Math solver ( MathSolver
) structured data
To help students, teachers, and others with math problems, you can use structured data to indicate the type of math problems and links to step-by-step walkthroughs for specific math problems. Here's an example of how math solvers may look in Google Search results (the appearance is subject to change):
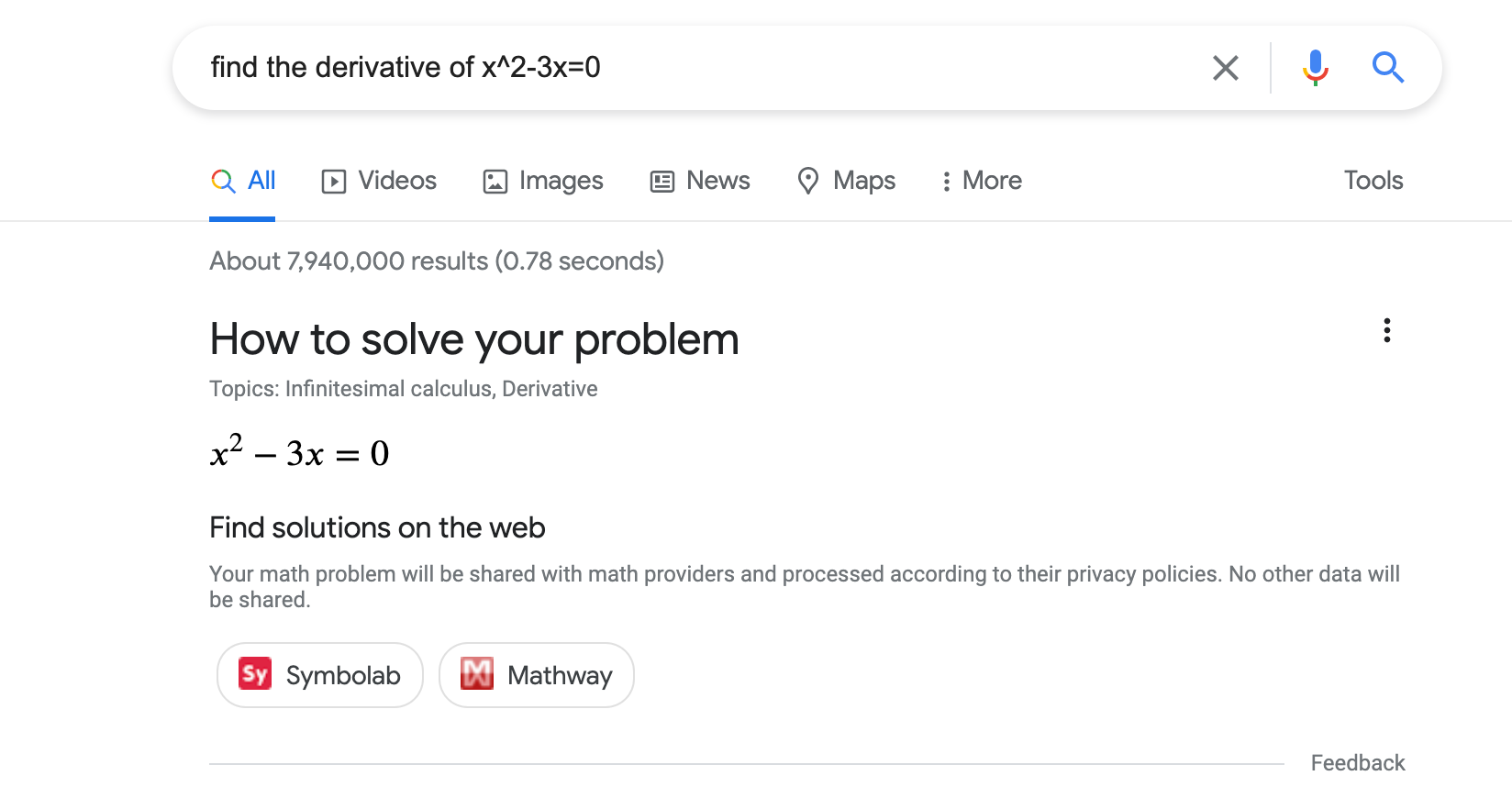
How to add structured data
Structured data is a standardized format for providing information about a page and classifying the page content. If you're new to structured data, you can learn more about how structured data works .
Here's an overview of how to build, test, and release structured data.
- Add the required properties . Based on the format you're using, learn where to insert structured data on the page .
- Follow the guidelines .
- Validate your code using the Rich Results Test and fix any critical errors. Consider also fixing any non-critical issues that may be flagged in the tool, as they can help improve the quality of your structured data (however, this isn't necessary to be eligible for rich results).
- Deploy a few pages that include your structured data and use the URL Inspection tool
to test how Google sees the page. Be sure that your page is
accessible to Google and not blocked by a robots.txt file, the
noindextag, or login requirements. If the page looks okay, you can ask Google to recrawl your URLs . - To keep Google informed of future changes, we recommend that you submit a sitemap . You can automate this with the Search Console Sitemap API .
Examples
One solver action
Here's an example of a math solver home page that has one solver action that can solve polynomial equations and derivative problems and is available in English and Spanish.
<html>
<head>
<title>An awesome math solver</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="application/ld+json">
[
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": ["MathSolver", "LearningResource"],
"name": "An awesome math solver",
"url": "https://www.mathdomain.com/",
"usageInfo": "https://www.mathdomain.com/privacy",
"inLanguage": "en",
"potentialAction": [{
"@type": "SolveMathAction",
"target": "https://mathdomain.com/solve?q={math_expression_string}",
"mathExpression-input": "required name=math_expression_string",
"eduQuestionType": ["Polynomial Equation","Derivative"]
}],
"learningResourceType": "Math solver"
},
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": ["MathSolver", "LearningResource"],
"name": "Un solucionador de matemáticas increíble",
"url": "https://es.mathdomain.com/",
"usageInfo": "https://es.mathdomain.com/privacy",
"inLanguage": "es",
"potentialAction": [{
"@type": "SolveMathAction",
"target": "https://es.mathdomain.com/solve?q={math_expression_string}",
"mathExpression-input": "required name=math_expression_string",
"eduQuestionType": ["Polynomial Equation","Derivative"]
}],
"learningResourceType": "Math solver"
}
]
</script>
</body>
</html>
Two solver actions
Here's an example of a math solver home page that has two solver endpoints: one endpoint can solve polynomial equations and the other endpoint can solve trigonometric equations. It is available only in English.
<html>
<head>
<title>An awesome math solver</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": ["MathSolver", "LearningResource"],
"name": "An awesome math solver",
"url": "https://www.mathdomain.com/",
"usageInfo": "https://www.mathdomain.com/privacy",
"inLanguage": "en",
"potentialAction": [{
"@type": "SolveMathAction",
"target": "https://mathdomain.com/solve?q={math_expression_string}",
"mathExpression-input": "required name=math_expression_string",
"eduQuestionType": "Polynomial Equation"
},
{
"@type": "SolveMathAction",
"target": "https://mathdomain.com/trig?q={math_expression_string}",
"mathExpression-input": "required name=math_expression_string",
"eduQuestionType": "Trigonometric Equation"
}],
"learningResourceType": "Math solver"
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Guidelines
For your page to be eligible for math solver rich results, you must follow these guidelines:
Technical Guidelines
- Add
MathSolverstructured data to the home page of your site. - Ensure that Googlebot can crawl your site efficiently .
- If you have several identical copies of the same math solver hosted under different URLs, use the canonical URLs on each copy of the page.
- We don't allow math solvers that are entirely hidden behind a login or paywall. Once users navigate from the feature on Google to your site, the solution and a step-by-step walkthrough for their initial problem must be accessible to them. Additional content can be behind a login or paywall.
Content guidelines
We created these Math Solver content guidelines to ensure that our users are connected with learning resources that are relevant. If we find content that violates these policies, we'll respond appropriately, which may include taking manual action and removing your pages from appearing in the math solver experience on Google.
- We don't allow promotional content disguised as a math solver, such as those posted by a third party (for example, affiliate programs ).
- You are responsible for the accuracy and quality of your math solver through this
feature. If a certain amount of your data is found to be inaccurate based on our quality
review processes, then your solver may be removed from the feature until you resolve the
issues depending on the severity. This applies to:
- The accuracy of the problem types your solver is capable of solving.
- The accuracy of your solutions for math problems your solver declares it can solve.
Structured data type definitions
You must include the required properties for your content to be eligible for display as a rich result. You can also include the recommended properties to add more information to your structured data, which could provide a better user experience.
MathSolver
A MathSolver
is a tool that assists students, teachers, and others
with math problems by laying out step-by-step solutions. Use MathSolver
structured data on your site's home page.
The full definition of MathSolver
is available at schema.org/MathSolver
.
The Google-supported properties are the following:
potentialAction
The action that leads to a mathematical explanation (for example, step-by-step solution or graph) of a math expression.
{ "@type" : "MathSolver" , "potentialAction" : [{ "@type" : "SolveMathAction" , "target" : "https://mathdomain.com/solve?q={math_expression_string}" , "mathExpression-input" : "required name=math_expression_string" , "eduQuestionType" : "Polynomial Equation" }] }
potentialAction.mathExpression-input
A placeholder for a mathematical expression (for example: x^2-3x=0) that is sent by Google to your website. You can then "solve" the math expression, which may involve simplifying, transforming, or solving for a specific variable. The string can take many formats (for example: LaTeX, Ascii-Math, or mathematical expressions that you can write with a keyboard).
For some problem types, the math_expression_string
indicates both the problem type and
parameters of the problem type. Here are some examples of the more complicated problem
types so that you can anticipate and parse them correctly.
Derivatives
Google will send a math_expression_string
in one of two forms:
-
( math_expression ) '
-
d / d variable math_expression
Examples :
-
( x ^ 2 + x ) ' -
d / dx ( x ^ 2 + x ) -
d / dy y ^ 2 + y
Integrals
Google
will
send
a
math_expression_string
in
one
of
two
forms
:
-
\ int math_expression
-
\int_{ from }^{ to } math_expression
Examples:
-
\int x^2+x -
\int_{0}^{2} x^2+x
Limits
Google will send a math_expression_string
in one of two forms:
-
\lim math_expression -
\ lim_ { variable \ rightarrow value } math_expression
Examples:
-
\lim_{x\rightarrow0} sin(x)/x -
\lim_{y\rightarrow\infty} sin(y)/y -
\lim sin(x)/x
url
The URL of the MathSolver
.
usageInfo
The privacy policy for your math problem solving site.
{ "@type" : "MathSolver" , "usageInfo" : "https://www.mathdomain.com/privacy" }
potentialAction.target
The URL target entrypoint for an action. The potentialAction.target
property accepts a string to represent the math expression that's being solved by the action.
{ "@type" : "MathSolver" , "potentialAction" : [{ "@type" : "SolveMathAction" , "target" : "https://mathdomain.com/solve?q={math_expression_string}" }] }
| Recommended properties | |
|---|---|
inLanguage
|
The language(s) that are supported by your math problem solving site. See this table for a list of possible languages. { "@type" : "MathSolver" , "inLanguage" : "es" } |
assesses
|
The problem type(s) that are solved with the { "@type" : "MathSolver" , "assesses" : "Polynomial Equation" } |
potentialAction.eduQuestionType
|
The problem type(s) that are capable of being solved by the { "@type" : "SolveMathAction" , "eduQuestionType" : "Polynomial Equation" } |
LearningResource
A LearningResource
indicates that the subject of the markup is a
resource that assists students, teachers, and others with educational learning. Use LearningResource
on your site's home page.
The full definition of LearningResource
is available at schema.org/LearningResource
.
The Google-supported properties are the following:
| Required properties | |
|---|---|
learningResourceType
|
The type of this learning resource. Use this fixed value: { "@type" : [ "MathSolver" , "LearningResource" ], "learningResourceType" : "Math Solver" } |
Problem Type Definitions
Use the following list of problem types as either the eduQuestionType
for a MathSolver.potentialAction
or for the assesses
field of a MathSolver
when the MathSolver
is accompanying a HowTo
that walks through a specific math problem.
The following table shows some examples for the problem types you can annotate:
Absolute Value Equation
Absolute value equations. For example: |x - 5| = 9
Algebra
A generic problem type that can be placed with other problem type. For example: polynomial equations, exponential equations, and radical expressions.
Arc Length
Arc length problems. For example: Determine the length of x = 4 (3 + y)^2, 1 < y < 4.
Arithmetic
Arithmetic problems. For example: Find the sum of 5 + 7.
Biquadratic Equation
Biquadratic equations. For example: x^4 - x^2 - 2 = 0.
Calculus
A generic problem type that can be placed with other problem types. For example: integrals, derivatives, and differential equations.
Characteristic Polynomial
Find the characteristic polynomial of {{1,2,5}, {3,-1,1}, {1,2,3}} .
Circle
Circle related problems. For example: Find the radius of x^2 + y^2 = 3.
Derivative
Derivative of 5x^4 + 2x^3 + 4x - 2.
Differential Equation
Differential equation problems. For example: y+dy/dx=5x.
Distance
Distance problems. For example: Find the distance between (6,-1) and (-3,2).
Eigenvalue
Eigenvalue problems. For example: Find the eigenvalues for the matrix [[-6, 3], [4, 5]].
Eigenvector
Eigenvector problems. For example: Find the eigenvector for the matrix [[-6, 3], [4, 5]] with eigenvalues of [-7, 6].
Ellipse
Ellipse problems. For example: Find the x and y intercepts of 9x^2 + 4y^2 = 36.
Exponential Equation
Exponential equations. For example: 7^x = 9.
Function
Polynomial simplifications. For example: (x-5)^2 * (x+5)^2.
Function Composition
f(g(x)) when f(x)=x^2-2x, g(x)=2x-2
Geometry
A generic problem type that can be placed with other problem types. For example: circle, ellipse, parabola, slope.
Hyperbola
Hyperbola problems. For example: Find the x-intercept of (x^2)/4 - (y^2)/5 = 1.
Inflection Point
Find the inflection point of f(x) = 1/2x^4 +x^3 - 6x^2.
Integral
Integral of sqrt (x^2 - y^2).
Intercept
Line intercept problems. For example: Find the x-intercept of the line y = 10x - 5.
Limit
Limit problems. For example: Find the limit of x as x approaches 1 for (x^2-1)/(x-1).
Line Equation
Line equation problems. For example: Find the equation of a line with points (-7,-4) and (-2,-6).
Linear Algebra
A generic problem type that can be placed with other problem types. For example: matrix and characteristic polynomial.
Linear Equation
Linear equations. For example: 4x - 3 = 2x + 9.
Linear Inequality
Linear inequalities. For example: 5x - 6 > 3x - 8.
Logarithmic Equation
Logarithmic equations. For example: log(x) = log(100).
Logarithmic Inequality
Logarithmic inequalities. For example: log(x) > log(100).
Matrix
{{1,2,5}, {3,-1,1}, {1,2,3}} row reduce
Midpoint
Midpoint problems. For example: find the midpoint between (-3, 7) and (5, -2).
Parabola
Parabola problems. For example: Find the vertex of y2 - 4x - 4y = 0.
Parallel
Parallel line problems. For example: Are the two lines parallel (y = 10x + 5, y = 20x + 10)?
Perpendicular
Perpendicular problems. For example: Are the two lines perpendicular (y = 10x + 5, y = 20x + 10)?
Polynomial Equation
Polynomial equations. For example: x^5 - 3x = 0.
Polynomial Expression
Polynomial expressions. For example: (x - 5)^4 * (x + 5)^2.
Polynomial Inequality
Polynomial inequalities. For example: x^4 - x^2 - 6 > x^3 - 3x^2.
Quadratic Equation
Quadratic equations. For example: x^2 - 3x - 4 = 0.
Quadratic Expression
Quadratic expressions. For example: x^2 - 3x - 2.
Quadratic Inequality
Quadratic inequalities. For example: x^2 - x - 6 > x^2 - 3x.
Radical Equation
Radical equations. For example: sqrt(x) - x = 0.
Radical Inequality
Radical inequalities. For example: sqrt(x) - x > 0.
Rational Equation
Rational equations. For example: 5/(x - 3) = 2/(x - 1).
Rational Expression
Rational expressions. For example: 1/(x^3 + 4x^2 + 5x + 2).
Rational Inequality
Rational inequalities. For example: 5/(x - 3) > 2/(x - 1).
Slope
Slope problems. For example: Find the slope of y = 10x + 5.
Statistics
Statistics problems. For example: Find the mean of a set of numbers (3, 8, 2, 10).
System of Equations
System of equations problems. For example: Solve 2x + 5y = 16;3x - 5y = - 1.
Trigonometry
Solve sin(t) + cos(t) = 1.


