PR
X
Calendar
Dec , 2025
Nov , 2025
Oct , 2025
Sep , 2025
Aug , 2025
Nov , 2025
Oct , 2025
Sep , 2025
Aug , 2025
Keyword Search
▼キーワード検索
Comments
Freepage List
基本事情 写経一覧表(総合)[更新日付]

関連情報(アジア)

関連情報(中南米)

関連情報(ヨーロッパ)

関連情報(中東地区)

関連情報(アフリカ)

関連情報(北米ほか)

「年月日」から記事にアクセスする方法

世界規模データ
外国政府の統計 の出所

自由が丘氏等の寄稿一覧表(総合と自由が丘氏)

仮想旅行・歴史

鈴村興太郎博士の講話など

宇治見氏寄稿「ブラジル日本移民100年史」等

寺尾公男遺稿集

金剛山仙人

青雲荘亭主

ピケティ理論、所得格差分析など

山崎博司氏「こころの友」HPの一部保存

諸問題その他

司馬遼太郎「日本人とは何か」

マドレーヌ氏特別寄稿
Tsunami氏&Tigers&Mitsuya & Moomin Papa

土佐の高知(ふるさと)
父の癌闘病記

大学時代の思い出

会社勤務時代の思い出(OB時代も)

地元
海外出張

福島第一原発事故、地震、災害などへの対応

スポーツ・健康・病気関連(総合)
神尾米さんの「現代テニス」

宇宙・地球の未知

PCなど家電一般&HPやML & Fishing Mails

政治、法務関係など
年金など

ドキュメンタリーやドラマ・小説など

気候変動、資源・エネルギーなど

各種統計など

調理など

公害

家事一般(DIYを含む)

宗教
Category
寄稿(宇治見、マドレーヌ、トキめき橋氏ほか)
(68)自由が丘氏寄稿文
(189)Tsunami氏寄稿、SCRAP記事、写経・感想など
(326)政治・経済(国内統計etc.)
(725)世界、国際比較(国際統計etc.)
(228)生活全般
(129)基本事情(各国)
(114)アジア州
(257)ヨーロッパ州
(293)北米地区
(206)中南米地区
(112)オセアニア州
(104)中東地区
(51)アフリカ州
(126)宇宙の不思議・開発etc.
(71)気候変動など
(7)津波・自然災害
(30)自然の脅威、驚異etc.
(47)資源・エネルギー(陸・海洋etc.)
(49)発電・原発事故・放射能事故
(74)金融(事件含む)
(128)PC・家電
(229)スポーツ・余暇・車
(264)栄養・健康
(143)病気・伝染病など
(191)事故・災害
(102)福祉・厚生・年金問題
(59)公害
(15)流通(商品)・廃棄関連
(17)新技術
(30)友人・知人・地縁等
(40)土佐の高知
(63)夢
(49)お墓・葬儀・戸籍
(24)ガーデニング&DIY
(14)TV番組
(15)海外旅行
(6)国防/テロなど
(41)財政・税・電子証明など
(28)自治体、地元、遺産など
(37)店舗
(6)公衆道徳/法律など
(26)裁判/調停
(7)宗教
(21)ブログ
(31)テンプレート(表形式etc.)
(3)DVD収録など
(6)ホームページ、ウエブ会議など
(48)祝い事など
(14)会社時代
(22)学生時代
(7)物語り
(43)経済学研究
(26)思考紀行
(73)作業中マーク(終了次第削除)
(0)洞察力
(1)カテゴリ: 北米地区
★
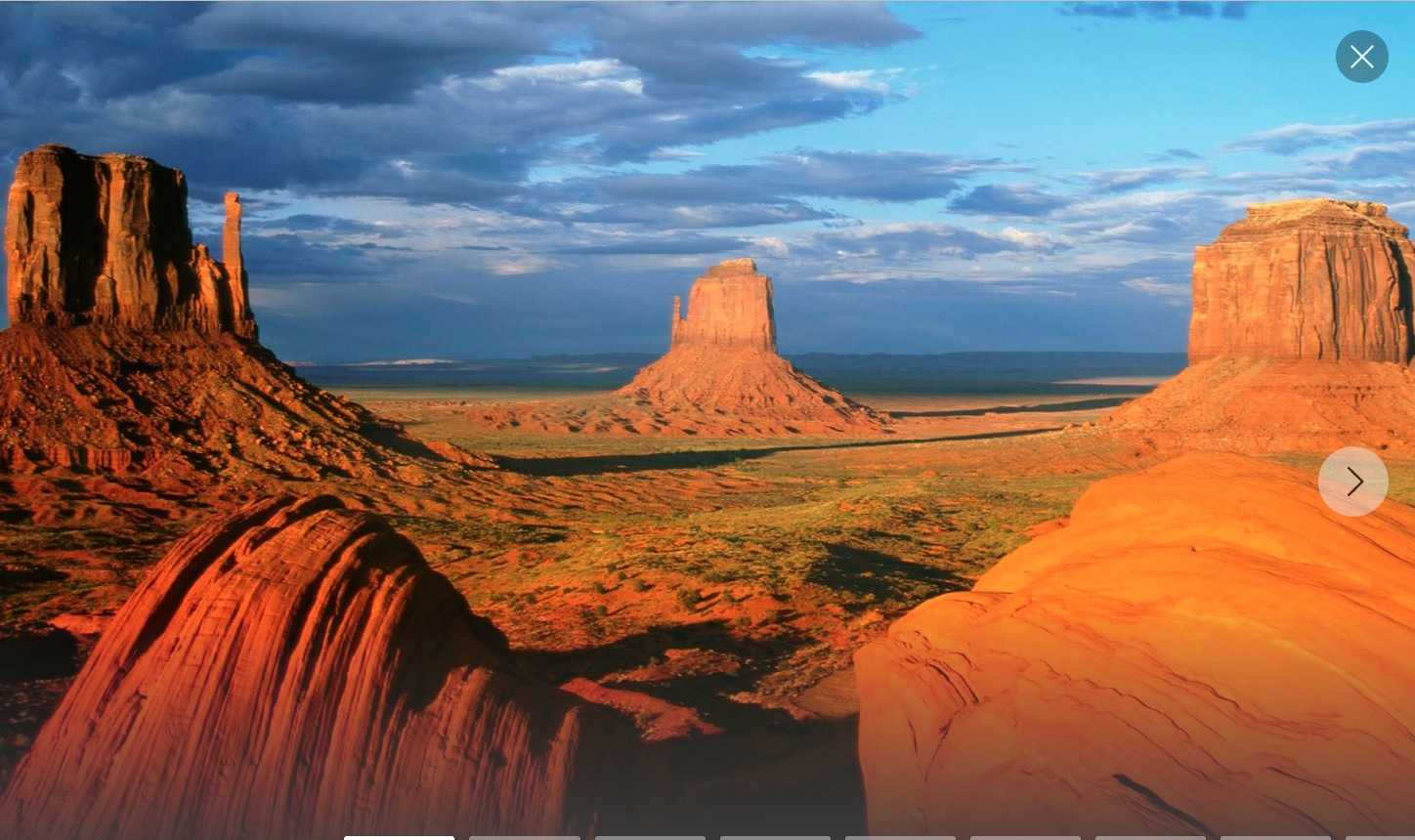

米国では居留地の失業は考えられない
★
米国の非農業部門の就労者数は季調済みで253千人と
増加した。
失業率は「3.4%」と、0.1%の改善で、 1969年月以来
の 最低(1953年10月が2位である)に当たる。
就業者数を業種別に見ると、新型コロナウイルス禍
から 持ち直しが続く娯楽・接客が前月比「31千人」増、
医療は「39.6千人」 増加となった。
平均時給は前月比「4.4%」増加と小幅ながら前月の
伸びを 上回った。
【ワシントン時事】
米労働省が5日発表した4月の雇用統計
(季節調整済み)によると、景気動向を敏感に反映
する非農業部門の就業者数は前月から
25万3,000人増加した。伸びは前月の
16万5,000人(改定)から拡大し、市場予想
(18万人)も上回った。
失業率は3.4%と、0.1ポイント改善した。
米連邦準備制度理事会(FRB)の利上げや、
相次ぐ銀行破綻による信用不安にもかかわらず、
米労働市場は堅調を保っている。
就業者数を業種別に見ると、新型コロナウイルス禍
からの持ち直しが続く娯楽・接客が前月比
3万1,000人増、医療は3万9,600人増となった。
平均時給は前年同月比「4.4%」増と、小幅ながら
前月の伸び率を上回った。
FRBは「労働市場は引き続き極めて逼迫している」
(パウエル議長)と分析。
人手不足による賃金上昇が、接客などサービス分野の
価格を押し上げていることに懸念を示す。
★
<WHOの指示を正確に受けて欲しい>
Don’t forget WHO's SAGE Guidance・・・
Following its 20-23 March meeting, WHO’s
Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on
Immunization (SAGE) revised the roadmap
for prioritizing the use of COVID-19 vaccines,
to reflect the impact of Omicron and high
population-level immunity due to infection
and vaccination.
The roadmap continues SAGE’s prioritization
of protecting populations at the greatest risk
of death and severe disease from SARS-CoV-2
infection and its focus on maintaining resilient
health systems. The roadmap newly considers
the cost-effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccination
for those at lower risk – namely healthy children
and adolescents – compared to other health
interventions.
The roadmap also includes revised recommenda-
tions on additional booster doses and the spacing
of boosters.
The current COVID-19 vaccines’ reduction of post-
COVID conditions is also considered but
the evidence on the extent of their impact is
inconsistent.
“Updated to reflect that much of the population is
either vaccinated or previously infected with COVID-
19, or both, the revised roadmap reemphasizes the
importance of vaccinating those still at-risk of severe
disease, mostly older adults and those with underlying
conditions, including with additional boosters,” stated
SAGE Chair Dr Hanna Nohynek. “Countries should
consider their specific context in deciding whether to
continue vaccinating low risk groups, like healthy child-
ren and adolescents, while not compromising the routine
vaccines that are so crucial for the health and well-being
of this age group.”
The revised roadmap outlines three priority-use groups
for COVID-19 vaccination: high, medium, and low.
These priority groups are principally based on risk of
severe disease and death, and consider vaccine
performance, cost-effectiveness, programmatic factors
and community acceptance.
The high priority group includes older adults; younger
adults with significant comorbidities (e.g. diabetes and
heart disease); people with immunocompromising
conditions (e.g. people living with HIV and transplant
recipients), including children aged 6 months and older;
pregnant persons; and frontline health workers.
For the high priority group, SAGE recommends an addi-
tional booster of either 6 or 12 months after the last
dose, with the timeframe depending on factors such as
age and immunocompromising conditions. All the
COVID-19 vaccine recommendations are time-limited,
applying for the current epidemiological scenario only,
and so the additional booster recommendations should
not be seen as for continued annual COVID-19 vaccine
boosters. The aim is to serve countries planning for the
near- to mid-term.
The medium priority group includes healthy adults –
usually under the age of 50-60 – without comorbidities
and children and adolescents with comorbidities.
SAGE recommends primary series and first booster
doses for the medium priority group.
Although additional boosters are safe for this group,
SAGE does not routinely recommend them, given the
comparatively low public health returns.
The low priority group includes healthy children and
adolescents aged 6 months to 17 years. Primary and
booster doses are safe and effective in children and
adolescents. However, considering the low burden of
disease, SAGE urges countries considering vaccination
of this age group to base their decisions on contextual
factors, such as the disease burden, cost effectiveness,
and other health or programmatic priorities and
opportunity costs.
The public health impact of vaccinating healthy children
and adolescents is comparatively much lower than the
established benefits of traditional essential vaccines for
children – such as the rotavirus, measles, and
pneumococcal conjugate vaccines – and of COVID-19
vaccines for high and medium priority groups.
Children with immunocompromising conditions and
comorbidities do face a higher risk of severe COVID-19,
so are included in the high and medium priority groups
respectively.
Though low overall, the burden of severe COVID-19 in
infants under 6 months is still higher than in children
aged 6 months to 5 years.
Vaccinating pregnant persons – including with an addi-
tional dose if more than 6 months have passed since
the last dose – protects both them and the fetus, while
helping to reduce the likelihood of hospitalization of
infants for COVID-19.
Countries that already have a policy in place for addi-
tional boosters should assess the evolving need based
on national disease burden, cost effectiveness and
opportunity costs.
Separate to the roadmap, SAGE also updated their
recommendations on bivalent COVID-19 vaccines,
now recommending that countries can consider using
BA.5 bivalent mRNA vaccine for the primary series.
★

米国では居留地の失業は考えられない
★
米国の非農業部門の就労者数は季調済みで253千人と
増加した。
失業率は「3.4%」と、0.1%の改善で、 1969年月以来
の 最低(1953年10月が2位である)に当たる。
就業者数を業種別に見ると、新型コロナウイルス禍
から 持ち直しが続く娯楽・接客が前月比「31千人」増、
医療は「39.6千人」 増加となった。
平均時給は前月比「4.4%」増加と小幅ながら前月の
伸びを 上回った。
【ワシントン時事】
米労働省が5日発表した4月の雇用統計
(季節調整済み)によると、景気動向を敏感に反映
する非農業部門の就業者数は前月から
25万3,000人増加した。伸びは前月の
16万5,000人(改定)から拡大し、市場予想
(18万人)も上回った。
失業率は3.4%と、0.1ポイント改善した。
米連邦準備制度理事会(FRB)の利上げや、
相次ぐ銀行破綻による信用不安にもかかわらず、
米労働市場は堅調を保っている。
就業者数を業種別に見ると、新型コロナウイルス禍
からの持ち直しが続く娯楽・接客が前月比
3万1,000人増、医療は3万9,600人増となった。
平均時給は前年同月比「4.4%」増と、小幅ながら
前月の伸び率を上回った。
FRBは「労働市場は引き続き極めて逼迫している」
(パウエル議長)と分析。
人手不足による賃金上昇が、接客などサービス分野の
価格を押し上げていることに懸念を示す。
★
<WHOの指示を正確に受けて欲しい>
Don’t forget WHO's SAGE Guidance・・・
Following its 20-23 March meeting, WHO’s
Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on
Immunization (SAGE) revised the roadmap
for prioritizing the use of COVID-19 vaccines,
to reflect the impact of Omicron and high
population-level immunity due to infection
and vaccination.
The roadmap continues SAGE’s prioritization
of protecting populations at the greatest risk
of death and severe disease from SARS-CoV-2
infection and its focus on maintaining resilient
health systems. The roadmap newly considers
the cost-effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccination
for those at lower risk – namely healthy children
and adolescents – compared to other health
interventions.
The roadmap also includes revised recommenda-
tions on additional booster doses and the spacing
of boosters.
The current COVID-19 vaccines’ reduction of post-
COVID conditions is also considered but
the evidence on the extent of their impact is
inconsistent.
“Updated to reflect that much of the population is
either vaccinated or previously infected with COVID-
19, or both, the revised roadmap reemphasizes the
importance of vaccinating those still at-risk of severe
disease, mostly older adults and those with underlying
conditions, including with additional boosters,” stated
SAGE Chair Dr Hanna Nohynek. “Countries should
consider their specific context in deciding whether to
continue vaccinating low risk groups, like healthy child-
ren and adolescents, while not compromising the routine
vaccines that are so crucial for the health and well-being
of this age group.”
The revised roadmap outlines three priority-use groups
for COVID-19 vaccination: high, medium, and low.
These priority groups are principally based on risk of
severe disease and death, and consider vaccine
performance, cost-effectiveness, programmatic factors
and community acceptance.
The high priority group includes older adults; younger
adults with significant comorbidities (e.g. diabetes and
heart disease); people with immunocompromising
conditions (e.g. people living with HIV and transplant
recipients), including children aged 6 months and older;
pregnant persons; and frontline health workers.
For the high priority group, SAGE recommends an addi-
tional booster of either 6 or 12 months after the last
dose, with the timeframe depending on factors such as
age and immunocompromising conditions. All the
COVID-19 vaccine recommendations are time-limited,
applying for the current epidemiological scenario only,
and so the additional booster recommendations should
not be seen as for continued annual COVID-19 vaccine
boosters. The aim is to serve countries planning for the
near- to mid-term.
The medium priority group includes healthy adults –
usually under the age of 50-60 – without comorbidities
and children and adolescents with comorbidities.
SAGE recommends primary series and first booster
doses for the medium priority group.
Although additional boosters are safe for this group,
SAGE does not routinely recommend them, given the
comparatively low public health returns.
The low priority group includes healthy children and
adolescents aged 6 months to 17 years. Primary and
booster doses are safe and effective in children and
adolescents. However, considering the low burden of
disease, SAGE urges countries considering vaccination
of this age group to base their decisions on contextual
factors, such as the disease burden, cost effectiveness,
and other health or programmatic priorities and
opportunity costs.
The public health impact of vaccinating healthy children
and adolescents is comparatively much lower than the
established benefits of traditional essential vaccines for
children – such as the rotavirus, measles, and
pneumococcal conjugate vaccines – and of COVID-19
vaccines for high and medium priority groups.
Children with immunocompromising conditions and
comorbidities do face a higher risk of severe COVID-19,
so are included in the high and medium priority groups
respectively.
Though low overall, the burden of severe COVID-19 in
infants under 6 months is still higher than in children
aged 6 months to 5 years.
Vaccinating pregnant persons – including with an addi-
tional dose if more than 6 months have passed since
the last dose – protects both them and the fetus, while
helping to reduce the likelihood of hospitalization of
infants for COVID-19.
Countries that already have a policy in place for addi-
tional boosters should assess the evolving need based
on national disease burden, cost effectiveness and
opportunity costs.
Separate to the roadmap, SAGE also updated their
recommendations on bivalent COVID-19 vaccines,
now recommending that countries can consider using
BA.5 bivalent mRNA vaccine for the primary series.
★
お気に入りの記事を「いいね!」で応援しよう
[北米地区] カテゴリの最新記事
-
トランプ大統領の米国の関税対策~カナダ… Mar 28, 2025
-
ウクライナ大統領の期待を米国大統領側が… Mar 1, 2025
-
露の旧友となりつつある返り咲き米国大統領 Feb 23, 2025
【毎日開催】
15記事にいいね!で1ポイント
10秒滞在
いいね!
--
/
--
© Rakuten Group, Inc.