This page refers to the XML version of the Custom Search JSON API, which is available only to Google Site Search customers.
- Overview
- Programmable Search Engine Request Format
- XML Results
Overview
The Google WebSearch service enables Google Site Search customers to display Google search results on their own web sites. The WebSearch service uses a simple HTTP-based protocol to serve search results. Search administrators have complete control over the way they request search results and the way they present those results to the end user. This document describes the technical details of the Google search request and results formats.
To retrieve Google WebSearch results, your application sends Google a simple HTTP request. Google then returns search results in XML format. XML-formatted results give you the ability to customize the way search results are displayed.
WebSearch Request Format
- Request Overview
- Query Terms
- Request Parameters
- Sample WebSearch Queries
- WebSearch Query Parameter Definitions
- Sample Image Queries
- Image Search Query Parameter Definitions
- Advanced Search
- Advanced Search Query Parameters
- Special Query Terms
- Request Limits
Request Overview
The Google search request is a standard HTTP GET
command. It
includes a collection of parameters relevant to your
queries. These parameters are included in the request URL as name=value
pairs separated by ampersand (&) characters. Parameters include
data like the search query and a unique engine ID ( cx
) that identifies the
engine that is making the HTTP request. The WebSearch or Image Search service returns
XML results in response to your HTTP requests.
Query Terms
Most search requests include one or more query terms. A query term appears as the value of a parameter in the search request.
Query terms can specify several types of information to filter and organize the search results that Google returns. Queries can specify:
- Words or phrasesto include or
exclude
- All of the words in a search query (default)
- An exact phrase in the search query
- Any word or phrase in a search query
- Where in a documentto look for the
search terms
- Anywhere in the document (default)
- Only in the body of the document
- Only in the document title
- Only in the document URL
- Only in links in the document
- Restrictions on the documents themselves
- Including or excluding documents of particular file types (such as PDF files or Word documents)
- Special URL queriesthat return
information about a given URL, rather than doing a search
- Queries that return general information about a URL, such as its Open Directory category, snippet or language
- Queries that return the set of web pages that link to a URL
- Queries that return a set of web pages similar to a given URL
Default Search
Search query parameter values must be URL-escaped. Note that you would substitute the plus sign ("+") for any whitespace sequences in the search query. This is discussed further in the URL Escaping section of this document.
The search query term is submitted to the WebSearch service using the q parameter. A sample search query term is:
q=horses+cows+pigs
By default, the Google WebSearch service only returns documents that include all of the terms in the search query.
Request Parameters
This section lists the parameters that you can use when making a search request. The parameters are split into two lists. The first list contains parameters that are relevant to all search requests. The second list contains parameters that are only relevant to advanced search requests.
Three request parameters are required:
- The client
parameter must be set to
google-csbe - The output
parameter specifies the
format of the returned XML results; results can be returned with (xml)
or without (
xml_no_dtd) a reference to Google's DTD. We recommend setting this value toxml_no_dtd. Note: If you do not specify this parameter, then results will be returned in HTML instead of XML. - The cx
parameter which represents the unique
ID of the engine.
The most commonly used request parameters other than the ones mentioned above are:
- num —the requested number of search results
- q —the search term(s)
- start —the starting index for the results
Sample WebSearch Queries
The examples below show a couple of WebSearch HTTP requests to illustrate how different query parameters are used. Definitions for the different query parameters are provided in the WebSearch Query Parameter Definitions and the Advanced Search Query Parameters sections of this document.
This request asks for the first 10 results ( start=0&num=10
)
for the query term "red sox" ( q=red+sox
). The query also
specifies that results should come from Canadian web sites ( cr=countryCA
)
and should be written in French ( lr=lang_fr
). Finally, the query
specifies values for the client
, output
,
and cx
parameters, all three of which are required.
http://www.google.com/search?
start=0
&num=10
&q=red+sox
&cr=countryCA
&lr=lang_fr
&client=google-csbe
&output=xml_no_dtd
&cx=00255077836266642015:u-scht7a-8i
This example uses some of the advanced search query
parameters
to further customize the search query. This request uses the as_q
parameter ( as_q=red+sox
) instead of the q
parameter. It also uses the as_eq
parameter to exclude any documents containing the word "Yankees" from the
search results ( as_eq=yankees
).
http://www.google.com/search?
start=0
&num=10
&as_q=red+sox
&as_eq=Yankees
&client=google-csbe
&output=xml_no_dtd
&cx=00255077836266642015:u-scht7a-8i
WebSearch Query Parameter Definitions
Optional. The c2coffparameter enables or disables the Simplified and Traditional Chinese Search feature.
The default value for this parameter is 0
(zero), meaning
that the feature is enabled. Values for the c2coff
parameter are:
| Value | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Disabled |
| 0 | Enabled |
q=google&c2coff=1
Required. The client
parameter must be set to google-csbe
.
q=google&client=google-csbe
Optional. The cr
parameter restricts search results to documents originating in a
particular country. You may use Boolean
operators
in the cr
parameter's
value.
Google WebSearch determines the country of a document by analyzing:
- the top-level domain (TLD) of the document's URL
- the geographic location of the Web server's IP address
See the Country (cr) Parameter Values section for a list of valid values for this parameter.
q=Frodo&cr=countryNZ
Required. The cx
parameter specifies a unique
code that identifies a custom
search engine. You must specify a Programmable Search Engine using the cx
parameter to retrieve search results from that engine.
To find the value of the cx
parameter, go to Control Panel > Codes
tab of your engine and you will find it in the text area
under 'Paste this code in the page where you'd like your search box to
appear. The search results will be shown on a Google-hosted page.'
q=Frodo&cx=00255077836266642015:u-scht7a-8i
Optional. The filterparameter activates or deactivates the automatic filtering of Google search results. See the Automatic Filtering section of this document for more information about Google's search results filters.
The default value for the filter
parameter is 1
,
which indicates that the feature is enabled. Valid values for this
parameter are:
| Value | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Disabled |
| 0 | Enabled |
Note:By default, Google applies filtering to all search results to improve the quality of those results.
q=google&filter=0
Optional. The gl
parameter value is a
two-letter country code. For WebSearch results, the gl
parameter boosts search results whose country of origin matches the
parameter value. See the Country Codes
section for a list of valid values.
Specifying a gl
parameter value in WebSearch requests
should improve the relevance of results. This is particularly
true for international customers and, even more specifically, for
customers in English-speaking countries other than the United States.
This request boosts documents written in the United Kingdom in
WebSearch results: q=pizza&gl=uk
Optional. The hl
parameter specifies the
interface language (host language) of your user interface. To improve
the performance and the quality of your search results, you are
strongly encouraged to set this parameter explicitly.
See the Interface Languages section of Internationalizing Queries and Results Presentation for more information and Supported Interface Languages for a list of supported languages.
This request targets ads for wine in French. ( Vin is the French term for wine.)
q=vin&ip=10.10.10.10&ad=w5& hl=fr
Optional. The hq
parameter appends the specified query terms to
the query, as if they were combined with a logical AND operator.
This request searches for 'pizza' AND 'cheese'. The expression is the same as q=pizza+cheese
.
q=pizza&hq=cheese
Optional. The ie
parameter sets the character
encoding scheme that should be used to interpret the query string. The
default ie
value is latin1
.
See the Character Encoding section for a discussion of when you might need to use this parameter.
See the Character Encoding
Schemes
section for the list of possible ie
values.
q=google&ie=utf8&oe=utf8
Optional. The lr
(language restrict) parameter restricts search results to documents
written in a particular language.
Google WebSearch determines the language of a document by analyzing:
- the top-level domain (TLD) of the document's URL
- language meta tags within the document
- the primary language used in the body text of the document
- secondary languages, if any, used in the body text of the document
See the Language ( lr
)
Collection Values
section for a list of valid values for this
parameter.
q=Frodo&lr=lang_en
Optional. The num
parameter identifies the
number of search results to return.
The default num
value is 10
, and the maximum
value is 20
. If you request more than 20 results, only 20
results will be returned.
Note:If the total number of search results is less than the requested number of results, all available search results will be returned.
q=google& num=10
Optional. The oe
parameter sets the character
encoding scheme that should be used to decode the XML result. The
default oe
value is latin1
.
See the Character Encoding section for a discussion of when you might need to use this parameter.
See the Character Encoding
Schemes
section for the list of possible oe
values.
q=google&ie=utf8& oe=utf8
Required. The output
parameter specifies the format of the XML results. The only valid
values for this parameter are xml
and xml_no_dtd
. The
chart below explains how these parameter values differ.
| Value | Output Format |
|---|---|
xml_no_dtd
|
The XML results will not include a
!DOCTYPE statement. (Recommended)
|
xml
|
The XML results will contain a Google
DTD reference. The second line of the result will identify the document
definition type (DTD) that the results use: <!DOCTYPE GSP SYSTEM "google.dtd"> |
output=xml_no_dtd
output=xml
Optional. The q
parameter specifies the search
query entered by the user. Even though this parameter is optional, you
must specify a value for at least one of the query parameters ( as_epq
, as_lq
, as_oq
, as_q
to get search results.
There are also a number of special query terms that can be
used as part of the q
parameter's
value. Please see Special Query Terms
for a list and definitions of these terms.
The Google Search Control Panel includes a report of the top
queries submitted using the q
parameter.
Note:The value specified for the qparameter must be URL-escaped.
q=vacation
&as_oq=london+paris
Optional. The safe
parameter indicates how search results should be filtered for adult and
pornographic content. The default value for the safe
parameter is off
. Valid parameter values
are:
| Value | Action |
|---|---|
off
|
Disable SafeSearch |
medium
|
Enable SafeSearch |
high
|
Enable a stricter version of SafeSearch |
See the Filtering Adult Content with SafeSearch section for more details about this feature.
q=adult&safe=high
Optional. The start
parameter indicates the first matching result that should be included
in the search results. The start
parameter uses a zero-based index, meaning the first result is 0, the
second result is 1 and so forth.
The start
parameter works in
conjunction with the num
parameter to determine
which search results to return. Note that no more than 1000 results will ever be returned for any query, even if more than 1000 documents match the query, so setting start to 1000 or more will produce no results.
start=10
Optional. The sort
parameter specifies that the results be sorted according to the specified expression. For example, sort by date.
sort=date
Optional. The ud
parameter indicates
whether the XML response should include the IDN-encoded URL for the search result.
IDN (International Domain Name) encoding allows domains to be displayed using local
languages, for example:
http://www.花井鮨.com
Valid values for this parameter are 1
(default), meaning the XML result should
include IDN-encoded URLs, and 0
, meaning the XML result should not include IDN-encoded
URLs. If the ud
parameter is set to 1
, the IDN-encoded URL will appear in
in the UD
tag in your XML results.
If the ud
parameter is set to 0
, the URL in the example above would be
displayed as:
http://www.xn--elq438j.com.
Note:This is a beta feature.
q=google&ud=1
Advanced Search
The additional query parameters listed below the image are relevant to advanced search queries. When you submit an advanced search, the values of several parameters (e.g. as_eq , as_epq , as_oq , etc.) are all factored into the query terms for that search. The image shows Google's Advanced Search page. On the image, the name of each advanced search parameter is written in red text inside of or next to the field on the page to which that parameter corresponds.
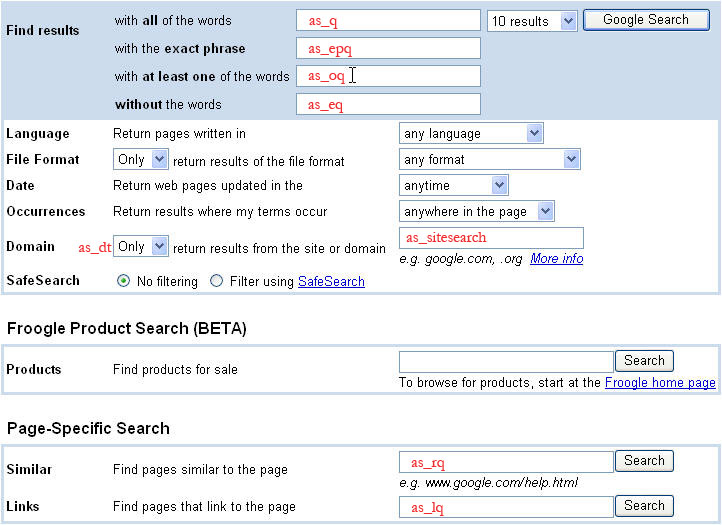
Advanced Search Query Parameters
Optional. The as_dt
parameter controls whether
to include or exclude results from the site named in the as_sitesearch
parameter. The
values i
and e
denote inclusion and exclusion respectively.
as_dt=i,as_dt=e
Optional. The as_epq
parameter identifies a
phrase that all documents in the search results must contain. You can
also use the phrase search
query term to
search for a phrase.
as_epq=abraham+lincoln
Optional. The as_eq
parameter identifies a word
or phrase that should not appear in any documents in the search
results. You can also use the exclude
query
term to ensure that a particular word or phrase will not appear in the
documents in a set of search results.
q=bass&as_eq=music
.
Optional. The as_lq
parameter specifies that
all search results should contain a link to a particular URL. You can also
use the link:
query term for this type of query.
as_lq=www.google.com
Optional. The as_nlo
parameter specifies the starting value for
a search range. Use as_nlo
and as_nhi
to append an inclusive search
range of as_nlo...as_nhi
to the query.
The following sets a search range of 5 to 10, inclusive:
as_nlo=5&as_nhi=10
Optional. The as_nhi
parameter specifies the
ending value for a search range. Use as_nlo
and as_nhi
to append an
inclusive search range of as_nlo...as_nhi
to the query.
The following sets a search range of 5 to 10, inclusive:
as_nlo=5&as_nhi=10
Optional. The as_oq
parameter provides
additional search terms to check for in a document, where each document
in the search results must contain at least one of the additional
search terms. You can also use the Boolean OR
query term for
this type of query.
q=vacation&as_oq=London+Paris
Optional. The as_q
parameter provides search
terms to check for in a document. This parameter is also commonly used
to allow users to specify additional terms to search for within a set
of search results.
q=president&as_q=John+Adams
Optional. The as_qdr
parameter requests search
results from a specified time period (quick date range). The following values are supported:
d[number]
requests results from the specified number of past days.
w[number]
requests results from the specified number of past weeks.
m[number]
requests results from the specified number of past months.
y[number]
requests results from the specified number of past years.
This example requests results from the past year:
as_qdr=y
This example requests results from the past 10 days:
as_qdr=d10
Optional. The as_sitesearch
parameter allows you to specify that all search results should be pages from a given site. By setting the as_dt
parameter, you can also use it to exclude pages from a given site from your search resutls.
q=vacation&as_sitesearch=www.google.com
Special Query Terms
Google WebSearch allows the use of several special query terms that
access additional capabilities of the Google search engine. These
special query terms should be included in the value of the q
request parameter. Like other query terms, the
special query terms must be URL-escaped
. A
number of the special query terms contain a colon (:). This character
must also be URL-escaped; its URL-escaped value is %3A
.
The link:
query term retrieves the set of Web pages
that link to a particular URL. The search query should be formatted as link:URL
with no space between the link:
query term and the URL.
The URL-escaped version of link:
is link%3A
.
You can also use the as_lq
request
parameter to submit a link:
request.
Note:You cannot specify any other query terms when
using link:
.
http://www.google.com/search? q=link%3Awww.example.com
The OR
query term retrieves documents that include one
of a series of (two or more) query terms. To use the OR
query
term, you would insert the search term OR
, in uppercase
letters, between each term in the series.
You can also use the as_oq request parameter to submit a search for any term in a set of terms.
Note: If a search request specifies the query "London+OR+Paris", the search results will include documents containing at least one of those two words. In some cases, documents in the search results may contain both words.
Search for London or Paris:
london OR
paris
Query term: q=london+OR+paris
Search for vacation and either London or Paris:
q=vacation+london+OR+paris
Search for vacation and one of London, Paris or chocolates:
q=vacation+london+OR+paris+OR+chocolates
Search for vacation and chocolates and either london or paris, with the least weight being given to chocolates:
q=vacation+london+OR+paris+chocolates
Search for vacation, chocolates and flowers in documents that also contain either London or Paris:
q=vacation+london+OR+paris+chocolates+flowers
Search for vacation and one of London or Paris and also search for one of chocolates or flowers:
q=vacation+london+OR+paris+chocolates+OR+flowers
The exclude ( -
) query term restricts results for a
particular search request to documents that do notcontain a
particular word or phrase. To use the exclude query term, you would
preface the word or phrase to be excluded from the matching documents
with "-" (a minus sign).
The URL-escaped version of -
is %2D
.
The exclude query term is useful when a search term has more than one meaning. For example, the word "bass" could return results about either fish or music. If you were looking for documents about fish, you could exclude documents about music from your search results by using the exclude query term.
You can also use the as_eq request parameter to exclude documents matching a particular word or phrase from search results.
bass -music
Query term:
q=bass+ %2Dmusic
The -filetype:
query term excludes documents with a
particular file extension, such as ".pdf" or ".doc" from search
results. The search query should be formatted as -filetype:EXTENSION
with no space between the -filetype:
query term and the
specified extension.
The URL-escaped version of -filetype:
is %2Dfiletype%3A
.
Note:
You can exclude multiple
file types from search results by adding more -filetype:
query
terms to your query. You should have one -filetype:
query term
in your search query for each file extension that should be excluded
from the search results.
Filetypes supported by Google include:
- Adobe Portable Document Format (pdf)
- Adobe PostScript (ps)
- Lotus 1-2-3 (wk1, wk2, wk3, wk4, wk5, wki, wks, wku)
- Lotus WordPro (lwp)
- Macwrite (mw)
- Microsoft Excel (xls)
- Microsoft PowerPoint (ppt)
- Microsoft Word (doc)
- Microsoft Works (wks, wps, wdb)
- Microsoft Write (wri)
- Rich Text Format (rtf)
- Shockwave Flash (swf)
- Text (ans, txt).
Additional filetypes may be added in the future. An up-to-date list can always be found in Google's file type FAQ .
This example returns documents that mention "Google" but that
are not PDF documents: q=Google+ %2Dfiletype%3Apdf
This example returns documents that mention "Google" but
excludes both PDF and Word documents: q=Google+ %2Dfiletype%3Apdf+%2Dfiletype%3Adoc
The filetype:
query term restricts search results to
documents with a particular file extension, such as ".pdf" or ".doc".
The search query should be formatted as filetype:EXTENSIONwith
no space between the filetype:
query term and the specified
extension.
The URL-escaped version of filetype:
is filetype%3A
.
You can restrict search
results to documents matching one of several file extensions by adding
more filetype:
query terms to your query. You should have one filetype:
query term in your search query for each file extension that should be included in the search results. Multiple filetype:
query terms must be separated using the OR
query term.
By default, search results will include documents with any file extension.
Filetypes supported by Google include:
- Adobe Portable Document Format (pdf)
- Adobe PostScript (ps)
- Lotus 1-2-3 (wk1, wk2, wk3, wk4, wk5, wki, wks, wku)
- Lotus WordPro (lwp)
- Macwrite (mw)
- Microsoft Excel (xls)
- Microsoft PowerPoint (ppt)
- Microsoft Word (doc)
- Microsoft Works (wks, wps, wdb)
- Microsoft Write (wri)
- Rich Text Format (rtf)
- Shockwave Flash (swf)
- Text (ans, txt).
Additional filetypes may be added in the future. An up-to-date list can always be found in Google's file type FAQ .
This example returns PDF documents that mention "Google": q=Google+ filetype%3Apdf
This example returns PDF and Word documents that mention
"Google": q=Google+ filetype%3Apdf+OR+filetype%3Adoc
The include (+) query term specifies that a word or phrase must occur in all documents included in the search results. To use the include query term, you would preface the word or phrase that must be included in all search results with "+" (a plus sign).
The URL-escaped version of +
(a plus sign) is %2B.
You should use +
before a common word that Google
normally discards before identifying search results.
Star Wars Episode +I
Query term:
q=Star+Wars+Episode+ %2BI
The allinlinks:
query term requires documents in
search results to contain all of the words in the search query in URL
links. The search query should be formatted as allinlinks:
followed by the words in your search query.
If your search query includes the allinlinks:
query
term, Google will only check the URL links in documents for the words
in your search query, ignoring other text in the documents, the
document titles and the URLs of each document. Note that the document
URL is different from the URL links contained in the document.
The URL-escaped version of allinlinks:
is allinlinks%3A
.
allinlinks: Google search
Query term:
q= allinlinks%3A+Google+search
The phrase search (") query term allows you to search for complete phrases by enclosing the phrases in quotation marks or by connecting them with hyphens.
The URL-escaped version of "
(a quotation mark) is %22
.
Phrase searches are particularly useful if you are searching for famous quotes or proper names.
You can also use the as_epq request parameter to submit a phrase search.
"Abraham Lincoln"
Query term:
q= %22Abraham+Lincoln%22
The allintext:
query term requires each document in
the search results to contain all of the words in the search query in
the body of the document. The query should be formatted as allintext:
followed by the words in your search query.
If your search query includes the allintext:
query
term, Google will only check the body text of documents for the words
in your search query, ignoring links in those documents, document
titles and document URLs.
The URL-escaped version of allintext:
is allintext%3A
.
User input:
allintext:Google search
Query term:
q=allintext%3AGoogle+search
The intitle:
query term restricts search results to
documents that contain a particular word in the document title. The
search query should be formatted as intitle:WORDwith no space
between the intitle:
query term and the following word.
Note:
You can specify more
than one word that must be included in the document title by putting
the intitle:
query term in front of each such word. You can
also use the allintitle:
query term to
specify that all query words must be included in the titles of
documents that are in the search results.
The URL-escaped version of intitle:
is intitle%3A
.
This example specifies that the word "Google" must appear in
the titles of any documents in the search results, and the word
"search" must appear anywhere in the titles, URLs, links or body text
of those documents:
User input: intitle:Google search
Query term: q= intitle%3AGoogle+search
The allintitle:
query term restricts search results to
documents that contain all of the query words in the document title. To
use the allintitle:
query term, include "allintitle:" at the
start of your search query.
Note:
Putting allintitle:
at the beginning of a search query is equivalent to putting intitle:
in front of each word in the search
query.
The URL-escaped version of allintitle:
is allintitle%3A.
This example specifies that the words "Google" and "search"
must appear in the titles of any documents in the search results:
User input: allintitle: Google search
Query term: q= allintitle%3A+Google+search
The inurl:
query term restricts search results to
documents that contain a particular word in the document URL. The
search query should be formatted as inurl:WORDwith no space
between the inurl:
query term and the following word.
The inurl:
query
term ignores punctuation and uses only the first word following the inurl:
operator. You can specify more than one word that must be included in
the document URL by putting the inurl:
query term in front of
each such word. You can also use the allinurl:
query term to specify that all query words must be included in the URLs
of documents that are in the search results.
The URL-escaped version of inurl:
is inurl%3A
.
This example specifies that the word "Google" must appear in
the URLs of any documents in the search results, and the word "search"
must appear anywhere in the titles, URLs, links or body text of those
documents:
User input: inurl:Google search
Query term: q= inurl%3AGoogle+search
The allinurl:
query term restricts search results to
documents that contain all of the query words in the document URL. To
use the allinurl:
query term, include allinurl:
at the start
of your search query.
The allinurl:
query term ignores punctuation, so it works only on words, not on URL
components. For example, allinurl: uk/scotland
will restrict results
to documents that contain the words "uk" and "scotland" in their URLs,
but will not require that those two words appear in any particular
order or that they be separated by a slash.
The URL-escaped version of allinurl:
is allinurl%3A
.
This example specifies that the words "Google" and "search"
must appear in the URLs of any documents in the search results:
User input: allinurl: Google search
Query term: q= allinurl%3A+Google+search
The info:
query term retrieves general information
about a URL as long as that URL is included in Google's search index.
The search query should be formatted as info:URLwith no space
between the info:
query term and the URL.
The URL-escaped version of info:
is info%3A.
Note:You cannot specify any other query terms when
using info:
.
info:www.google.com
Query term:
q= info%3Awww.google.com
Sample Image Queries
The examples below show a couple of Image HTTP requests to illustrate how different query parameters are used. Definitions for the different query parameters are provided in the Image Query Parameter Definitions sections of this document.
This request asks for the first 5 results ( start=0&num=5
) for the query term "monkey" ( q=monkey
), of filetype .png. Finally, the query specifies values for the client
, output
, and cx
parameters, all three of which are required.
http : //www.google.com/cse? searchtype = image start = 0 & num = 5 & q = monkey & as_filetype = png & client = google - csbe & output = xml_no_dtd & cx = 00255077836266642015 : u - scht7a - 8 i
Image Search Query Parameters
Optional. Returns images of a specified type. Allowed values are: bmp
, gif
, png
, jpg
, and svg
.
q=google&as_filetype=png
Optional. Returns images of a specified size, where size can be one of:
-
icon(small) -
small|medium|large|xlarge(medium) -
xxlarge(large) -
huge(extra-large)
q=google&as_filetype=png&imgsz=icon
Optional. Returns images of a type, which can be one of:
-
clipart(clipart) -
face(face) -
lineart(lineart) -
news(news) -
photo(photo)
q=google&as_filetype=png&imgtype=photo
Optional. Returns black and white, grayscale, or color images:
-
mono(black and white) -
gray(grayscale) -
color(color)
q=google&as_filetype=png&imgc=gray
Optional. Returns images of a specific dominant color:
-
yellow -
green -
teal -
blue -
purple -
pink -
white -
gray -
black -
brown
q=google&as_filetype=png&imgcolor=yellow
Optional. Filters based on licensing. Supported values include:
-
cc_publicdomain -
cc_attribute -
cc_sharealike -
cc_noncommercial -
cc_nonderived
q=cats&as_filetype=png&as_rights=cc_attribute
Request Limits
The chart below lists limitations on the search requests that you send to Google:
| Component | Limit | Comment |
|---|---|---|
|
Search request length
|
2048 bytes | |
|
Number of query terms
|
10 | includes terms in the following parameters: q , as_epq , as_eq , as_lq , as_oq , as_q |
|
Number of results
|
20 | If you set the num parameter to a number greater than 20, only 20 results are returned. To get more results, you would need to send multiple requests and increment the value of the start parameter with each request. |
Internationalizing Queries and Results Presentation
The Google WebSearch service enables you to search for documents in multiple languages. You can specify the character encoding that should be used to interpret your HTTP request and to encode your XML response (using the ie and oe search parameters). You can also filter results to only include documents written in certain languages.
The following sections discuss issues related to searching in multiple languages:
Character Encoding
Servers send data, such as web pages, to user agents, such as browsers, as a sequence of encoded bytes. The user agent then decodes the bytes into a sequence of characters. When sending requests to the WebSearch service, you can specify the encoding schemes for both your search query and for the XML response that you receive.
You can use the ie
request parameter to specify
the encoding mechanism for the characters in your HTTP request. You can
also use the oe
parameter to specify the encoding
scheme that Google should use to encode your XML response. If you are
using an encoding scheme other than ISO-8859-1
(or latin1
), please ensure that you specify the correct values
for the ie
and oe
parameters.
Note:If you are providing search functionality for multiple
languages, we recommend you use the utf8
(UTF-8) encoding value
for both the ie
and oe
parameters.
Please refer to the Character Encoding Schemes appendix for a complete list of the values that you can use for the ie and oe parameters.
For more general information about character encoding, please see http://www.w3.org/TR/REC-html40/charset.html .
Interface Languages
You can use the hl request parameter to identify the language of your graphical interface. The hl parameter value may affect XML search results, especially on international queries when language restriction (using the lr parameter) is not explicitly specified. In such cases, the hl parameter may promote search results in the same language as the user's input language.
We suggest you explicitly set the hl parameter in search results to ensure that Google selects the highest quality search results for each query.
Please see the Supported Interface Languages section for a complete list of valid values for the hl parameter.
Searching for Documents Written in Specific Languages
You can use the lr request parameter to restrict search results to documents that are written in a particular language or set of languages.
The lr parameter supports Boolean Operators to allow you to specify multiple languages that should be included (or excluded) from search results.
The following examples show how you might use Boolean Operators to request documents in different languages.
For documents written in Japanese:
lr=lang_jp
For documents written in Italian or German:
lr=lang_it|lang_de
For documents not written in Hungarian or Czech:
lr=(-lang_hu).(-lang_cs)
Please see the Language Collection Values section for a complete list of possible values for the lr parameter and the Boolean Operators section for a complete discussion of the use of these operators.
Simplified and Traditional Chinese Search
Simplified Chinese and Traditional Chinese are two writing variants of the Chinese language. The same concept may be written differently in each variant. Given a query in one of the variants, the Google WebSearch service can return results that include pages in both variants.
To use this feature:
- Set the c2coff
request parameter to 0
and - Do one of the following:
The following example shows the query parameters you would include in a request for results in both simplified and traditional Chinese. (Note that additional required information, such as the client , is not included in the example.)
search?hl=zh-CN
&lr=lang_zh-TW|lang_zh-CN
&c2coff=0
Filtering Results
Google WebSearch provides a number of ways to filter your search results:
- Automatic Filtering of Search Results
- Language and Country Filtering
- Filtering Adult Content with SafeSearch
Automatic Filtering of Search Results
In an effort to provide the best search results possible, Google uses two techniques to automatically filter search results that are generally considered undesirable:
-
Duplicate Content—If multiple documents contain the same information, then only the most relevant document of that set is included in your search results.
-
Host Crowding—If there are many search results from the same site, Google may not show all the results from that site or may show the results lower in
the ranking than they otherwise would have been.
We recommend you leave these filters on for typical search requests because the filters significantly enhance the quality of most search results. However, you can bypass these automatic filters by setting the filter query parameter to 0in your search request.
Language and Country Filtering
The Google WebSearch service returns results from a master index of all Web documents. The master index contains subcollections of documents that are grouped by particular attributes, including language and country of origin.
You can use the lr and cr request parameters to restrict search results to subcollections of documents that are written in particular languages or originate from particular countries, respectively.
Google WebSearch determines the language of a document by analyzing:
- the top-level domain (TLD) of the document's URL
- language meta tags within the document
- the primary language used in the body text of the document
Please also see the definition of the lr
parameter, the section on Searching for
Documents Written in Specific Languages
and the Language Collection Values
that can be
used as values for the lr
parameter for more
information on restricting results based on language.
Google WebSearch determines the country of a document by analyzing:
- the top-level domain (TLD) of the document's URL
- the geographic location of the Web server's IP address
Please also see the definition of the cr parameter and the Country Collection Values that can be used as values for the cr parameter for more information on restricting results by country of origin.
Note: You can combine language values and country values to customize your search results. For example, you could request documents that are written in French and come from France or Canada, or you could request documents that come from Holland and are not written in English. The lr and cr parameters both support Boolean Operators .
Filtering Adult Content with SafeSearch
Many Google customers do not want to display search results for sites that contain adult content. Using our SafeSearch filter, you can screen for search results that contain adult content and eliminate them. Google's filters use proprietary technology to check keywords, phrases and URLs. While no filters are 100 percent accurate, SafeSearch will remove the overwhelming majority of adult content from your search results.
Google strives to keep SafeSearch as current and comprehensive as possible by continually crawling the Web and by incorporating updates from user suggestions.
SafeSearch is available in the following languages:
English
French
German
Portuguese (Brazilian)
Spanish
Traditional Chinese
You can adjust the degree to which Google filters your results for adult content using the safe query parameter. The following table explains Google's SafeSearch settings and how those settings will affect your search results:
| SafeSearch Level | Description |
|---|---|
| high | Enables a stricter version of safe search. |
| medium | Blocks web pages containing pornography and other explicit sexual content. |
| off | Does not filter adult content from search results. |
*The default SafeSearch setting is off.
If you have SafeSearch activated and you find sites that contain offensive content in your results, please email the site's URL to safesearch@google.com , and we will investigate the site.
XML Results
- Google XML Results DTD
- About the XML Response
- XML Results for Regular and Advanced Search Queries
- Regular/Advanced Search: Sample Query and XML Result
- Regular/Advanced Search: XML Tags
Google XML Results DTD
Google uses the same DTD to describe the XML format for all types of search results. Many of the tags and attributes are applicable for all search types. Some tags, however, are applicable only for certain search types. Consequently, the definitions in the DTD may be less restrictive than the definitions given in this document.
This document describes those aspects of the DTD that are relevant for WebSearch. When you look at the DTD, if you're working on WebSearch, you can safely ignore tags and attributes that are not documented here. If the definition differs between the DTD and the documentation, that fact is noted in this document.
Google can return XML results either with or without a reference to the most recent DTD. The DTD is a guide to help search administrators and XML parsers understand Google's XML results. Because Google's XML grammar may change from time to time, you should not configure your parser to use the DTD to validate each XML result.
Additionally, you should not configure your XML parser to fetch the DTD each time you submit a search request. Google updates the DTD infrequently, and these requests create unnecessary delay and bandwidth requirements.
Google recommends that you use the xml_no_dtdoutput format to get XML results. If you specify the xml output format in your search request, the only difference is the inclusion of the following line in the XML results:
< !DOCTYPE GSP SYSTEM "google.dtd" >
You can access the latest DTD at http://www.google.com/google.dtd .
Please note that not all features in the DTD may be available or supported at this time.
About the XML Response
- All element values are valid HTML suitable for display unless otherwise noted in the XML tag definitions.
- Some element values are URLs that need to be HTML-encoded before they are displayed.
- Your XML parser should ignore undocumented attributes and tags. This allows your application to continue working without modification if Google adds more features to the XML output.
- Certain characters must be escaped when included as values in
XML tags. Your XML processor should convert these entities back to the
appropriate characters. If you do not convert entities properly, the
browser may, for example, render the & character as "&".
The XML
Standard
documents these characters; these characters are
reproduced in the table below:
Character Escaped Forms Entity Character Code Ampersand& & & Single Quote' ' ' Double Quote" " " Greater Than> > > Less Than< < <
XML Results for Regular and Advanced Search Queries
Regular/Advanced Search: Sample Query and XML Result
This sample WebSearch request asks for 10 results ( num=10
)
about the search term "socer" ( q=socer
), which is the word
"soccer" intentionally spelled wrong for this example.)
http://www.google.com/search?
q=socer
&hl=en
&start=10
&num=10
&output=xml
&client=google-csbe
&cx=00255077836266642015:u-scht7a-8i
This request yields the XML result below. Note that there are several comments in the XML result to indicate where certain tags not included in the result would appear.
< ? xml version = "1.0" encoding = "ISO-8859-1" standalone = "no" ? >
< GSP VER = "3.2" >
< TM >0 . 452923 < / TM >
< Q >socer< / Q >
< PARAM name = "cx" value = "00255077836266642015:u-scht7a-8i" original_value = "00255077836266642015%3Au-scht7a-8i" / >
< PARAM name = "hl" value = "en" original_value = "en" / >
< PARAM name = "q" value = "socer" original_value = "socer" / >
< PARAM name = "output" value = "xml" original_value = "xml" / >
< PARAM name = "client" value = "google-csbe" original_value = "google-csbe" / >
< PARAM name = "num" value = "10" original_value = "10" / >
< Spelling >
< Suggestion q = "soccer" >< b><i>soccer < / i >< / b >< / Suggestion >
< / Spelling >
< Context >
< title >Sample Vacation CSE < / title >
< Facet >
< FacetItem >
< label >restaurants< / label >
< anchor_text >restaurants< / anchor_text >
< / FacetItem >
< FacetItem >
< label>wineries < / label >
< anchor_text>wineries < / anchor_text >
< / FacetItem >
< / Facet >
< Facet >
< FacetItem >
< label>golf_courses < / label >
< anchor_text>golf courses < / anchor_text >
< / FacetItem >
< / Facet >
< Facet >
< FacetItem >
< label>hotels < / label >
< anchor_text>hotels < / anchor_text >
< / FacetItem >
< / Facet >
< Facet >
< FacetItem >
< label>nightlife < / label >
< anchor_text>nightlife < / anchor_text >
< / FacetItem >
< / Facet >
< Facet >
< FacetItem >
< label>soccer_sites < / label >
< anchor_text>soccer sites < / anchor_text >
< / FacetItem >
< / Facet >
< / Context >
< RES SN = "1" EN = "10" >
< M >6080< / M >
/*
* The FI tag after the comment indicates that the result
* set has been filtered. If the number of results were exact, the
* FI tag would be replaced by an XT tag in the same format.
*/
< FI / >
< NB >
/*
* Since the request is for the first page of results, the PU tag,
* which contains a link to the previous page of search results,
* is not included in this XML result. If the sample result did include
* a previous page of results, it would be listed here, in the same format
* as the NU tag on the following line
*/
< NU > / search ? q = socer&hl = en&lr = & ie = UTF-8&output = xml&client = test&start = 10&sa = N < / NU >
< / NB >
< R N = "1" >
< U >http :// www . soccerconnection . net /</ U >
< UE >http :// www . soccerconnection . net /</ UE >
< T >SoccerConnection . net < / T >
< CRAWLDATE >May 21 , 2007 < / CRAWLDATE >
< S ><b>soccer< / b > ; players ; coaches ; ball ; world cup ; < b > ...</ b >< / S >
< Label>transcodable_pages < / Label >
< Label>accessible < / Label >
< Label>soccer_sites < / Label >
< LANG >en< / LANG >
< HAS >
< DI >
< DT >SoccerConnection . net < / DT >
< DS >Post your < b>soccer < / b > resume directly on the Internet .</ DS >
< / DI >
< L / >
< C SZ = "8k" CID = "kWAPoYw1xIUJ" / >
< RT / >
< / HAS >
< / R >
/*
* The result includes nine more results, each enclosed by an R tag.
*/
< / RES >
< / GSP >
Regular/Advanced Search: XML Tags
XML responses for regular search requests and advanced search requests both use the same set of XML tags. These XML tags are shown in the XML example above and explained in the tables below.
The XML tags below are listed alphabetically by tag name, and each tag definition contains a description of the tag, an example showing how the tag would appear in an XML result and the format of the tag's content. If the tag is a subtag of another XML tag or if the tag has subtags or attributes of its own, that information is also provided in the tag's definition table.
Certain symbols may be displayed next to some subtags in the definitions below. These symbols, and their meanings, are:
* = zero or more instances of the subtag
+ = one or more instances of the subtag
| A | B | C | D | F | G | H | I | L | M | N | P | Q | R | S | T | U | X |
The <anchor_text>tag specifies the text that you should display to users to identify a refinement label associated with a search result set. Since refinement labels replace nonalphanumeric characters with underscores, you should not display the value of the <label> tag in your user interface. Instead, you should display the value of the <anchor_text>tag.
This tag encapsulates the contents of a block in a body line of a promotion result. Each block has subtags T , U , and L . A nonempty T tag denotes that the block contains text; nonempty U and L tags denote that the block contains a link (with URL given in the U subtag and anchor text in the L subtag).
The <C>tag indicates that the WebSearch service
can retrieve a cached version of this search result URL. You cannot
retrieve cached pages through the XML API, but you can redirect users
to www.google.com
for this
content.
| Name | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
SZ
|
Text (Integer + "k") | Provides the size of the cached version of the search result in kilobytes ("k"). |
|
CID
|
Text | Identifies a document in Google's cache.
To fetch the document from the cache, send a search term built as
follows: cache: CIDtext : escapedURL The escaped URL is available in the UE tag. |
The <CRAWLDATE>tag identifies the date that the
page was last crawled. CRAWLDATE
is not returned for every search result page.
The <DS>tag provides the summary listed for a single category in the ODP directory.
The <DT>tag provides the title for a single category listed in the ODP directory.
The <Facet>tag contains a logical grouping of <FacetItem> tags. You can create these groupings using the Programmable Search Engine Engine XML Specification format . If you do not create these groupings, the results_xml_tag_Context><Context> tag will contain up to four <Facet>tags. The items within each <Facet>tag will be grouped for display purposes but may not have a logical relationship.
The <FacetItem>tag encapsulates information about a refinement label associated with a set of search results.
The <GSP>tag encapsulates all data returned in Google XML search results. "GSP" is an abbreviation for "Google Search Protocol".
| Name | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
VER
|
Text (Integer) | The VERattribute specifies the version of the search results output. The current output version is "3.2". |
The <label>tag specifies a refinement label that you can use to filter the search results that you receive. To use a refinement label, add the string more: [[label tag value]] to the value of the qparameter in your HTTP request to Google as shown in the following example. Please note that this value must be URL-escaped before you send the query to Google.
This example uses the refinement label golf_coursesto
filter search results about Palm Springs:
q=Palm+Springs+more:golf_courses
The URL-escaped version of this query is:
q=Palm+Springs+more%3Agolf_courses
Note:The <label>tag is not the same as the <Label>tag, which identifies a refinement label associated with a particular URL in your search results.
The <LANG>tag contains Google's best guess of the language of the search result.
The <M>tag identifies the estimated total number of results for the search.
Note:This estimate may not be accurate.
The <NU>tag contains a relative link to the next page of search results.
&output=xml&client=test&start=10</NU>
The <PARAM>tag identifies an input parameter submitted in the HTTP request associated with the XML result. Information about the parameter is contained in the tag attributes—name, value, original_value—and there will be one PARAM tag for each parameter submitted in the HTTP request.
| Name | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
name
|
Text | Input parameter name. |
|
value
|
HTML | HTML-formatted version of the input parameter value. |
|
original_value
|
Text | Original URL-escaped version of the input parameter value. |
The <PU>tag provides a relative link to the previous page of search results.
&client=test&start=10</PU>
The <Q>tag identifies the search query submitted in the HTTP request associated with the XML result.
<Q>pizza</Q>
The <R>tag encapsulates the details of an individual search result.
Note:The definition of the <R>tag for WebSearch is more restrictive than in the DTD .
| Name | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
N
|
Text (Integer) | Indicates the index (1-based) of this search result. |
|
MIME
|
Text | Indicates the MIME type of the search result. |
The <RES>tag encapsulates the set of individual search results and details about those results.
| Name | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
SN
|
Text (Integer) | Indicates the index (1-based) of the first search result returned in this result set. |
|
EN
|
Text (Integer) | Indicates the index (1-based) of the last search result returned in this result set. |
The <S>tag contains an excerpt for a search result that shows query terms highlighted in bold. Line breaks are included in the excerpt for proper text wrapping.
The <Spelling>tag encapsulates an alternate spelling suggestion for the submitted query. This tag only appears on the first page of search results. Spelling suggestions are available in English, Chinese, Japanese and Korean.
Note:Google will only return spelling suggestions for queries where the gl parameter value is in lowercase letters.
| Name | Format | Description |
| q | Text | The qattribute specifies the URL-escaped version of the spelling suggestion. |
As a child of <Context>, the <title>tag contains the name of your Programmable Search Engine.
As a child of <Facet>, the <title>tag provides a title for a set of facets.
As a child of <Context>: <title>My Search Engine</title>
As a child of <Facet>: <title>facet title</title>
The <TM>tag identifies the total server time needed to return search results, measured in seconds.
The <UD>tag provides the IDN-encoded (International Domain Name) URL for the search result. The value allows domains to be displayed using local languages. For example, the IDN-encoded URL http://www.%E8%8A%B1%E4%BA%95.comcould be decoded and displayed as http://www.花井鮨.com. This <UD>tag will only be included in search results for requests that included the ud parameter.
Note:This is a beta feature.
XML Results for Image Search Queries
This sample Image request asks for 5 results (num=5) about the search term "monkey" (q=monkey).
http : //www.google.com/cse? searchtype = image & num = 2 & q = monkey & client = google - csbe & output = xml_no_dtd & cx = 00255077836266642015 : u - scht7a - 8 i
This request yields the XML result below.
<GSP VER="3.2">
<TM>0.395037</TM>
<Q>monkeys</Q>
<PARAM name="cx" value="011737558837375720776:mbfrjmyam1g" original_value="011737558837375720776:mbfrjmyam1g" url_<escaped_value="011737558837375720776%3Ambfrjmyam1g" js_escaped_value="011737558837375720776:mbfrjmyam1g"/>
<PARAM name="client" value="google-csbe" original_value="google-csbe" url_escaped_value="google-csbe" js_escaped_value="google-csbe"/>
<PARAM name="q" value="monkeys" original_value="monkeys" url_escaped_value="monkeys" js_escaped_value="monkeys"/>
<PARAM name="num" value="2" original_value="2" url_escaped_value="2" js_escaped_value="2"/>
<PARAM name="output" value="xml_no_dtd" original_value="xml_no_dtd" url_escaped_value="xml_no_dtd" js_escaped_value="xml_no_dtd"/>
<PARAM name="adkw" value="AELymgUP4VYSok20wy9SeYczEZ5UXxpBmRsJH4oC4aXhVuZgwGKuponcNXjrYkkw2bRv1BylIm89ndJ-Q4vxvyW0tcbiqipcQC9op_cBG84T12WMvX8660A" original_value="AELymgUP4VYSok20wy9SeYczEZ5UXxpBmRsJH4oC4aXhVuZgwGKuponcNXjrYkkw2bRv1BylIm89ndJ-Q4vxvyW0tcbiqipcQC9op_cBG84T12WMvX8660A" url_escaped_value="AELymgUP4VYSok20wy9SeYczEZ5UXxpBmRsJH4oC4aXhVuZgwGKuponcNXjrYkkw2bRv1BylIm89ndJ-Q4vxvyW0tcbiqipcQC9op_cBG84T12WMvX8660A" js_escaped_value="AELymgUP4VYSok20wy9SeYczEZ5UXxpBmRsJH4oC4aXhVuZgwGKuponcNXjrYkkw2bRv1BylIm89ndJ-Q4vxvyW0tcbiqipcQC9op_cBG84T12WMvX8660A"/>
<PARAM name="hl" value="en" original_value="en" url_escaped_value="en" js_escaped_value="en"/>
<PARAM name="oe" value="UTF-8" original_value="UTF-8" url_escaped_value="UTF-8" js_escaped_value="UTF-8"/>
<PARAM name="ie" value="UTF-8" original_value="UTF-8" url_escaped_value="UTF-8" js_escaped_value="UTF-8"/>
<PARAM name="boostcse" value="0" original_value="0" url_escaped_value="0" js_escaped_value="0"/>
<Context>
<title>domestigeek</title>
</Context>
<ARES/>
<RES SN="1" EN="2">
<M>2500000</M>
<NB>
<NU>/images?q=monkeys&num=2&hl=en&client=google-csbe&cx=011737558837375720776:mbfrjmyam1g&boostcse=0&output=xml_no_dtd
&ie=UTF-8&oe=UTF-8&tbm=isch&ei=786oTsLiJaaFiALKrPChBg&start=2&sa=N
</NU>
</NB>
<RG START="1" SIZE="2"/>
<R N="1" MIME="image/jpeg">
<RU>http://www.flickr.com/photos/fncll/135465558/</RU>
<U>
http://farm1.static.flickr.com/46/135465558_123402af8c.jpg
</U>
<UE>
http://farm1.static.flickr.com/46/135465558_123402af8c.jpg
</UE>
<T>Computer <b>Monkeys</b> | Flickr - Photo Sharing!</T>
<RK>0</RK>
<BYLINEDATE>1146034800</BYLINEDATE>
<S>Computer <b>Monkeys</b> | Flickr</S>
<LANG>en</LANG>
<IMG WH="500" HT="305" IID="ANd9GcQARKLwzi-t4lpWi2AERV3kJb4ansaQzTn3MNDZR9fD_JDiktPKByKUBLs">
<SZ>88386</SZ>
<IN/>
</IMG>
<TBN TYPE="0" WH="130" HT="79" URL="http://t0.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcQARKLwzi-
t4lpWi2AERV3kJb4ansaQzTn3MNDZR9fD_JDiktPKByKUBLs"/>
</R>
<R N="2" MIME="image/jpeg">
<RU>
http://www.flickr.com/photos/flickerbulb/187044366/
</RU>
<U>
http://farm1.static.flickr.com/73/187044366_506a1933f4.jpg
</U>
<UE>
http://farm1.static.flickr.com/73/187044366_506a1933f4.jpg
</UE>
<T>
one. ugly. <b>monkey</b>. | Flickr - Photo Sharing!
</T>
<RK>0</RK>
<BYLINEDATE>1152514800</BYLINEDATE>
<S>one. ugly. <b>monkey</b>.</S>
<LANG>en</LANG>
<IMG WH="400" HT="481" IID="ANd9GcQ3Qom0bYbee4fThCQVi96jMEwMU6IvVf2b8K5vERKVw-
EF4tQQnDDKOq0"><SZ>58339</SZ>
<IN/>
</IMG>
<TBN TYPE="0" WH="107" HT="129" URL="http://t1.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcQ3Qom0bYbee4fThCQ
Vi96jMEwMU6IvVf2b8K5vERKVw-EF4tQQnDDKOq0"/>
</R>
</RES>
</GSP>
Image Search: XML Tags
The table below shows additional XML tags used in XML responses for image search queries.
Certain symbols may be displayed next to some subtags in the definitions below. These symbols, and their meanings, are:
* = zero or more instances of the subtag
+ = one or more instances of the subtag
The <RG>tag encloses the details of an individual image search result.
| Name | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
N
|
Text (Integer) | Indicates the index (1-based) of this search result. |
|
MIME
|
Text | Indicates the MIME type of the search result. |

