First-party and third-party cookies can be blocked by browser restrictions, user settings, developer flags , or enterprise policy .
User settings
Users can access browser settings to block all on-device site storage, or only third-party cookies.
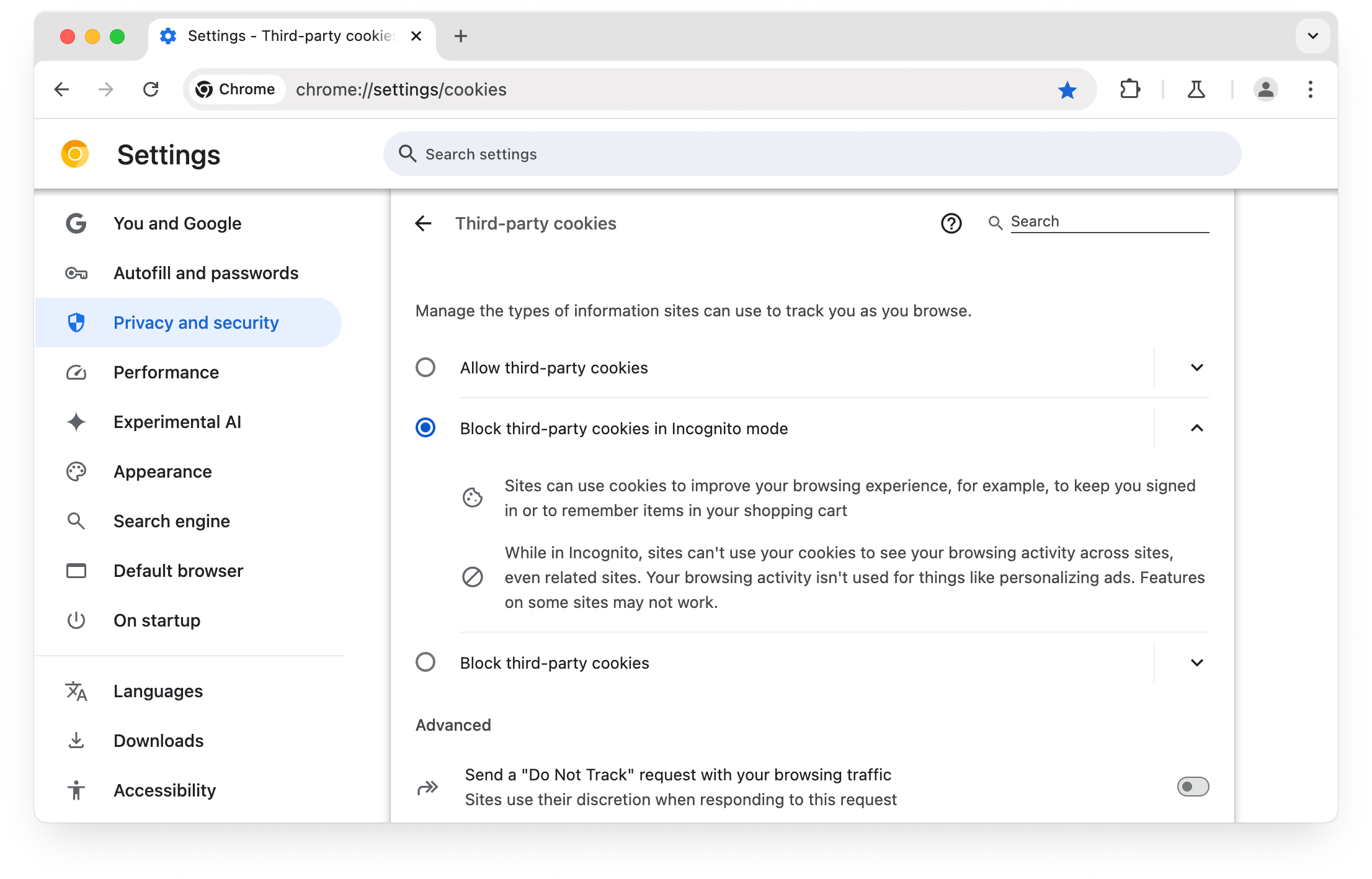
In Chrome, you can block third-party cookies by selecting the three dots in the
upper right corner of your browser window, then selecting Settingson the
drop-down menu displayed. Go to Privacy and security> Third-party
cookiesand select Block third-party cookies. Alternatively, you can
navigate directly to the chrome://settings/cookies
page.
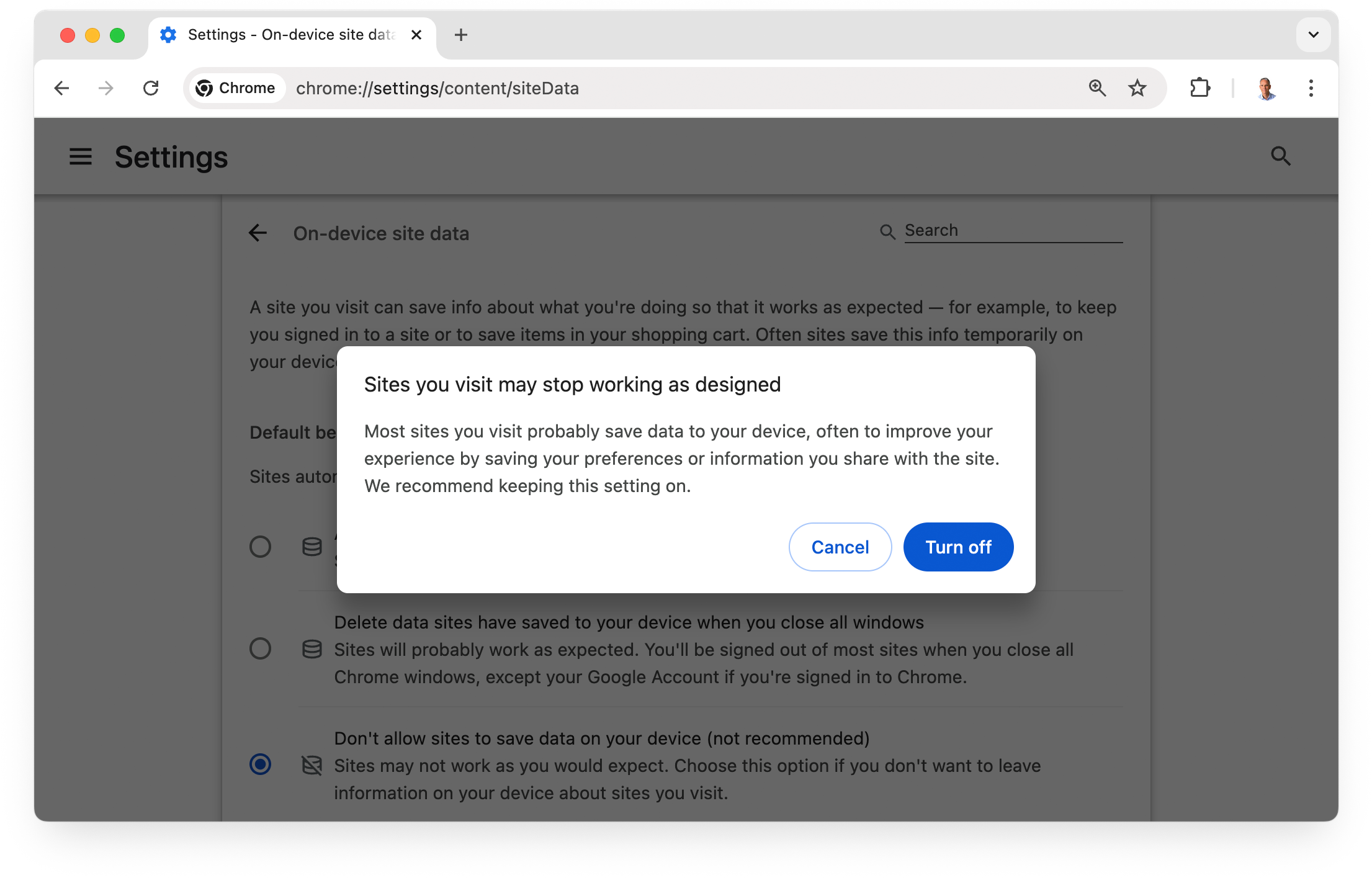
You can block local storage of all site data, including cookies,
from the On-device site datapage in Google Chrome. Select Settings> Privacy and security> Site settings> Additional content settings> On-device site dataor navigate directly to chrome://settings/content/siteData
.
Note that many sites won't function properly if you choose to block all site storage.
Browser flags
As a developer, the best way to test your site for breakage without third-party cookies in Chrome
is to use the test-third-party-cookie-phaseout
flag. This flag makes Chrome
behave as it does when third-party cookies are restricted, so it's ideal for
testing the user experience without cross-site cookies.
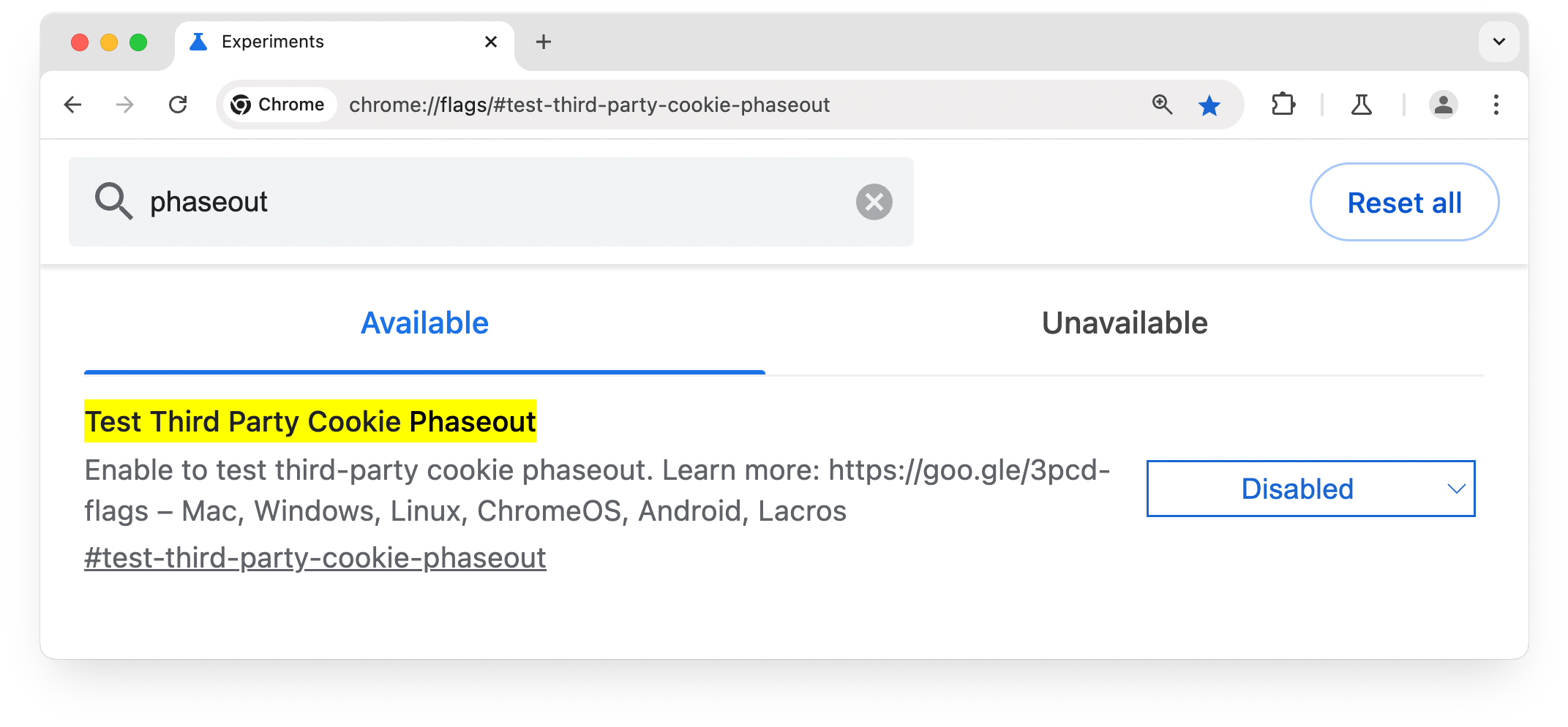
You can enable the test-third-party-cookie-phaseout
flag in two ways:
- Chrome flags:
Navigate tochrome://flags/#test-third-party-cookie-phaseoutand set the flag asEnabled - Command line:
Launch Chrome with the flag--test-third-party-cookie-phaseout
The phaseout flag is available on Windows, macOS, and Linux:
- Windows:
chrome.exe --test-third-party-cookie-phaseout - macOS:
open -a Google\ Chrome --args --test-third-party-cookie-phaseout - Linux:
google-chrome --test-third-party-cookie-phaseout
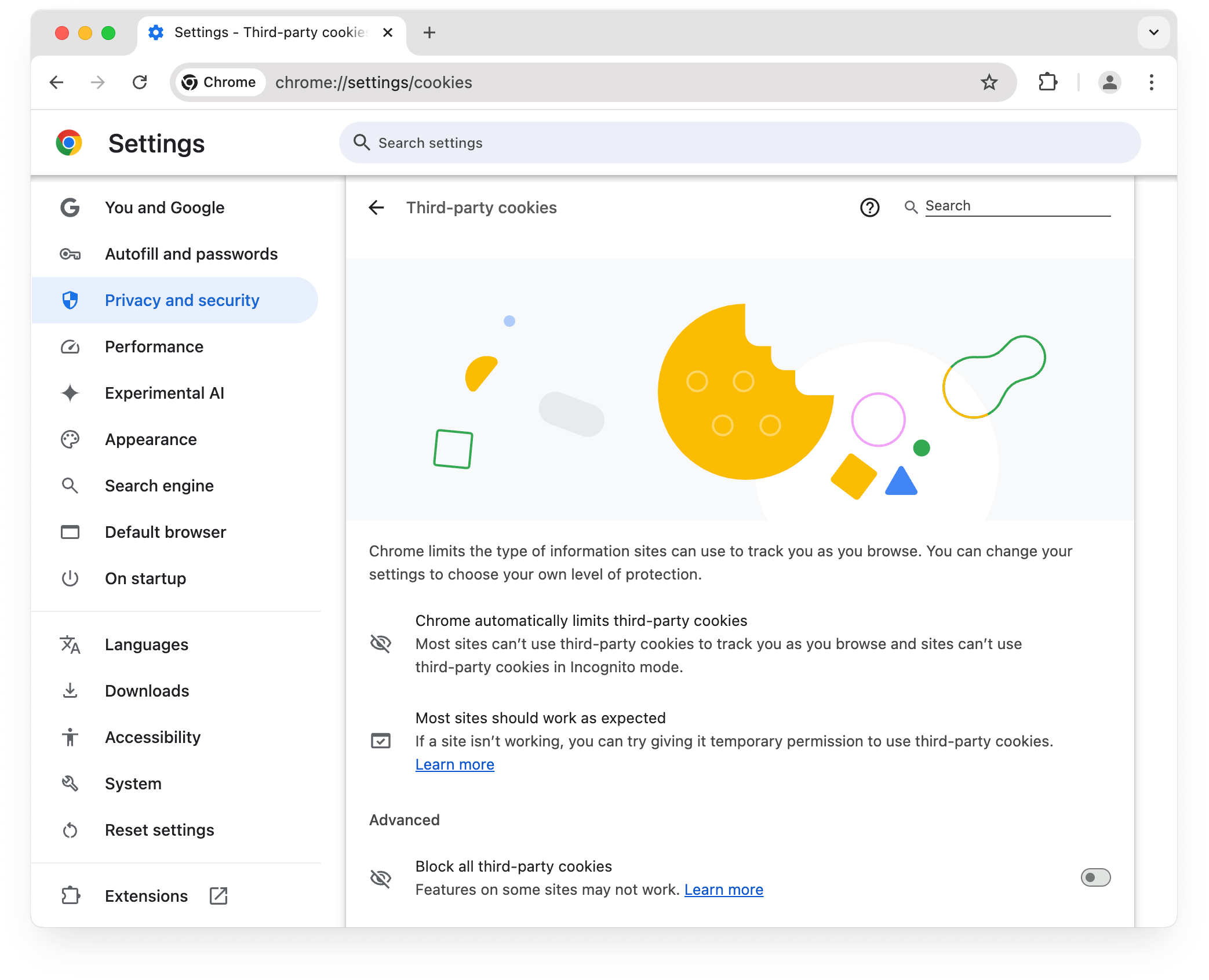
Browser restrictions
To facilitate testing, Google Chrome has restricted third-party cookies by default for 1% of users
. If you're in this group,
third-party cookies will be limited by default, and your chrome://settings/cookies
page will appear as follows.
Other web browsers apply their own cookie policies. For example, Safari has Tracking Prevention , and Firefox has Enhanced Tracking Protection .
Enterprise policy
Cookies may also be blocked by organizational policies set through Chrome Enterprise.
For more information, refer to Chrome Enterprise third-party cookie policies .


