Autocomplete (Legacy) is accompanied by a map, you can bias location by map viewport.
- In situations when a user does not choose one of the Place Autocomplete (Legacy) predictions, generally
because none of those predictions are the result-address wanted, you can reuse the original
user input to attempt to get more relevant results:
- If you expect the user to enter only address information, reuse the original user input in a call to the Geocoding API .
- If you expect the user to enter queries for a specific place by name or address, use a Place Details (Legacy) request. If results are only expected in a specific region, use location biasing .
- Users inputting subpremise addresses, such as addresses for specific units or apartments within a building. For example, the Czech address "Stroupežnického 3191/17, Praha" yields a partial prediction in Place Autocomplete (Legacy).
- Users inputting addresses with road-segment prefixes like "23-30 29th St, Queens" in New York City or "47-380 Kamehameha Hwy, Kaneohe" on the island of Kauai in Hawai'i.
Location biasing
Bias results to a specified area by passing a location
parameter and a radius
parameter. This instructs Place Autocomplete (Legacy) to prefer
showing results
within the defined area. Results outside of the defined area may still be
displayed. You can use the includedRegionCodes
parameter to filter results
to show only those places within a specified country.
Location restricting
Restrict results to a specified area by passing a locationRestriction
parameter.
You may also restrict results to the region defined by location
and a radius
parameter, by adding the strictbounds
parameter. This instructs Place Autocomplete (Legacy) to return only
results within that region.
Troubleshooting
Although a wide variety of errors can occur, the majority of the errors your app is likely to experience are usually caused by configuration errors (for example, the wrong API key was used, or the API key was configured incorrectly), or quota errors (your app has exceeded its quota). See Usage Limits for more information about quotas.
Errors that occur in the use of the autocomplete controls are returned in the didFailAutocompleteWithError()
method of the various delegate protocols. The code
property of the supplied NSError
object is set to one of the values of
the GMSPlacesErrorCode
enumeration.


