Page Summary
-
Smart Lock for Passwords is deprecated and migration to Credential Manager is recommended for continued security and usability.
-
The Credentials API can be used to automatically sign users into your app by requesting and retrieving stored credentials.
-
To request credentials, you need to create a
CredentialsClientobject and aCredentialRequestobject specifying the sign-in systems. -
Successful credential requests result in a
Credentialobject that can be used to complete the user's sign-in process. -
When multiple credentials are saved or no credentials are found, specific handling is required to prompt the user or guide them through sign-up/sign-in.
Automatically sign users into your app by using the Credentials API to request and retrieve stored credentials for your users.
Before you begin
Configure an Android Studio project .
Create a CredentialsClient object
To request stored credentials, you must create an instance of CredentialsClient
to access the Credentials API:
CredentialsClient mCredentialsClient;
// ...
mCredentialsApiClient = Credentials.getClient(this);
Create a CredentialRequest object
A CredentialRequest
object specifies the
sign-in systems from which you want to request credentials. Build a CredentialRequest
using the setPasswordLoginSupported
method for
password-based sign-in, and the setAccountTypes()
method for federated
sign-in services such as Google Sign-In.
mCredentialRequest = new CredentialRequest.Builder()
.setPasswordLoginSupported(true)
.setAccountTypes(IdentityProviders.GOOGLE, IdentityProviders.TWITTER)
.build();
Use the constants defined in IdentityProviders
to specify commonly-used sign-in providers. For other sign-in providers, use any
string that uniquely identifies the provider. You must use the same provider identifier
to store credentials as you use to retrieve the credentials.
Request stored credentials
After you have created CredentialsClient
and CredentialRequest
objects, pass the request object
to the CredentialsClient.request()
method to request credentials stored for your app.
mCredentialsClient
.
request
(
mCredentialRequest
).
addOnCompleteListener
(
new
OnCompleteListener<CredentialRequestResponse>
()
{
@Override
public
void
onComplete
(
@NonNull
Task<CredentialRequestResponse>
task
)
{
if
(
task
.
isSuccessful
())
{
//
See
"Handle successful credential requests"
onCredentialRetrieved
(
task
.
getResult
().
getCredential
());
return
;
}
//
See
"Handle unsuccessful and incomplete credential requests"
//
...
}
}
);
Define a callback to handle successful and failed requests using the addOnCompleteListener()
method.
Handle successful credential requests
 On a successful credential request, use the resulting
On a successful credential request, use the resulting Credential
object to complete the user's sign-in to your app. Use the getAccountType()
method
to determine the type of retrieved credentials, then complete the appropriate sign-in
process. For example, for Google Sign-In, create a GoogleSignInClient
object that
includes the user's ID, then use the object to start the sign-in flow. For password-based
sign-in, use the user's ID and password from the Credential object to complete your app's
sign-in process.
private
void
onCredentialRetrieved
(
Credential
credential
)
{
String
accountType
=
credential.getAccountType()
;
if
(accountType
==
null)
{
//
Sign
the
user
in
with
information
from
the
Credential.
signInWithPassword(credential.getId(),
credential.getPassword())
;
}
else
if
(
accountType
.
equals
(
IdentityProviders
.
GOOGLE
))
{
//
The
user
has
previously
signed
in
with
Google
Sign-In.
Silently
//
sign
in
the
user
with
the
same
ID.
//
See
https
:
//
developers
.
google
.
com
/
identity
/
sign-in
/
android
/
GoogleSignInOptions
gso
=
new
GoogleSignInOptions
.
Builder
(
GoogleSignInOptions
.
DEFAULT_SIGN_IN
)
.
requestEmail
()
.
build
();
GoogleSignInClient
signInClient
=
GoogleSignIn.getClient(this,
gso)
;
Task<GoogleSignInAccount>
task
=
signInClient.silentSignIn()
;
//
...
}
}
Handle multiple saved credentials
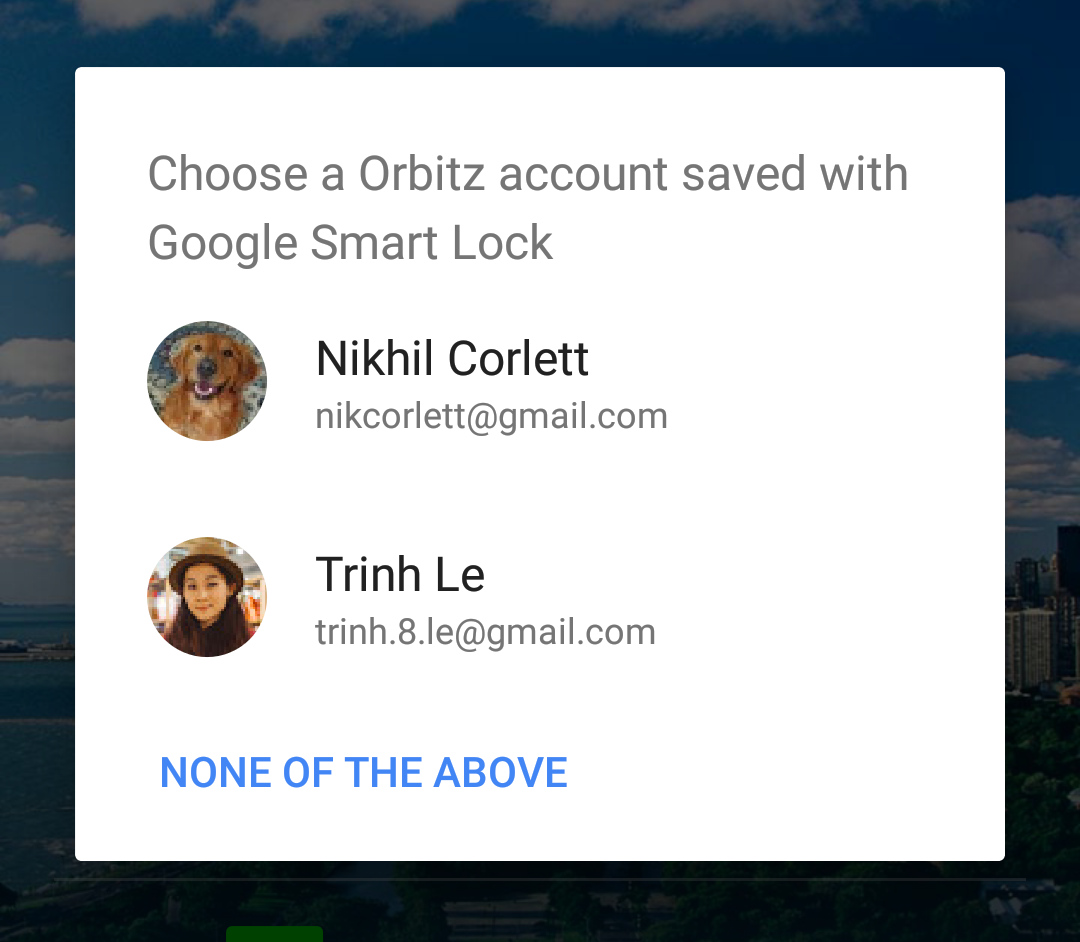
When user input is required to select a credential, the request()
task will
fail with a ResolvableApiException
. Check that getStatusCode()
returns RESOLUTION_REQUIRED
and
call the exception's startResolutionForResult()
method to prompt the user
to choose an account. Then, retrieve the user's chosen credentials from the
activity's onActivityResult()
method by passing Credential.EXTRA_KEY
to the getParcelableExtra()
method.
mCredentialsClient . request ( request ). addOnCompleteListener ( new OnCompleteListener() { @Override public void onComplete ( @NonNull Task task ) { if ( task . isSuccessful ()) { // ... return ; } Exception e = task . getException (); if ( e instanceof ResolvableApiException ) { // This is most likely the case where the user has multiple saved // credentials and needs to pick one . This requires showing UI to // resolve the read request . ResolvableApiException rae = ( ResolvableApiException ) e ; resolveResult ( rae , RC_READ ); } else if ( e instanceof ApiException ) { // The user must create an account or sign in manually . Log . e ( TAG , "Unsuccessful credential request." , e ); ApiException ae = ( ApiException ) e ; int code = ae . getStatusCode (); // ... } } } );
private void resolveResult(ResolvableApiException rae, int requestCode) {
try {
rae.startResolutionForResult(MainActivity.this, requestCode);
mIsResolving = true;
} catch (IntentSender.SendIntentException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Failed to send resolution.", e);
hideProgress();
}
}
@Override
public
void
onActivityResult
(
int
requestCode
,
int
resultCode
,
Intent
data
)
{
super
.
onActivityResult
(
requestCode
,
resultCode
,
data
);
//
...
if
(
requestCode
==
RC_READ
)
{
if
(
resultCode
==
RESULT_OK
)
{
Credential
credential
=
data
.
getParcelableExtra
(
Credential
.
EXTRA_KEY
);
onCredentialRetrieved
(
credential
);
}
else
{
Log
.
e
(
TAG
,
"Credential Read: NOT OK"
);
Toast
.
makeText
(
this
,
"Credential Read Failed"
,
Toast
.
LENGTH_SHORT
).
show
();
}
}
//
...
}
When stored credentials are not found, users must create an account or manually
sign in. If getStatusCode()
returns SIGN_IN_REQUIRED
,
you can optionally expedite the sign-up and sign-in processes by prompting the
user to choose recently used sign-in information, such as email address and
name, and automatically filling some fields of the forms with that information.
See Provide sign-in hints to a user
for details.
On successful sign in, allow users to save their credentials to automate future authentication on all their devices.

