抽象クラス
前回《203》、仮想関数からの派生関数 Rectangle を作成しました。
Rectangl関数は四角形クラスでしたが、今回は、横線クラス HorzLine と縦線クラス VertLine を作成します。
※ '-' で描く横線クラス … HorzLine
※ '|' で描く縦線クラス … VertLine
この2つの関数には、"線"という共通点があります。"線"ならば、その線の長さをデータメンバとして持っていなければなりません。
そこで、まず、直線クラス Line を考えます。線を描く方法は、横線と縦線で異なるので関数 draw は、ここではまだ定義できません。
class Shape {
public:
virtual void draw() = 0;
};
class Line : public Shape {
int length; // 線の長さ
public:
};
この Lineクラスは、Shapeクラスの public派生クラスですが、
基底クラス Shape の純粋仮想関数 draw をオーバーライドしていません。
そのため、 Lineクラスにおいても、draw は純粋仮想関数のままです。
純粋仮想関数を有するクラスは、 抽象クラスです。
したがって、 Lineクラスは、まだ抽象クラス です。
次のプログラムでは、Lineクラスの public派生クラスとして、
横線クラス HorzLine,縦線クラス VertLine を定義しています。
// ------------------------------------
#include <iostream>
// 図形クラス(抽象クラス) Shape
class Shape {
public:
virtual ~Shape() = 0;
// 純粋仮想デストラクタ
virtual void draw() const = 0;
// 描画
// 純粋仮想関数
};
inline Shape::~Shape() { }
// 長方形クラス Rectangle
class Rectangle : public Shape {
int width; // 横幅
int height; // 高さ
public:
Rectangle(int w, int h)
: width(w), height(h) { }
void draw() const {
for (int i = 1; i <= height; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= width; j++)
std::cout << '*';
std::cout << '\n';
}
}
};
// 直線クラス(抽象クラス) Line
class Line : public Shape {
protected:
int length; // 線の長さ
public:
Line(int len) : length(len) { }
};
// 横線クラス HorzLine
class HorzLine : public Line {
public:
HorzLine(int len) : Line(len) { }
void draw() const {
for (int i = 1; i <= length; i++)
std::cout << '-';
std::cout << '\n';
}
};
// 縦線クラス VertLine
class VertLine : public Line {
public:
VertLine(int len) : Line(len) { }
void draw() const {
for (int i = 1; i <= length; i++)
std::cout << "|\n";
}
};
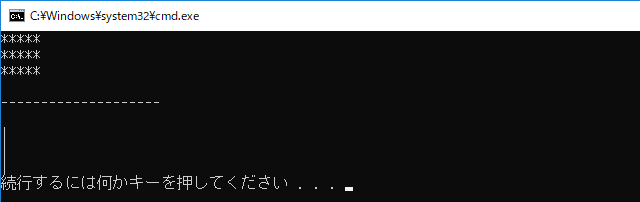
int main() {
Rectangle a(5, 3);
HorzLine c(20);
VertLine d(3);
a.draw(); std::cout << '\n';
c.draw(); std::cout << '\n';
d.draw();
}
// ------------------------------------