Page Summary
-
When a native ad loads, your app receives a native ad object using GADAdLoaderDelegate protocol messages and is responsible for displaying it.
-
The GADNativeAdView class, a UIView, should be used by publishers to display a GADNativeAd, with all asset UIViews as its subviews.
-
The SDK automatically handles tasks like recording clicks and impressions, and displaying the AdChoices overlay when you register views with GADNativeAdView IBOutlets and the GADNativeAd object.
-
For indirect native ads, the SDK adds an AdChoices overlay, requiring space in your native ad view's preferred corner and clear placement.
-
You must display an ad attribution to denote that a view is an advertisement when showing programmatic native ads.
Display a system-defined native ad format
When a native ad loads, your app will receive a native ad object using one of
the GADAdLoaderDelegate
protocol messages. Your app is then responsible for
displaying the ad (though it doesn't necessarily have to do so immediately).
To make displaying system-defined ad formats easier, the SDK offers some useful
resources.
GADNativeAdView
For the GADNativeAd
, there is a corresponding "ad view"
class: GADNativeAdView
.
This ad view class is a UIView
that publishers should use to display the ad.
A single GADNativeAdView
, for example, can display a single instance of
a GADNativeAd
. Each of the UIView
objects used to display that ad's
assets should be subviews of that GADNativeAdView
object.
If you were displaying an ad in a UITableView
, for example, the
view hierarchy for one of the cells might look like this:
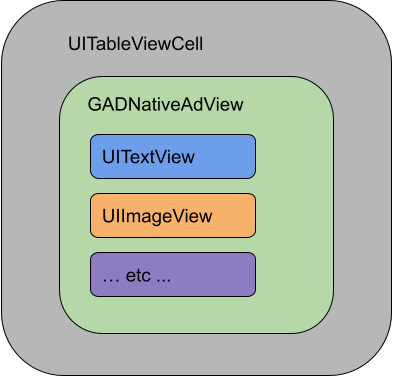
The GADNativeAdView
class also provides IBOutlets
used to register
the view used for each individual asset, and a method to register the GADNativeAd
object itself. Registering the views in this way allows the SDK to automatically
handle tasks such as:
- Recording clicks.
- Recording impressions (when the first pixel is visible on the screen).
- Displaying the AdChoices overlay.
AdChoices overlay
For indirect native ads (delivered through AdMob backfill or through Ad Exchange or AdSense), an AdChoices overlay is added by the SDK. Leave space in your preferred corner of your native ad view for the automatically inserted AdChoices logo. Also, make sure the AdChoices overlay is placed on content that allows the icon to be clearly seen. For more information on the overlay's appearance and function, see the programmatic native ads implementation guidelines .
Ad attribution
When displaying programmatic native ads, you must display an ad attribution to denote that the view is an advertisement.Code example
This section shows how to display native ads using views loaded dynamically
from xib files. This can be a very useful approach when using GADAdLoaders
configured to request multiple formats.
Lay out the UIViews
The first step is to lay out the UIViews
that will display native ad assets.
You can do this in the Interface Builder as you would when creating any other
xib file. Here's how the layout for a native
ad might look:
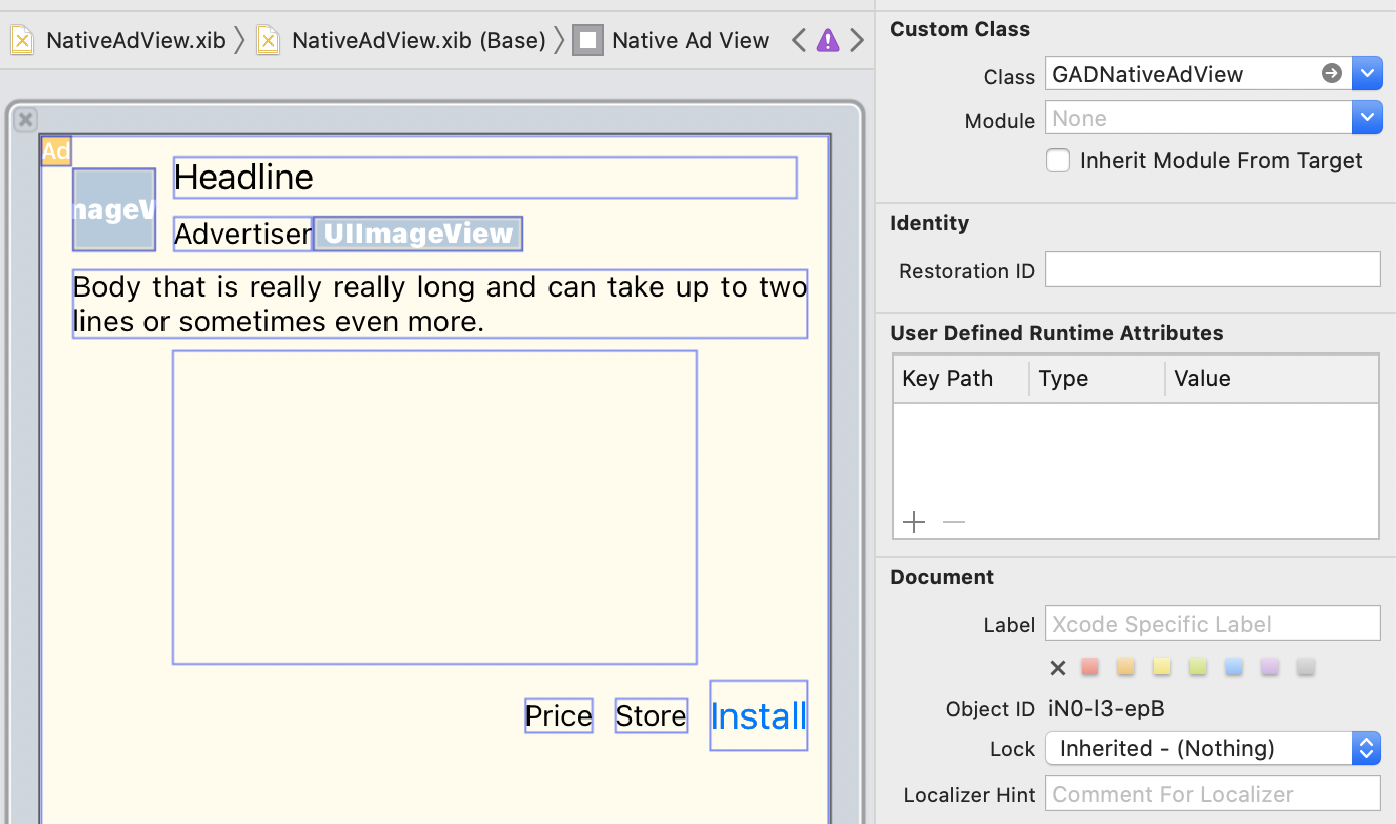
Note the Custom Class value in the top right of the image. It's set to
GADNativeAdView
.
This is the ad view class that is used to display a GADNativeAd
.
You'll also need to set the custom class for the GADMediaView
, which is used
to display the video or image for the ad.
Link outlets to views
Once the views are in place and you've assigned the correct ad view class to
the layout, link the ad view's asset outlets to the UIViews
you've created.
Here's how you might link the ad view's asset outlets to the UIViews
created
for an ad: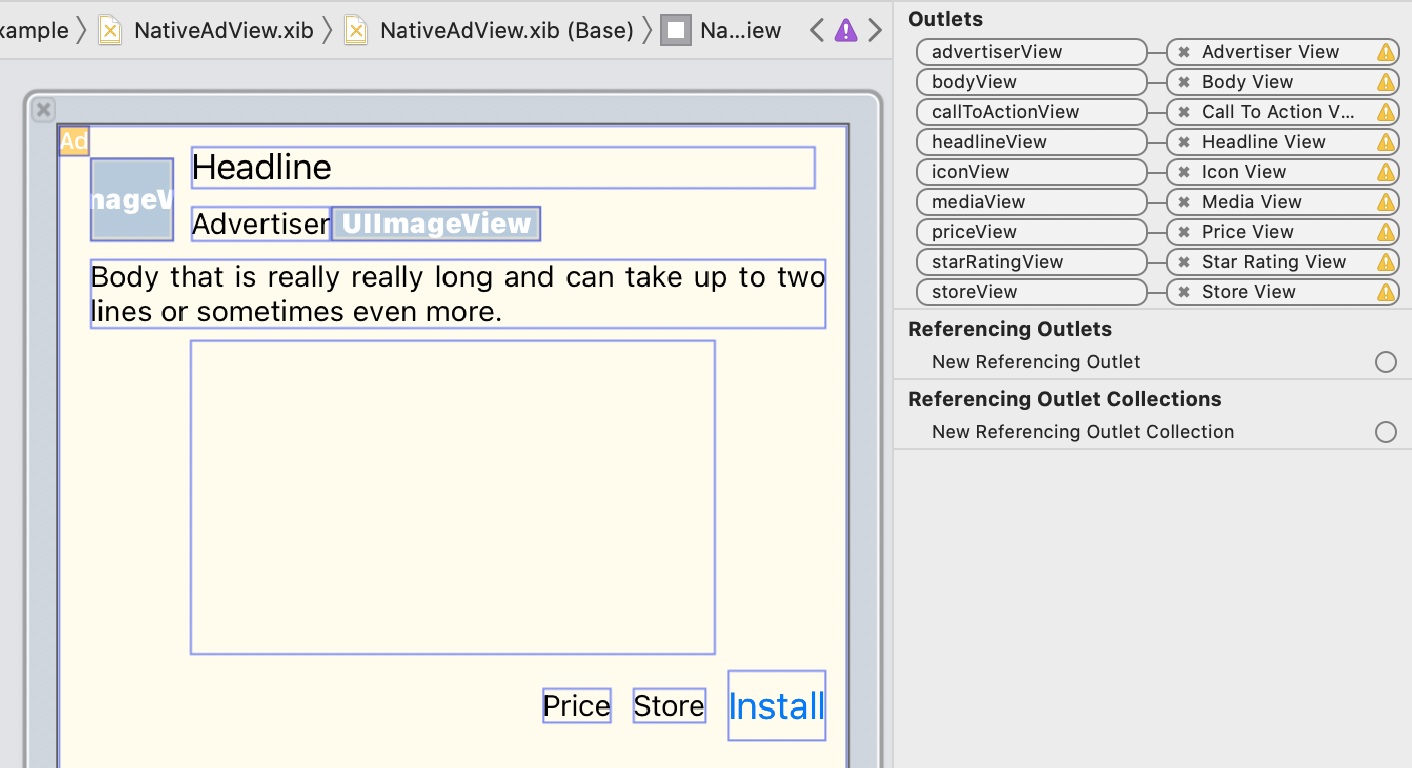
In the outlet panel, the outlets in GADNativeAdView
have been linked to
the UIViews
laid out in the Interface Builder. This lets
the SDK know which UIView
displays which asset.
It's also important to remember that these outlets represent the views that are
clickable in the ad.
Display the ad
After the layout is complete and the outlets are linked, add the following code to your app that displays an ad once it has loaded:
Swift
func
adLoader
(
_
adLoader
:
AdLoader
,
didReceive
nativeAd
:
NativeAd
)
{
// ...
// Set ourselves as the native ad delegate to be notified of native ad events.
nativeAd
.
delegate
=
self
// Populate the native ad view with the native ad assets.
// The headline and mediaContent are guaranteed to be present in every native ad.
(
nativeAdView
.
headlineView
as
?
UILabel
)?.
text
=
nativeAd
.
headline
nativeAdView
.
mediaView
?.
mediaContent
=
nativeAd
.
mediaContent
// Some native ads will include a video asset, while others do not. Apps can use the
// GADVideoController's hasVideoContent property to determine if one is present, and adjust their
// UI accordingly.
let
mediaContent
=
nativeAd
.
mediaContent
if
mediaContent
.
hasVideoContent
{
// By acting as the delegate to the GADVideoController, this ViewController receives messages
// about events in the video lifecycle.
mediaContent
.
videoController
.
delegate
=
self
videoStatusLabel
.
text
=
"Ad contains a video asset."
}
else
{
videoStatusLabel
.
text
=
"Ad does not contain a video."
}
// This app uses a fixed width for the GADMediaView and changes its height to match the aspect
// ratio of the media it displays.
if
let
mediaView
=
nativeAdView
.
mediaView
,
nativeAd
.
mediaContent
.
aspectRatio
>
0
{
let
aspectRatioConstraint
=
NSLayoutConstraint
(
item
:
mediaView
,
attribute
:
.
width
,
relatedBy
:
.
equal
,
toItem
:
mediaView
,
attribute
:
.
height
,
multiplier
:
CGFloat
(
nativeAd
.
mediaContent
.
aspectRatio
),
constant
:
0
)
mediaView
.
addConstraint
(
aspectRatioConstraint
)
nativeAdView
.
layoutIfNeeded
()
}
// These assets are not guaranteed to be present. Check that they are before
// showing or hiding them.
(
nativeAdView
.
bodyView
as
?
UILabel
)?.
text
=
nativeAd
.
body
nativeAdView
.
bodyView
?.
isHidden
=
nativeAd
.
body
==
nil
(
nativeAdView
.
callToActionView
as
?
UIButton
)?.
setTitle
(
nativeAd
.
callToAction
,
for
:
.
normal
)
nativeAdView
.
callToActionView
?.
isHidden
=
nativeAd
.
callToAction
==
nil
(
nativeAdView
.
iconView
as
?
UIImageView
)?.
image
=
nativeAd
.
icon
?.
image
nativeAdView
.
iconView
?.
isHidden
=
nativeAd
.
icon
==
nil
(
nativeAdView
.
starRatingView
as
?
UIImageView
)?.
image
=
imageOfStars
(
from
:
nativeAd
.
starRating
)
nativeAdView
.
starRatingView
?.
isHidden
=
nativeAd
.
starRating
==
nil
(
nativeAdView
.
storeView
as
?
UILabel
)?.
text
=
nativeAd
.
store
nativeAdView
.
storeView
?.
isHidden
=
nativeAd
.
store
==
nil
(
nativeAdView
.
priceView
as
?
UILabel
)?.
text
=
nativeAd
.
price
nativeAdView
.
priceView
?.
isHidden
=
nativeAd
.
price
==
nil
(
nativeAdView
.
advertiserView
as
?
UILabel
)?.
text
=
nativeAd
.
advertiser
nativeAdView
.
advertiserView
?.
isHidden
=
nativeAd
.
advertiser
==
nil
// In order for the SDK to process touch events properly, user interaction should be disabled.
nativeAdView
.
callToActionView
?.
isUserInteractionEnabled
=
false
// Associate the native ad view with the native ad object. This is
// required to make the ad clickable.
// Note: this should always be done after populating the ad views.
nativeAdView
.
nativeAd
=
nativeAd
}
SwiftUI
Create a view model
Create a view model that loads a native ad, and publishes native ad data changes:
import
GoogleMobileAds
class
NativeAdViewModel
:
NSObject
,
ObservableObject
,
NativeAdLoaderDelegate
{
@
Published
var
nativeAd
:
NativeAd
?
private
var
adLoader
:
AdLoader
!
func
refreshAd
()
{
adLoader
=
AdLoader
(
adUnitID
:
"ca-app-pub-3940256099942544/3986624511"
,
// The UIViewController parameter is optional.
rootViewController
:
nil
,
adTypes
:
[.
native
],
options
:
nil
)
adLoader
.
delegate
=
self
adLoader
.
load
(
Request
())
}
func
adLoader
(
_
adLoader
:
AdLoader
,
didReceive
nativeAd
:
NativeAd
)
{
// Native ad data changes are published to its subscribers.
self
.
nativeAd
=
nativeAd
nativeAd
.
delegate
=
self
}
func
adLoader
(
_
adLoader
:
AdLoader
,
didFailToReceiveAdWithError
error
:
Error
)
{
print
(
"
\(
adLoader
)
failed with error:
\(
error
.
localizedDescription
)
"
)
}
}
Create a UIViewRepresentable
Create a UIViewRepresentable
for NativeView
, and subscribe to the data changes in the ViewModel
class:
private
struct
NativeAdViewContainer
:
UIViewRepresentable
{
typealias
UIViewType
=
NativeAdView
// Observer to update the UIView when the native ad value changes.
@
ObservedObject
var
nativeViewModel
:
NativeAdViewModel
func
makeUIView
(
context
:
Context
)
-
>
NativeAdView
{
return
Bundle
.
main
.
loadNibNamed
(
"NativeAdView"
,
owner
:
nil
,
options
:
nil
)?.
first
as
!
NativeAdView
}
func
updateUIView
(
_
nativeAdView
:
NativeAdView
,
context
:
Context
)
{
guard
let
nativeAd
=
nativeViewModel
.
nativeAd
else
{
return
}
// Each UI property is configurable using your native ad.
(
nativeAdView
.
headlineView
as
?
UILabel
)?.
text
=
nativeAd
.
headline
nativeAdView
.
mediaView
?.
mediaContent
=
nativeAd
.
mediaContent
(
nativeAdView
.
bodyView
as
?
UILabel
)?.
text
=
nativeAd
.
body
(
nativeAdView
.
iconView
as
?
UIImageView
)?.
image
=
nativeAd
.
icon
?.
image
(
nativeAdView
.
starRatingView
as
?
UIImageView
)?.
image
=
imageOfStars
(
from
:
nativeAd
.
starRating
)
(
nativeAdView
.
storeView
as
?
UILabel
)?.
text
=
nativeAd
.
store
(
nativeAdView
.
priceView
as
?
UILabel
)?.
text
=
nativeAd
.
price
(
nativeAdView
.
advertiserView
as
?
UILabel
)?.
text
=
nativeAd
.
advertiser
(
nativeAdView
.
callToActionView
as
?
UIButton
)?.
setTitle
(
nativeAd
.
callToAction
,
for
:
.
normal
)
// For the SDK to process touch events properly, user interaction should be disabled.
nativeAdView
.
callToActionView
?.
isUserInteractionEnabled
=
false
// Associate the native ad view with the native ad object. This is required to make the ad
// clickable.
// Note: this should always be done after populating the ad views.
nativeAdView
.
nativeAd
=
nativeAd
}
Add the view to the view hierarchy
The following code demonstrates adding the UIViewRepresentable
to the view
hierarchy:
struct
NativeContentView
:
View
{
// Single source of truth for the native ad data.
@
StateObject
private
var
nativeViewModel
=
NativeAdViewModel
()
var
body
:
some
View
{
ScrollView
{
VStack
(
spacing
:
20
)
{
// Updates when the native ad data changes.
NativeAdViewContainer
(
nativeViewModel
:
nativeViewModel
)
.
frame
(
minHeight
:
300
)
// minHeight determined from xib.


