This page contains code snippets and descriptions of the features available for customizing an Android TV Receiver app.
Configuring libraries
To make Cast Connect APIs available to your Android TV app:
- Open the
build.gradlefile inside your application module directory. - Verify that
google()is included in the listedrepositories.repositories { google() } - Depending on your target device type for your app, add the latest versions
of the libraries to your dependencies:
- For Android Receiver app:
dependencies { implementation ' com . google . android . gms : play - services - cast - tv : 21.1.1 ' implementation ' com . google . android . gms : play - services - cast : 22.1.0 ' }
- For Android Sender app:
dependencies { implementation ' com . google . android . gms : play - services - cast : 21.1.1 ' implementation ' com . google . android . gms : play - services - cast - framework : 22.1.0 ' }
- For Android Receiver app:
- Save the changes and click
Sync Project with Gradle Filesin the toolbar.
- Make sure you
Podfileis targetinggoogle-cast-sdk4.8.3 or higher - Target iOS 14 or higher. See Release Notes
for more details.
platform: ios, '14' def target_pods pod 'google-cast-sdk', '~>4.8.3' end
- Requires Chromium browser version M87 or higher.
- Add the Web Sender API library to your project
< script src = "//www.gstatic.com/cv/js/sender/v1/cast_sender.js?loadCastFramework=1" >< / script >
AndroidX requirement
New versions of Google Play Services require an app to have been updated to use
the androidx
namespace. Follow the instructions for migrating to AndroidX
.
Android TV app—prerequisites
In order to support Cast Connect in your Android TV app, you must create and support events from a media session. The data provided by your media session provides the basic information—for example, position, playback state, etc.—for your media status. Your media session also is used by the Cast Connect library to signal when it has received certain messages from a sender, like pause.
For more information on media session and how to initialize a media session, see the working with a media session guide .
Media session lifecycle
Your app should create a media session when playback starts and release it when it can’t be controlled any more. For example, if your app is a video app, you should release the session when the user exits the playback activity—either by selecting 'back' to browse other content or by backgrounding the app. If your app is a music app, you should release it when your app is no longer playing any media.
Updating session status
The data in your media session should be kept up-to-date with the status of your player. For example, when playback is paused, you should update the playback state as well as the supported actions. The following tables list what states you are responsible for keeping up to date.
MediaMetadataCompat
| Metadata Field | Description |
|---|---|
| METADATA_KEY_TITLE (required) | The media title. |
| METADATA_KEY_DISPLAY_SUBTITLE | The subtitle. |
| METADATA_KEY_DISPLAY_ICON_URI | The icon URL. |
| METADATA_KEY_DURATION (required) | Media duration. |
| METADATA_KEY_MEDIA_URI | The Content ID. |
| METADATA_KEY_ARTIST | The artist. |
| METADATA_KEY_ALBUM | The album. |
PlaybackStateCompat
| Required Method | Description |
|---|---|
| setActions() | Sets supported media commands. |
| setState() | Set the playing state and current position. |
MediaSessionCompat
| Required Method | Description |
|---|---|
| setRepeatMode() | Sets repeat mode. |
| setShuffleMode() | Sets shuffle mode. |
| setMetadata() | Sets media metadata. |
| setPlaybackState() | Sets playback state. |
private fun updateMediaSession () { val metadata = MediaMetadataCompat . Builder () . putString ( MediaMetadataCompat . METADATA_KEY_TITLE , "title" ) . putString ( MediaMetadataCompat . METADATA_KEY_DISPLAY_SUBTITLE , "subtitle" ) . putString ( MediaMetadataCompat . METADATA_KEY_DISPLAY_ICON_URI , mMovie . getCardImageUrl ()) . build () val playbackState = PlaybackStateCompat . Builder () . setState ( PlaybackStateCompat . STATE_PLAYING , player . getPosition (), player . getPlaybackSpeed (), System . currentTimeMillis () ) . build () mediaSession . setMetadata ( metadata ) mediaSession . setPlaybackState ( playbackState ) }
private void updateMediaSession() {
MediaMetadataCompat metadata =
new MediaMetadataCompat.Builder()
.putString(MediaMetadataCompat.METADATA_KEY_TITLE, "title")
.putString(MediaMetadataCompat.METADATA_KEY_DISPLAY_SUBTITLE, "subtitle")
.putString(MediaMetadataCompat.METADATA_KEY_DISPLAY_ICON_URI,mMovie.getCardImageUrl())
.build();
PlaybackStateCompat playbackState =
new PlaybackStateCompat.Builder()
.setState(
PlaybackStateCompat.STATE_PLAYING,
player.getPosition(),
player.getPlaybackSpeed(),
System.currentTimeMillis())
.build();
mediaSession.setMetadata(metadata);
mediaSession.setPlaybackState(playbackState);
}
Handling transport control
Your app should implement media session transport control callback. The following table shows what transport control actions they need to handle:
MediaSessionCompat.Callback
| Actions | Description |
|---|---|
| onPlay() | Resume |
| onPause() | Pause |
| onSeekTo() | Seek to a position |
| onStop() | Stop the current media |
class MyMediaSessionCallback : MediaSessionCompat . Callback () { override fun onPause () { // Pause the player and update the play state. ... } override fun onPlay () { // Resume the player and update the play state. ... } override fun onSeekTo ( long pos ) { // Seek and update the play state. ... } ... } mediaSession . setCallback ( MyMediaSessionCallback () );
public MyMediaSessionCallback extends MediaSessionCompat . Callback { public void onPause () { // Pause the player and update the play state . ... } public void onPlay () { // Resume the player and update the play state . ... } public void onSeekTo ( long pos ) { // Seek and update the play state . ... } ... } mediaSession . setCallback ( new MyMediaSessionCallback ());
Configuring Cast support
When a launch request is sent out by a sender application, an intent is created
with an application namespace. Your application is responsible for handling it
and creating an instance of the CastReceiverContext
object when the TV app is launched. The CastReceiverContext
object is needed
to interact with Cast while the TV app is running. This object enables your TV
application to accept Cast media messages coming from any connected senders.
Android TV setup
Adding a launch intent filter
Add a new intent filter to the activity that you want to handle the launch intent from your sender app:
<activity android:name="com.example.activity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.google.android.gms.cast.tv.action.LAUNCH" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
Specify receiver options provider
You need to implement a ReceiverOptionsProvider
to provide CastReceiverOptions
:
class MyReceiverOptionsProvider : ReceiverOptionsProvider { override fun getOptions ( context : Context?) : CastReceiverOptions { return CastReceiverOptions . Builder ( context ) . setStatusText ( "My App" ) . build () } }
public class MyReceiverOptionsProvider implements ReceiverOptionsProvider { @ Override public CastReceiverOptions getOptions ( Context context ) { return new CastReceiverOptions . Builder ( context ) . setStatusText ( "My App" ) . build (); } }
Then specify the options provider in your AndroidManifest
:
< meta
-
data
android
:
name
=
"com.google.android.gms.cast.tv.RECEIVER_OPTIONS_PROVIDER_CLASS_NAME"
android
:
value
=
"com.example.mysimpleatvapplication.MyReceiverOptionsProvider"
/
>
The ReceiverOptionsProvider
is used to provide the CastReceiverOptions
when CastReceiverContext
is initialized.
Cast receiver context
Initialize the CastReceiverContext
when your app is created:
override fun onCreate () { CastReceiverContext . initInstance ( this ) ... }
@Override public void onCreate () { CastReceiverContext . initInstance ( this ); ... }
Start the CastReceiverContext
when your app moves to the foreground:
CastReceiverContext . getInstance (). start ()
CastReceiverContext.getInstance().start();
Call stop()
on the CastReceiverContext
after the app goes into the background for video apps or apps that don't support
background playback:
// Player has stopped. CastReceiverContext . getInstance (). stop ()
// Player has stopped. CastReceiverContext . getInstance (). stop ();
Additionally, if your app does support playing in the background, call stop()
on the CastReceiverContext
when it stops playing while in the background.
We strongly recommend you use the LifecycleObserver from the androidx.lifecycle
library to manage calling CastReceiverContext.start()
and CastReceiverContext.stop()
,
especially if your native app has multiple activities. This avoids race
conditions when you call start()
and stop()
from different activities.
// Create a LifecycleObserver class. class MyLifecycleObserver : DefaultLifecycleObserver { override fun onStart ( owner : LifecycleOwner ) { // App prepares to enter foreground. CastReceiverContext . getInstance (). start () } override fun onStop ( owner : LifecycleOwner ) { // App has moved to the background or has terminated. CastReceiverContext . getInstance (). stop () } } // Add the observer when your application is being created. class MyApplication : Application () { fun onCreate () { super . onCreate () // Initialize CastReceiverContext. CastReceiverContext . initInstance ( this /* android.content.Context */ ) // Register LifecycleObserver ProcessLifecycleOwner . get (). lifecycle . addObserver ( MyLifecycleObserver ()) } }
// Create a LifecycleObserver class . public class MyLifecycleObserver implements DefaultLifecycleObserver { @ Override public void onStart ( LifecycleOwner owner ) { // App prepares to enter foreground . CastReceiverContext . getInstance () . start (); } @ Override public void onStop ( LifecycleOwner owner ) { // App has moved to the background or has terminated . CastReceiverContext . getInstance () . stop (); } } // Add the observer when your application is being created . public class MyApplication extends Application { @ Override public void onCreate () { super . onCreate (); // Initialize CastReceiverContext . CastReceiverContext . initInstance ( this /* android . content . Context */ ); // Register LifecycleObserver ProcessLifecycleOwner . get () . getLifecycle () . addObserver ( new MyLifecycleObserver ()); } }
// In AndroidManifest.xml set MyApplication as the application class
< application
...
android
:
name
=
".MyApplication"
>
Connecting MediaSession to MediaManager
When you create a MediaSession
,
you also need to provide the current MediaSession
token to CastReceiverContext
so it knows where to send the commands and retrieve the media playback state:
val mediaManager : MediaManager = receiverContext . getMediaManager () mediaManager . setSessionCompatToken ( currentMediaSession . getSessionToken ())
MediaManager mediaManager = receiverContext.getMediaManager(); mediaManager.setSessionCompatToken(currentMediaSession.getSessionToken());
When you release your MediaSession
due to inactive playback, you should set a
null token on MediaManager
:
myPlayer . stop () mediaSession . release () mediaManager . setSessionCompatToken ( null )
myPlayer.stop(); mediaSession.release(); mediaManager.setSessionCompatToken(null);
If your app supports playing media while your app is in the background, instead
of calling CastReceiverContext.stop()
when your app is sent to the background, you should call it only when your app
is in the background and no longer playing media. For example:
class MyLifecycleObserver : DefaultLifecycleObserver { ... // App has moved to the background. override fun onPause ( owner : LifecycleOwner ) { mIsBackground = true myStopCastReceiverContextIfNeeded () } } // Stop playback on the player. private fun myStopPlayback () { myPlayer . stop () myStopCastReceiverContextIfNeeded () } // Stop the CastReceiverContext when both the player has // stopped and the app has moved to the background. private fun myStopCastReceiverContextIfNeeded () { if ( mIsBackground && myPlayer . isStopped ()) { CastReceiverContext . getInstance (). stop () } }
public class MyLifecycleObserver implements DefaultLifecycleObserver { ... // App has moved to the background. @ Override public void onPause ( LifecycleOwner owner ) { mIsBackground = true ; myStopCastReceiverContextIfNeeded (); } } // Stop playback on the player. private void myStopPlayback () { myPlayer . stop (); myStopCastReceiverContextIfNeeded (); } // Stop the CastReceiverContext when both the player has // stopped and the app has moved to the background. private void myStopCastReceiverContextIfNeeded () { if ( mIsBackground && myPlayer . isStopped ()) { CastReceiverContext . getInstance (). stop (); } }
Using Exoplayer with Cast Connect
If you are using Exoplayer
, you can use the MediaSessionConnector
to automatically maintain the session and all related information including the
playback state instead of tracking the changes manually.
MediaSessionConnector.MediaButtonEventHandler
can be used to handle MediaButton events by calling setMediaButtonEventHandler(MediaButtonEventHandler)
which are otherwise handled by MediaSessionCompat.Callback
by default.
To integrate MediaSessionConnector
in your app, add the following to your player activity class or to wherever you
manage your media session:
class PlayerActivity : Activity () { private var mMediaSession : MediaSessionCompat? = null private var mMediaSessionConnector : MediaSessionConnector? = null private var mMediaManager : MediaManager? = null override fun onCreate ( savedInstanceState : Bundle?) { ... mMediaSession = MediaSessionCompat ( this , LOG_TAG ) mMediaSessionConnector = MediaSessionConnector ( mMediaSession !! ) ... } override fun onStart () { ... mMediaManager = receiverContext . getMediaManager () mMediaManager !! . setSessionCompatToken ( currentMediaSession . getSessionToken ()) mMediaSessionConnector !! . setPlayer ( mExoPlayer ) mMediaSessionConnector !! . setMediaMetadataProvider ( mMediaMetadataProvider ) mMediaSession !! . isActive = true ... } override fun onStop () { ... mMediaSessionConnector !! . setPlayer ( null ) mMediaSession !! . release () mMediaManager !! . setSessionCompatToken ( null ) ... } }
public class PlayerActivity extends Activity { private MediaSessionCompat mMediaSession ; private MediaSessionConnector mMediaSessionConnector ; private MediaManager mMediaManager ; @ Override protected void onCreate ( Bundle savedInstanceState ) { ... mMediaSession = new MediaSessionCompat ( this , LOG_TAG ); mMediaSessionConnector = new MediaSessionConnector ( mMediaSession ); ... } @ Override protected void onStart () { ... mMediaManager = receiverContext . getMediaManager (); mMediaManager . setSessionCompatToken ( currentMediaSession . getSessionToken ()); mMediaSessionConnector . setPlayer ( mExoPlayer ); mMediaSessionConnector . setMediaMetadataProvider ( mMediaMetadataProvider ); mMediaSession . setActive ( true ); ... } @ Override protected void onStop () { ... mMediaSessionConnector . setPlayer ( null ); mMediaSession . release (); mMediaManager . setSessionCompatToken ( null ); ... } }
Sender app setup
Enable Cast Connect support
Once you have updated your sender app with Cast Connect support, you can declare
its readiness by setting the androidReceiverCompatible
flag on LaunchOptions
to true.
Requires play-services-cast-framework
version 19.0.0
or higher.
The androidReceiverCompatible
flag is set in LaunchOptions
(which is part of CastOptions
):
class CastOptionsProvider : OptionsProvider { override fun getCastOptions ( context : Context?) : CastOptions { val launchOptions : LaunchOptions = Builder () . setAndroidReceiverCompatible ( true ) . build () return CastOptions . Builder () . setLaunchOptions ( launchOptions ) ... . build () } }
public class CastOptionsProvider implements OptionsProvider { @ Override public CastOptions getCastOptions ( Context context ) { LaunchOptions launchOptions = new LaunchOptions . Builder () . setAndroidReceiverCompatible ( true ) . build (); return new CastOptions . Builder () . setLaunchOptions ( launchOptions ) ... . build (); } }
Requires google-cast-sdk
version v4.4.8
or
higher.
The androidReceiverCompatible
flag is set in GCKLaunchOptions
(which is part of GCKCastOptions
):
let options = GCKCastOptions ( discoveryCriteria : GCKDiscoveryCriteria ( applicationID : kReceiverAppID )) ... let launchOptions = GCKLaunchOptions () launchOptions . androidReceiverCompatible = true options . launchOptions = launchOptions GCKCastContext . setSharedInstanceWith ( options )
Requires Chromium browser version M87
or higher.
const context = cast . framework . CastContext . getInstance (); const castOptions = new cast . framework . CastOptions (); castOptions . receiverApplicationId = kReceiverAppID ; castOptions . androidReceiverCompatible = true ; context . setOptions ( castOptions );
Cast Developer Console setup
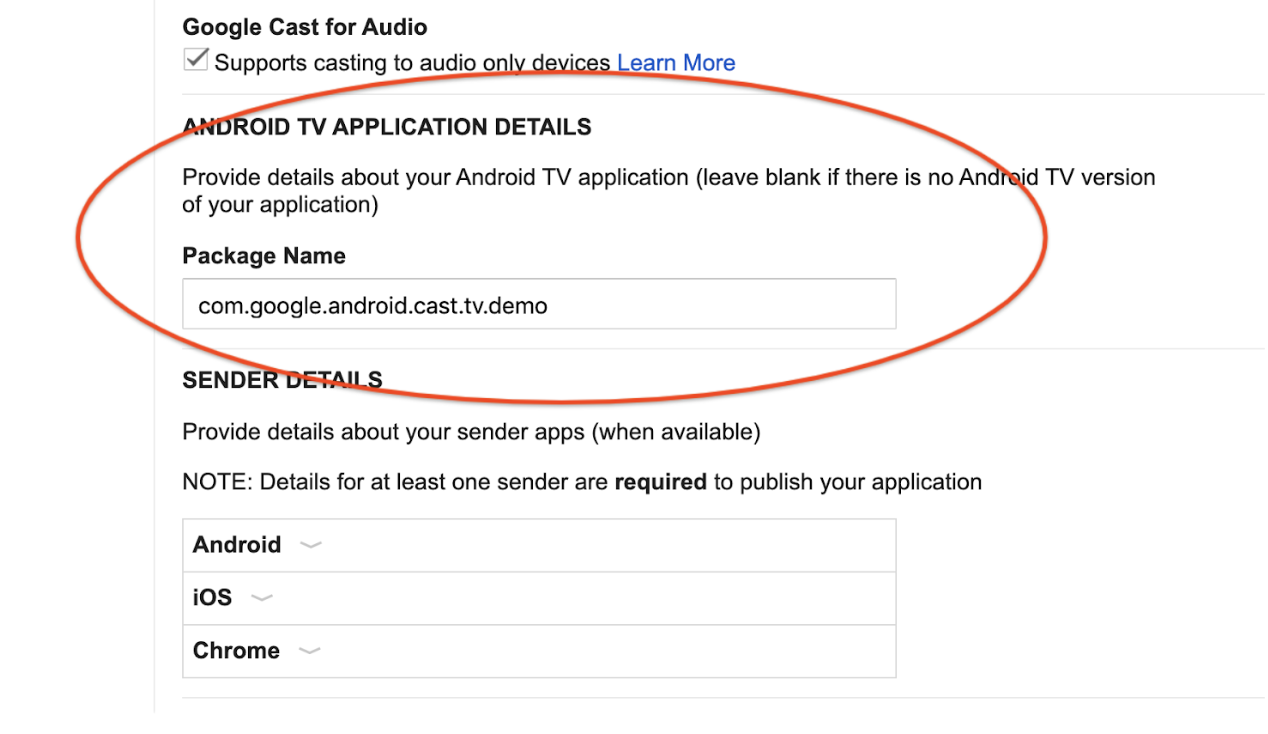
Configure the Android TV app
Add the package name of your Android TV app in Cast Developer Console to associate it with your Cast App ID.
Register developer devices
Register the serial number of the Android TV device that you are going to use for development in the Cast Developer Console .
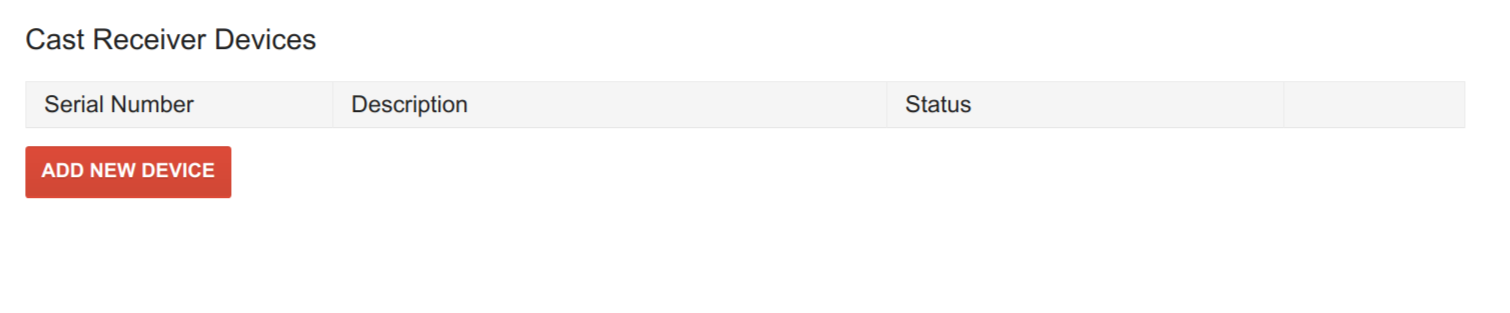
Without registration, Cast Connect will only work for apps installed from the Google Play Store due to security reasons.
For further information about registering a Cast or Android TV device for Cast development, see the registration page .
Loading media
If you have already implemented deep link support in your Android TV app, then you should have a similar definition configured in your Android TV Manifest:
<activity android:name="com.example.activity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<data android:scheme="https"/>
<data android:host="www.example.com"/>
<data android:pathPattern=".*"/>
</intent-filter>
</activity>
Load by entity on sender
On the senders, you can pass the deep link by setting the entity
in the media
information for the load request:
val mediaToLoad = MediaInfo . Builder ( "some-id" ) . setEntity ( "https://example.com/watch/some-id" ) ... . build () val loadRequest = MediaLoadRequestData . Builder () . setMediaInfo ( mediaToLoad ) . setCredentials ( "user-credentials" ) ... . build () remoteMediaClient . load ( loadRequest )
MediaInfo mediaToLoad = new MediaInfo . Builder ( "some-id" ) . setEntity ( "https://example.com/watch/some-id" ) ... . build (); MediaLoadRequestData loadRequest = new MediaLoadRequestData . Builder () . setMediaInfo ( mediaToLoad ) . setCredentials ( "user-credentials" ) ... . build (); remoteMediaClient . load ( loadRequest );
let mediaInfoBuilder = GCKMediaInformationBuilder ( entity : "https://example.com/watch/some-id" ) ... mediaInformation = mediaInfoBuilder . build () let mediaLoadRequestDataBuilder = GCKMediaLoadRequestDataBuilder () mediaLoadRequestDataBuilder . mediaInformation = mediaInformation mediaLoadRequestDataBuilder . credentials = "user-credentials" ... let mediaLoadRequestData = mediaLoadRequestDataBuilder . build () remoteMediaClient ?. loadMedia ( with : mediaLoadRequestData )
Requires Chromium browser version M87
or higher.
let mediaInfo = new chrome . cast . media . MediaInfo ( 'some-id"' , 'video/mp4' ); mediaInfo . entity = 'https://example.com/watch/some-id' ; ... let request = new chrome . cast . media . LoadRequest ( mediaInfo ); request . credentials = 'user-credentials' ; ... cast . framework . CastContext . getInstance (). getCurrentSession (). loadMedia ( request );
The load command is sent via an intent with your deep link and the package name you defined in the developer console.
Setting ATV credentials on sender
It is possible that your Web Receiver app and Android TV app support different
deep links and credentials
(for example if you are handling authentication
differently on the two platforms). To address this, you can provide alternate entity
and credentials
for Android TV:
val mediaToLoad = MediaInfo . Builder ( "some-id" ) . setEntity ( "https://example.com/watch/some-id" ) . setAtvEntity ( "myscheme://example.com/atv/some-id" ) ... . build () val loadRequest = MediaLoadRequestData . Builder () . setMediaInfo ( mediaToLoad ) . setCredentials ( "user-credentials" ) . setAtvCredentials ( "atv-user-credentials" ) ... . build () remoteMediaClient . load ( loadRequest )
MediaInfo mediaToLoad = new MediaInfo . Builder ( "some-id" ) . setEntity ( "https://example.com/watch/some-id" ) . setAtvEntity ( "myscheme://example.com/atv/some-id" ) ... . build (); MediaLoadRequestData loadRequest = new MediaLoadRequestData . Builder () . setMediaInfo ( mediaToLoad ) . setCredentials ( "user-credentials" ) . setAtvCredentials ( "atv-user-credentials" ) ... . build (); remoteMediaClient . load ( loadRequest );
let mediaInfoBuilder = GCKMediaInformationBuilder ( entity : "https://example.com/watch/some-id" ) mediaInfoBuilder . atvEntity = "myscheme://example.com/atv/some-id" ... mediaInformation = mediaInfoBuilder . build () let mediaLoadRequestDataBuilder = GCKMediaLoadRequestDataBuilder () mediaLoadRequestDataBuilder . mediaInformation = mediaInformation mediaLoadRequestDataBuilder . credentials = "user-credentials" mediaLoadRequestDataBuilder . atvCredentials = "atv-user-credentials" ... let mediaLoadRequestData = mediaLoadRequestDataBuilder . build () remoteMediaClient ?. loadMedia ( with : mediaLoadRequestData )
Requires Chromium browser version M87
or higher.
let mediaInfo = new chrome . cast . media . MediaInfo ( 'some-id"' , 'video/mp4' ); mediaInfo . entity = 'https://example.com/watch/some-id' ; mediaInfo . atvEntity = 'myscheme://example.com/atv/some-id' ; ... let request = new chrome . cast . media . LoadRequest ( mediaInfo ); request . credentials = 'user-credentials' ; request . atvCredentials = 'atv-user-credentials' ; ... cast . framework . CastContext . getInstance (). getCurrentSession (). loadMedia ( request );
If the Web Receiver app is launched, it uses the entity
and credentials
in
the load request. However if your Android TV app is launched, the SDK overrides
the entity
and credentials
with your atvEntity
and atvCredentials
(if specified).
Loading by Content ID or MediaQueueData
If you are not using entity
or atvEntity
, and are using Content ID or
Content URL in your Media Information or use the more detailed Media Load
Request Data, you need to add the following predefined intent filter in
your Android TV app:
<activity android:name="com.example.activity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.google.android.gms.cast.tv.action.LOAD"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
On the sender side, similar to load by entity
, you
can create a load request with your content information and call load()
.
val mediaToLoad = MediaInfo . Builder ( "some-id" ). build () val loadRequest = MediaLoadRequestData . Builder () . setMediaInfo ( mediaToLoad ) . setCredentials ( "user-credentials" ) ... . build () remoteMediaClient . load ( loadRequest )
MediaInfo mediaToLoad = new MediaInfo . Builder ( "some-id" ) . build (); MediaLoadRequestData loadRequest = new MediaLoadRequestData . Builder () . setMediaInfo ( mediaToLoad ) . setCredentials ( "user-credentials" ) ... . build (); remoteMediaClient . load ( loadRequest );
let mediaInfoBuilder = GCKMediaInformationBuilder ( contentId : "some-id" ) ... mediaInformation = mediaInfoBuilder . build () let mediaLoadRequestDataBuilder = GCKMediaLoadRequestDataBuilder () mediaLoadRequestDataBuilder . mediaInformation = mediaInformation mediaLoadRequestDataBuilder . credentials = "user-credentials" ... let mediaLoadRequestData = mediaLoadRequestDataBuilder . build () remoteMediaClient ?. loadMedia ( with : mediaLoadRequestData )
Requires Chromium browser version M87
or higher.
let mediaInfo = new chrome . cast . media . MediaInfo ( 'some-id"' , 'video/mp4' ); ... let request = new chrome . cast . media . LoadRequest ( mediaInfo ); ... cast . framework . CastContext . getInstance (). getCurrentSession (). loadMedia ( request );
Handling load requests
In your activity, to handle these load requests, you need to handle the intents in your activity lifecycle callbacks:
class MyActivity : Activity () { override fun onStart () { super . onStart () val mediaManager = CastReceiverContext . getInstance (). getMediaManager () // Pass the intent to the SDK. You can also do this in onCreate(). if ( mediaManager . onNewIntent ( intent )) { // If the SDK recognizes the intent, you should early return. return } // If the SDK doesn't recognize the intent, you can handle the intent with // your own logic. ... } // For some cases, a new load intent triggers onNewIntent() instead of // onStart(). override fun onNewIntent ( intent : Intent ) { val mediaManager = CastReceiverContext . getInstance (). getMediaManager () // Pass the intent to the SDK. You can also do this in onCreate(). if ( mediaManager . onNewIntent ( intent )) { // If the SDK recognizes the intent, you should early return. return } // If the SDK doesn't recognize the intent, you can handle the intent with // your own logic. ... } }
public class MyActivity extends Activity { @ Override protected void onStart () { super . onStart (); MediaManager mediaManager = CastReceiverContext . getInstance () . getMediaManager (); // Pass the intent to the SDK . You can also do this in onCreate () . if ( mediaManager . onNewIntent ( getIntent ())) { // If the SDK recognizes the intent , you should early return . return ; } // If the SDK doesn 't recognize the intent, you can handle the intent with // your own logic . ... } // For some cases , a new load intent triggers onNewIntent () instead of // onStart () . @ Override protected void onNewIntent ( Intent intent ) { MediaManager mediaManager = CastReceiverContext . getInstance () . getMediaManager (); // Pass the intent to the SDK . You can also do this in onCreate () . if ( mediaManager . onNewIntent ( intent )) { // If the SDK recognizes the intent , you should early return . return ; } // If the SDK doesn 't recognize the intent, you can handle the intent with // your own logic . ... } }
If MediaManager
detects the intent is a load intent, it extracts a MediaLoadRequestData
object from the intent, and invoke MediaLoadCommandCallback.onLoad()
.
You need to override this method to handle the load request. The callback must
be registered before MediaManager.onNewIntent()
is called (it's recommended to be on an Activity or Application onCreate()
method).
class MyActivity : Activity () { override fun onCreate ( savedInstanceState : Bundle?) { super . onCreate ( savedInstanceState ) val mediaManager = CastReceiverContext . getInstance (). getMediaManager () mediaManager . setMediaLoadCommandCallback ( MyMediaLoadCommandCallback ()) } } class MyMediaLoadCommandCallback : MediaLoadCommandCallback () { override fun onLoad ( senderId : String? , loadRequestData : MediaLoadRequestData ): Task{ return Tasks . call { // Resolve the entity into your data structure and load media. val mediaInfo = loadRequestData . getMediaInfo () if ( ! checkMediaInfoSupported ( mediaInfo )) { // Throw MediaException to indicate load failure. throw MediaException ( MediaError . Builder () . setDetailedErrorCode ( DetailedErrorCode . LOAD_FAILED ) . setReason ( MediaError . ERROR_REASON_INVALID_REQUEST ) . build () ) } myFillMediaInfo ( MediaInfoWriter ( mediaInfo )) myPlayerLoad ( mediaInfo . getContentUrl ()) // Update media metadata and state (this clears all previous status // overrides). castReceiverContext . getMediaManager () . setDataFromLoad ( loadRequestData ) ... castReceiverContext . getMediaManager (). broadcastMediaStatus () // Return the resolved MediaLoadRequestData to indicate load success. return loadRequestData } } private fun myPlayerLoad ( contentURL : String ) { myPlayer . load ( contentURL ) // Update the MediaSession state. val playbackState : PlaybackStateCompat = Builder () . setState ( player . getState (), player . getPosition (), System . currentTimeMillis () ) ... . build () mediaSession . setPlaybackState ( playbackState ) }
public class MyActivity extends Activity { @ Override protected void onCreate ( Bundle savedInstanceState ) { super . onCreate ( savedInstanceState ); MediaManager mediaManager = CastReceiverContext . getInstance () . getMediaManager (); mediaManager . setMediaLoadCommandCallback ( new MyMediaLoadCommandCallback ()); } } public class MyMediaLoadCommandCallback extends MediaLoadCommandCallback { @ Override public TaskonLoad ( String senderId , MediaLoadRequestData loadRequestData ) { return Tasks . call (() -> { // Resolve the entity into your data structure and load media . MediaInfo mediaInfo = loadRequestData . getMediaInfo (); if ( ! checkMediaInfoSupported ( mediaInfo )) { // Throw MediaException to indicate load failure . throw new MediaException ( new MediaError . Builder () . setDetailedErrorCode ( DetailedErrorCode . LOAD_FAILED ) . setReason ( MediaError . ERROR_REASON_INVALID_REQUEST ) . build ()); } myFillMediaInfo ( new MediaInfoWriter ( mediaInfo )); myPlayerLoad ( mediaInfo . getContentUrl ()); // Update media metadata and state ( this clears all previous status // overrides ) . castReceiverContext . getMediaManager () . setDataFromLoad ( loadRequestData ); ... castReceiverContext . getMediaManager () . broadcastMediaStatus (); // Return the resolved MediaLoadRequestData to indicate load success . return loadRequestData ; }); } private void myPlayerLoad ( String contentURL ) { myPlayer . load ( contentURL ); // Update the MediaSession state . PlaybackStateCompat playbackState = new PlaybackStateCompat . Builder () . setState ( player . getState (), player . getPosition (), System . currentTimeMillis ()) ... . build (); mediaSession . setPlaybackState ( playbackState ); }
To process the load intent, you can parse the intent into the data structures
we defined
( MediaLoadRequestData
for load requests).
Supporting media commands
Basic playback control support
Basic integration commands includes the commands that are compatible with media session. These commands are notified via media session callbacks. You need to register a callback to media session to support this (you might be doing this already).
private class MyMediaSessionCallback : MediaSessionCompat . Callback () { override fun onPause () { // Pause the player and update the play state. myPlayer . pause () } override fun onPlay () { // Resume the player and update the play state. myPlayer . play () } override fun onSeekTo ( pos : Long ) { // Seek and update the play state. myPlayer . seekTo ( pos ) } ... } mediaSession . setCallback ( MyMediaSessionCallback ())
private class MyMediaSessionCallback extends MediaSessionCompat . Callback { @ Override public void onPause () { // Pause the player and update the play state . myPlayer . pause (); } @ Override public void onPlay () { // Resume the player and update the play state . myPlayer . play (); } @ Override public void onSeekTo ( long pos ) { // Seek and update the play state . myPlayer . seekTo ( pos ); } ... } mediaSession . setCallback ( new MyMediaSessionCallback ());
Supporting Cast control commands
There are some Cast commands that are not available in MediaSession
,
such as skipAd()
or setActiveMediaTracks()
.
Also, some queue commands needs to be implemented here because the Cast queue
is not fully compatible with MediaSession
queue.
class MyMediaCommandCallback : MediaCommandCallback () { override fun onSkipAd ( requestData : RequestData?) : Task < Void?> { // Skip your ad ... return Tasks . forResult ( null ) } } val mediaManager = CastReceiverContext . getInstance (). getMediaManager () mediaManager . setMediaCommandCallback ( MyMediaCommandCallback ())
public class MyMediaCommandCallback extends MediaCommandCallback { @ Override public TaskonSkipAd ( RequestData requestData ) { // Skip your ad ... return Tasks . forResult ( null ); } } MediaManager mediaManager = CastReceiverContext . getInstance () . getMediaManager (); mediaManager . setMediaCommandCallback ( new MyMediaCommandCallback ());
Specify supported media commands
As with your Cast receiver, your Android TV app should specify which commands
are supported, so senders can enable or disable certain UI controls. For
commands that are part of MediaSession
,
specify the commands in PlaybackStateCompat
.
Additional commands should be specified in the MediaStatusModifier
.
// Set media session supported commands val playbackState : PlaybackStateCompat = PlaybackStateCompat . Builder () . setActions ( PlaybackStateCompat . ACTION_PLAY or PlaybackStateCompat . ACTION_PAUSE ) . setState ( PlaybackStateCompat . STATE_PLAYING ) . build () mediaSession . setPlaybackState ( playbackState ) // Set additional commands in MediaStatusModifier val mediaManager = CastReceiverContext . getInstance (). getMediaManager () mediaManager . getMediaStatusModifier () . setMediaCommandSupported ( MediaStatus . COMMAND_QUEUE_NEXT )
// Set media session supported commands PlaybackStateCompat playbackState = new PlaybackStateCompat . Builder () . setActions ( PlaybackStateCompat . ACTION_PLAY | PlaybackStateCompat . ACTION_PAUSE ) . setState ( PlaybackStateCompat . STATE_PLAYING ) . build (); mediaSession . setPlaybackState ( playbackState ); // Set additional commands in MediaStatusModifier MediaManager mediaManager = CastReceiverContext . getInstance (). getMediaManager (); mediaManager . getMediaStatusModifier () . setMediaCommandSupported ( MediaStatus . COMMAND_QUEUE_NEXT );
Hide unsupported buttons
If your Android TV app only supports basic media control but your Web Receiver app supports more advanced control, you should make sure your sender app behave correctly when casting to the Android TV app. For example, if your Android TV app doesn’t support changing playback rate while your Web Receiver app does, you should set the supported actions correctly on each platform and make sure your sender app renders UI properly.
Modifying MediaStatus
To support advanced features like tracks, ads, live, and queueing, your Android
TV app needs to provide additional information that can't be ascertained via MediaSession
.
We provide the MediaStatusModifier
class for you to achieve this. MediaStatusModifier
will always operate on the MediaSession
which you have set in CastReceiverContext
.
To create and broadcast MediaStatus
:
val mediaManager : MediaManager = castReceiverContext . getMediaManager () val statusModifier : MediaStatusModifier = mediaManager . getMediaStatusModifier () statusModifier . setLiveSeekableRange ( seekableRange ) . setAdBreakStatus ( adBreakStatus ) . setCustomData ( customData ) mediaManager . broadcastMediaStatus ()
MediaManager mediaManager = castReceiverContext.getMediaManager();
MediaStatusModifier statusModifier = mediaManager.getMediaStatusModifier();
statusModifier
.setLiveSeekableRange(seekableRange)
.setAdBreakStatus(adBreakStatus)
.setCustomData(customData);
mediaManager.broadcastMediaStatus();
Our client library will get the base MediaStatus
from MediaSession
, your
Android TV app can specify additional status and override status via a MediaStatus
modifier.
Some states and metadata can set both in MediaSession
and MediaStatusModifier
. We strongly
recommend you only set them in MediaSession
. You can still use the modifier to override the states in MediaSession
—this is discouraged because the status in the modifier always
have a higher priority than values provided by MediaSession
.
Intercepting MediaStatus before sending out
Same as the Web Receiver SDK, if you want to do some finishing touches before
sending out, you can specify a MediaStatusInterceptor
to process the MediaStatus
to
be sent. We pass in a MediaStatusWriter
to manipulate the MediaStatus
before it is sent out.
mediaManager . setMediaStatusInterceptor ( object : MediaStatusInterceptor { override fun intercept ( mediaStatusWriter : MediaStatusWriter ) { // Perform customization. mediaStatusWriter . setCustomData ( JSONObject ( "{data: \"my Hello\"}" )) } })
mediaManager . setMediaStatusInterceptor ( new MediaStatusInterceptor () { @Override public void intercept ( MediaStatusWriter mediaStatusWriter ) { // Perform customization . mediaStatusWriter . setCustomData ( new JSONObject ( "{data: \" my Hello \ "}" )); } } );
Handling user credentials
Your Android TV app might only allow certain users to launch or join the app session. For example, only allow a sender to launch or join if:
- The sender app is logged into same account and profile as ATV app.
- The sender app is logged into same account, but different profile as ATV app.
If your app can handle multiple or anonymous users, you may allow additional any user to join the ATV session. If the user provides credentials, your ATV app needs to handle their credentials so their progress and other user data can be properly tracked.
When your sender app launches or joins your Android TV app, your sender app should provide the credentials that represents who is joining the session.
Before a sender launches and joins your Android TV app, you can specify a launch checker to see if the sender credentials are allowed. If not, the Cast Connect SDK falls back to launching your Web Receiver.
Sender app launch credentials data
On the sender side, you can specify the CredentialsData
to represent who is
joining the session.
The credentials
is a string which can be user-defined, as long as your ATV
app can understand it. The credentialsType
defines which platform the CredentialsData
is coming from or can be a custom value. By default it is set
to the platform that it is being sent from.
The CredentialsData
is only passed to your Android TV app during launch or
join time. If you set it again while you are connected, it won't be passed to
your Android TV app. If your sender switches the profile while connected, you
could either stay in the session, or call SessionManager.endCurrentCastSession(boolean stopCasting)
if you think the new profile is incompatible with the session.
The CredentialsData
for each sender can be retrieved using getSenders
on the CastReceiverContext
to get the SenderInfo
, getCastLaunchRequest()
to get the CastLaunchRequest
,
and then getCredentialsData()
.
Requires play-services-cast-framework
version 19.0.0
or higher.
CastContext . getSharedInstance (). setLaunchCredentialsData ( CredentialsData . Builder () . setCredentials ( "{\"userId\": \"abc\"}" ) . build () )
CastContext.getSharedInstance().setLaunchCredentialsData(
new CredentialsData.Builder()
.setCredentials("{\"userId\": \"abc\"}")
.build());
Requires google-cast-sdk
version v4.8.3
or
higher.
Can be called anytime after the options are set: GCKCastContext.setSharedInstanceWith(options)
.
GCKCastContext . sharedInstance (). setLaunch ( GCKCredentialsData ( credentials : "{ \" userId \" : \" abc \" }" )
Requires Chromium browser version M87
or higher.
Can be called anytime after the options are set: cast.framework.CastContext.getInstance().setOptions(options);
.
let credentialsData = new chrome . cast . CredentialsData ( "{\"userId\": \"abc\"}" ); cast . framework . CastContext . getInstance (). setLaunchCredentialsData ( credentialsData );
Implementing ATV launch request checker
The CredentialsData
is passed to your Android TV app when a sender tries to launch or join. You can
implement a LaunchRequestChecker
.
to allow or reject this request.
If a request is rejected, the Web Receiver is loaded instead of launching natively into the ATV app. You should reject a request if your ATV is unable to handle the user requesting to launch or join. Examples could be that a different user is logged into the ATV app than is requesting and your app is unable to handle switching credentials, or there is not a user currently logged into the ATV app.
If a request is allowed, the ATV app launches. You can customize this
behavior depending on if your app supports sending load requests when a user
is not logged into the ATV app or if there is a user mismatch. This behavior is
fully cusomizable in the LaunchRequestChecker
.
Create a class implementing the CastReceiverOptions.LaunchRequestChecker
interface:
class MyLaunchRequestChecker : LaunchRequestChecker { override fun checkLaunchRequestSupported ( launchRequest : CastLaunchRequest ): Task{ return Tasks . call { myCheckLaunchRequest ( launchRequest ) } } } private fun myCheckLaunchRequest ( launchRequest : CastLaunchRequest ): Boolean { val credentialsData = launchRequest . getCredentialsData () ?: return false // or true if you allow anonymous users to join. // The request comes from a mobile device, e.g. checking user match. return if ( credentialsData . credentialsType == CredentialsData . CREDENTIALS_TYPE_ANDROID ) { myCheckMobileCredentialsAllowed ( credentialsData . getCredentials ()) } else false // Unrecognized credentials type. }
public class MyLaunchRequestChecker implements CastReceiverOptions . LaunchRequestChecker { @ Override public TaskcheckLaunchRequestSupported ( CastLaunchRequest launchRequest ) { return Tasks . call (() -> myCheckLaunchRequest ( launchRequest )); } } private boolean myCheckLaunchRequest ( CastLaunchRequest launchRequest ) { CredentialsData credentialsData = launchRequest . getCredentialsData (); if ( credentialsData == null ) { return false ; // or true if you allow anonymous users to join. } // The request comes from a mobile device, e.g. checking user match. if ( credentialsData . getCredentialsType (). equals ( CredentialsData . CREDENTIALS_TYPE_ANDROID )) { return myCheckMobileCredentialsAllowed ( credentialsData . getCredentials ()); } // Unrecognized credentials type. return false ; }
Then set it in your ReceiverOptionsProvider
:
class MyReceiverOptionsProvider : ReceiverOptionsProvider { override fun getOptions ( context : Context?) : CastReceiverOptions { return CastReceiverOptions . Builder ( context ) ... . setLaunchRequestChecker ( MyLaunchRequestChecker ()) . build () } }
public class MyReceiverOptionsProvider implements ReceiverOptionsProvider { @ Override public CastReceiverOptions getOptions ( Context context ) { return new CastReceiverOptions . Builder ( context ) ... . setLaunchRequestChecker ( new MyLaunchRequestChecker ()) . build (); } }
Resolving true
in the LaunchRequestChecker
launches the ATV app and false
launches your Web Receiver app.
Sending & Receiving Custom Messages
The Cast protocol allows you to send custom string messages between senders and
your receiver application. You must register a namespace (channel) to send
messages across before initializing your CastReceiverContext
.
Android TV—Specify Custom Namespace
You need to specify your supported namespaces in your CastReceiverOptions
during setup:
class MyReceiverOptionsProvider : ReceiverOptionsProvider { override fun getOptions ( context : Context?) : CastReceiverOptions { return CastReceiverOptions . Builder ( context ) . setCustomNamespaces ( Arrays . asList ( "urn:x-cast:com.example.cast.mynamespace" ) ) . build () } }
public class MyReceiverOptionsProvider implements ReceiverOptionsProvider { @ Override public CastReceiverOptions getOptions ( Context context ) { return new CastReceiverOptions . Builder ( context ) . setCustomNamespaces ( Arrays . asList ( "urn:x-cast:com.example.cast.mynamespace" )) . build (); } }
Android TV—Sending Messages
// If senderId is null, then the message is broadcasted to all senders. CastReceiverContext . getInstance (). sendMessage ( "urn:x-cast:com.example.cast.mynamespace" , senderId , customString )
// If senderId is null, then the message is broadcasted to all senders. CastReceiverContext . getInstance (). sendMessage ( "urn:x-cast:com.example.cast.mynamespace" , senderId , customString );
Android TV—Receive Custom Namespace Messages
class MyCustomMessageListener : MessageReceivedListener { override fun onMessageReceived ( namespace : String , senderId : String? , message : String ) { ... } } CastReceiverContext . getInstance (). setMessageReceivedListener ( "urn:x-cast:com.example.cast.mynamespace" , new MyCustomMessageListener ());
class MyCustomMessageListener implements CastReceiverContext . MessageReceivedListener { @ Override public void onMessageReceived ( String namespace , String senderId , String message ) { ... } } CastReceiverContext . getInstance (). setMessageReceivedListener ( "urn:x-cast:com.example.cast.mynamespace" , new MyCustomMessageListener ());

