Page Summary
-
Interpolation in Earth Engine converts a
FeatureCollectioninto a continuousImageby using numeric data from feature properties to estimate values at new locations. -
Inverse Distance Weighted (IDW) interpolation in Earth Engine is based on a specific method and includes a decay factor parameter.
-
Kriging is another interpolation method in Earth Engine that uses a semi-variogram model fit to known data points.
Interpolation from vector to raster in Earth Engine creates an Image
from a FeatureCollection
. Specifically, Earth Engine uses numeric data
stored in a property of the features to interpolate values at new locations outside
of the features. The interpolation results in a continuous Image
of
interpolated values up to the distance specified.
Inverse Distance Weighted Interpolation
The inverse distance weighting (IDW) function in Earth Engine is based on the method
described by Basso
et al. (1999)
. An additional control parameter is added in the form of a
decay factor ( gamma
) on the inverse distance. Other parameters include the
mean and standard deviation of the property to interpolate and the maximum range
distance over which to interpolate. The following example creates an interpolated surface of methane concentration
to fill spatial gaps in the original raster dataset. The FeatureCollection
is generated by sampling a two-week methane composite.
// Import two weeks of S5P methane and composite by mean . var ch4 = ee . ImageCollection ( 'COPERNICUS/S5P/OFFL/L3_CH4' ) . select ( 'CH4_column_volume_mixing_ratio_dry_air' ) . filterDate ( '2019-08-01' , '2019-08-15' ) . mean () . rename ( 'ch4' ); // Define an area to perform interpolation over . var aoi = ee . Geometry . Polygon ( [[[ - 95.68487605978851 , 43.09844605027055 ], [ - 95.68487605978851 , 37.39358590079781 ], [ - 87.96148738791351 , 37.39358590079781 ], [ - 87.96148738791351 , 43.09844605027055 ]]], null , false ); // Sample the methane composite to generate a FeatureCollection . var samples = ch4 . addBands ( ee . Image . pixelLonLat ()) . sample ({ region : aoi , numPixels : 1500 , scale : 1000 , projection : 'EPSG:4326' }) . map ( function ( sample ) { var lat = sample . get ( 'latitude' ); var lon = sample . get ( 'longitude' ); var ch4 = sample . get ( 'ch4' ); return ee . Feature ( ee . Geometry . Point ([ lon , lat ]), { ch4 : ch4 }); }); // Combine mean and standard deviation reducers for efficiency . var combinedReducer = ee . Reducer . mean () . combine ({ reducer2 : ee . Reducer . stdDev (), sharedInputs : true }); // Estimate global mean and standard deviation from the points . var stats = samples . reduceColumns ({ reducer : combinedReducer , selectors : [ 'ch4' ]}); // Do the interpolation , valid to 70 kilometers . var interpolated = samples . inverseDistance ({ range : 7e4 , propertyName : 'ch4' , mean : stats . get ( 'mean' ), stdDev : stats . get ( 'stdDev' ), gamma : 0.3 }); // Define visualization arguments . var band_viz = { min : 1800 , max : 1900 , palette : [ '0D0887' , '5B02A3' , '9A179B' , 'CB4678' , 'EB7852' , 'FBB32F' , 'F0F921' ]}; // Display to map . Map . centerObject ( aoi , 7 ); Map . addLayer ( ch4 , band_viz , 'CH4' ); Map . addLayer ( interpolated , band_viz , 'CH4 Interpolated' );
Note that, as specified by the range
parameter, the interpolation only
exists up to 70 kilometers from the nearest measurement station.
Kriging
Kriging is an interpolation method that uses a modeled estimate of semi-variance to create an image of interpolated values that is an optimal combination of the values at known locations. The Kriging estimator requires parameters that describe the shape of a semi-variogram fit to the known data points. These parameters are illustrated by Figure 1.
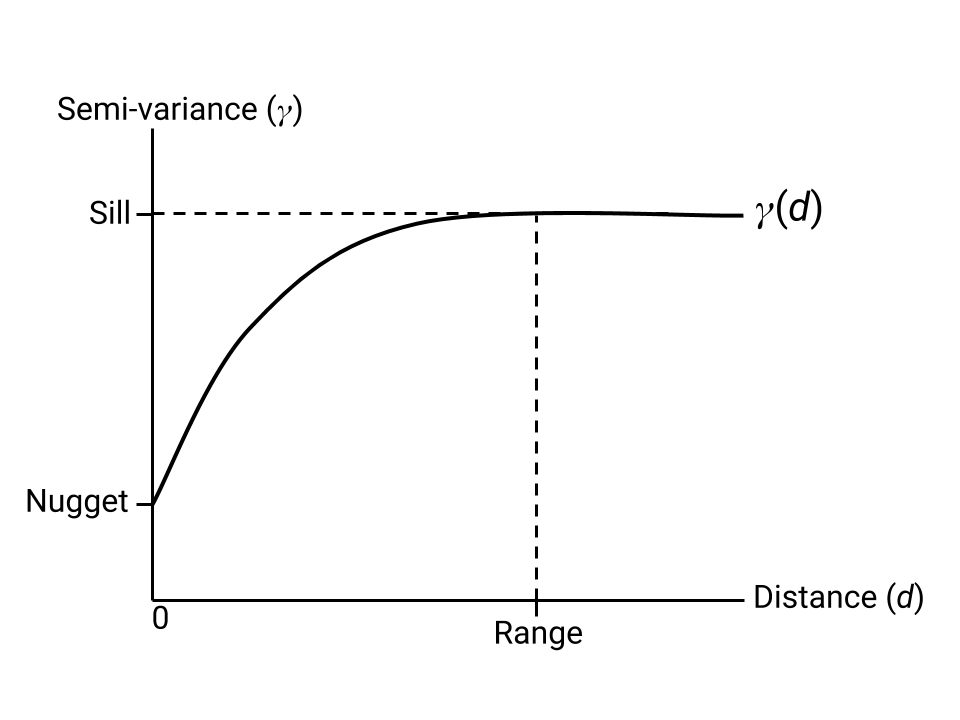
nugget
, sill
and range
parameters illustrated on a idealized variogram function.The following example samples a sea surface temperature (SST) image at random locations, then interpolates SST from the sample using Kriging:
// Load an image of sea surface temperature ( SST ). var sst = ee . Image ( 'NOAA/AVHRR_Pathfinder_V52_L3/20120802025048' ) . select ( 'sea_surface_temperature' ) . rename ( 'sst' ) . divide ( 100 ); // Define a geometry in which to sample points var geometry = ee . Geometry . Rectangle ([ - 65.60 , 31.75 , - 52.18 , 43.12 ]); // Sample the SST image at 1000 random locations . var samples = sst . addBands ( ee . Image . pixelLonLat ()) . sample ({ region : geometry , numPixels : 1000 }) . map ( function ( sample ) { var lat = sample . get ( 'latitude' ); var lon = sample . get ( 'longitude' ); var sst = sample . get ( 'sst' ); return ee . Feature ( ee . Geometry . Point ([ lon , lat ]), { sst : sst }); }); // Interpolate SST from the sampled points . var interpolated = samples . kriging ({ propertyName : 'sst' , shape : 'exponential' , range : 100 * 1000 , sill : 1.0 , nugget : 0.1 , maxDistance : 100 * 1000 , reducer : 'mean' , }); var colors = [ '00007F' , '0000FF' , '0074FF' , '0DFFEA' , '8CFF41' , 'FFDD00' , 'FF3700' , 'C30000' , '790000' ]; var vis = { min : - 3 , max : 40 , palette : colors }; Map . setCenter ( - 60.029 , 36.457 , 5 ); Map . addLayer ( interpolated , vis , 'Interpolated' ); Map . addLayer ( sst , vis , 'Raw SST' ); Map . addLayer ( samples , {}, 'Samples' , false );
The size of the neighborhood in which to perform the interpolation is specified by the maxDistance
parameter. Larger sizes will result in smoother output but
slower computations.

