A rubric
is a template that teachers can use when grading student
submissions. The Classroom API lets you to act on behalf of the
teacher to manage these rubrics, as well as read rubric grades on
student submissions.
 Figure 1.View of a sample rubric on a Classroom assignment.
Figure 1.View of a sample rubric on a Classroom assignment.
This guide explains the basic concepts and functionality of the Rubrics API. See these Help Center articles to learn about the general structure of a rubric and how rubric grading is done in the Classroom UI.
Prerequisites
This guide assumes you have the following:
- Python 3.8.6 or greater
- The pip package management tool
- A Google Cloud project .
- A Google Workspace for Education account with Google Classroom enabled and a Google Workspace for Education Plus license assigned to it. You can request an upgraded developer demo account if you don't have one.
- A test Class with at least one test student account. If you don't have a Classroom class that you can use for testing, create one in the UI and add a test student .
Authorize credentials for a desktop application
To authenticate as an end user and access user data in your app, you need to create one or more OAuth 2.0 Client IDs. A client ID is used to identify a single app to Google's OAuth servers. If your app runs on multiple platforms, you must create a separate client ID for each platform.
- Navigate to the Google Cloud Credentials page in the Google Cloud console.
- Click Create Credentials> OAuth client ID.
- Click Application type> Desktop app.
- In the Namefield, type a name for the credential. This name is only shown in the Google Cloud console. For example, "Rubrics client".
- Click Create. The OAuth client created screen appears, showing your new Client ID and Client secret.
- Click Download JSON, followed by OK. The newly created credential appears under OAuth 2.0 Client IDs.
- Save the downloaded JSON file as
credentials.json, and move the file to your working directory. - Click Create Credentials> API Keyand note the API key.
See Create access credentials to learn more.
Configure OAuth scopes
Depending on your project's existing OAuth scopes, you may need to configure addition scopes.
- Navigate to the OAuth consent screen .
- Click Edit App> Save and Continueto get to the Scopes screen.
- Click Add or Remove Scopes.
- Add the following scopes if you don't already have them:
-
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.coursework.students -
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.courses
-
- Then Click Update> Save and Continue> Save and Continue> Back to Dashboard.
See Configure the OAuth consent screen to learn more.
The classroom.coursework.students
scope enables read and write access to
rubrics (along with access to CourseWork
), and the classroom.courses
scope
allows reading and writing courses.
The scopes required for a given method are listed in the reference documentation
for the method. See courses.courseWork.rubrics.create
authorization scopes
as an example. You can see all Classroom scopes in OAuth 2.0 Scopes for Google
APIs
.
Configure the sample
In your working directory, install the Google client library for Python:
pip
install
--upgrade
google-api-python-client
google-auth-httplib2
google-auth-oauthlib
Create a file called main.py
that builds the client library and authorizes the
user, using your API key in place of YOUR_API_KEY
:
import
json
import
os.path
from
google.auth.transport.requests
import
Request
from
google.oauth2.credentials
import
Credentials
from
google_auth_oauthlib.flow
import
InstalledAppFlow
from
googleapiclient.discovery
import
build
from
googleapiclient.errors
import
HttpError
# If modifying these scopes, delete the file token.json.
SCOPES
=
[
'https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.courses'
,
'https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.coursework.students'
]
def
build_authenticated_service
(
api_key
):
"""Builds the Classroom service."""
creds
=
None
# The file token.json stores the user's access and refresh tokens, and is
# created automatically when the authorization flow completes for the first
# time.
if
os
.
path
.
exists
(
'token.json'
):
creds
=
Credentials
.
from_authorized_user_file
(
'token.json'
,
SCOPES
)
# If there are no (valid) credentials available, let the user log in.
if
not
creds
or
not
creds
.
valid
:
if
creds
and
creds
.
expired
and
creds
.
refresh_token
:
creds
.
refresh
(
Request
())
else
:
flow
=
InstalledAppFlow
.
from_client_secrets_file
(
'credentials.json'
,
SCOPES
)
creds
=
flow
.
run_local_server
(
port
=
0
)
# Save the credentials for the next run.
with
open
(
'token.json'
,
'w'
)
as
token
:
token
.
write
(
creds
.
to_json
())
try
:
# Build the Classroom service.
service
=
build
(
serviceName
=
"classroom"
,
version
=
"v1"
,
credentials
=
creds
,
discoveryServiceUrl
=
f
"https://classroom.googleapis.com/$discovery/rest?labels=DEVELOPER_PREVIEW&key=
{
api_key
}
"
)
return
service
except
HttpError
as
error
:
print
(
'An error occurred:
%s
'
%
error
)
if
__name__
==
'__main__'
:
service
=
build_authenticated_service
(
YOUR_API_KEY
)
Run the script using python main.py
. You should be prompted to sign in and
consent to OAuth scopes.
Create an assignment
A rubric is associated with an assignment, or CourseWork
, and is only
meaningful in the context of that CourseWork
. Rubrics can only be created by
the Google Cloud project that created the parent CourseWork
item
. For the
purposes of this guide, create a new CourseWork
assignment with a script.
Add the following to main.py
:
def
get_latest_course
(
service
):
"""Retrieves the last created course."""
try
:
response
=
service
.
courses
()
.
list
(
pageSize
=
1
)
.
execute
()
courses
=
response
.
get
(
"courses"
,
[])
if
not
courses
:
print
(
"No courses found. Did you remember to create one in the UI?"
)
return
course
=
courses
[
0
]
return
course
except
HttpError
as
error
:
print
(
f
"An error occurred:
{
error
}
"
)
return
error
def
create_coursework
(
service
,
course_id
):
"""Creates and returns a sample coursework."""
try
:
coursework
=
{
"title"
:
"Romeo and Juliet analysis."
,
"description"
:
"""Write a paper arguing that Romeo and Juliet were
time travelers from the future."""
,
"workType"
:
"ASSIGNMENT"
,
"state"
:
"PUBLISHED"
,
}
coursework
=
service
.
courses
()
.
courseWork
()
.
create
(
courseId
=
course_id
,
body
=
coursework
)
.
execute
()
return
coursework
except
HttpError
as
error
:
print
(
f
"An error occurred:
{
error
}
"
)
return
error
Now update main.py
to retrieve the course_id
of the test class you just
created, create a new sample assignment, and retrieve the assignment's coursework_id
:
if
__name__
==
'__main__'
:
service
=
build_authenticated_service
(
YOUR_API_KEY
)
course
=
get_latest_course
(
service
)
course_id
=
course
.
get
(
"id"
)
course_name
=
course
.
get
(
"name"
)
print
(
f
"'
{
course_name
}
' course ID:
{
course_id
}
"
)
coursework
=
create_coursework
(
service
,
course_id
)
coursework_id
=
coursework
.
get
(
"id"
)
print
(
f
"Assignment created with ID
{
coursework_id
}
"
)
#TODO(developer): Save the printed course and coursework IDs.
Save the course_id
and coursework_id
. These are needed for all rubrics CRUD
operations.
You should now have a sample CourseWork
in Classroom.
 Figure 2.View of a sample assignment in Classroom.
Figure 2.View of a sample assignment in Classroom.
Check user eligibility
Creating and updating rubrics requires that the both the user making the request, and the corresponding course owner, have a Google Workspace for Education Plus license assigned to them. Classroom supports a user eligibility endpoint to enable developers to determine the capabilities a user has access to.
Update and run main.py
to confirm that your test account has access to the
rubrics capability:
if
__name__
==
'__main__'
:
service
=
build_authenticated_service
(
YOUR_API_KEY
)
capability
=
service
.
userProfiles
()
.
checkUserCapability
(
userId
=
'me'
,
# Specify the preview version. checkUserCapability is
# supported in V1_20240930_PREVIEW and later.
previewVersion
=
"V1_20240930_PREVIEW"
,
capability
=
"CREATE_RUBRIC"
)
.
execute
()
if
not
capability
.
get
(
'allowed'
):
print
(
'User ineligible for rubrics creation.'
)
# TODO(developer): in a production app, this signal could be used to
# proactively hide any rubrics related features from users or encourage
# them to upgrade to the appropriate license.
else
:
print
(
'User eligible for rubrics creation.'
)
Create a rubric
Now you're ready to start managing rubrics.
A rubric can be created on a CourseWork
with a create()
call containing
the full rubric object, where the ID properties for criteria and levels are
omitted (these are generated on creation).
Add the following function to main.py
:
def
create_rubric
(
service
,
course_id
,
coursework_id
):
"""Creates an example rubric on a coursework."""
try
:
body
=
{
"criteria"
:
[
{
"title"
:
"Argument"
,
"description"
:
"How well structured your argument is."
,
"levels"
:
[
{
"title"
:
"Convincing"
,
"description"
:
"A compelling case is made."
,
"points"
:
30
},
{
"title"
:
"Passable"
,
"description"
:
"Missing some evidence."
,
"points"
:
20
},
{
"title"
:
"Needs Work"
,
"description"
:
"Not enough strong evidence.."
,
"points"
:
0
},
]
},
{
"title"
:
"Spelling"
,
"description"
:
"How well you spelled all the words."
,
"levels"
:
[
{
"title"
:
"Perfect"
,
"description"
:
"No mistakes."
,
"points"
:
20
},
{
"title"
:
"Great"
,
"description"
:
"A mistake or two."
,
"points"
:
15
},
{
"title"
:
"Needs Work"
,
"description"
:
"Many mistakes."
,
"points"
:
5
},
]
},
{
"title"
:
"Grammar"
,
"description"
:
"How grammatically correct your sentences are."
,
"levels"
:
[
{
"title"
:
"Perfect"
,
"description"
:
"No mistakes."
,
"points"
:
20
},
{
"title"
:
"Great"
,
"description"
:
"A mistake or two."
,
"points"
:
15
},
{
"title"
:
"Needs Work"
,
"description"
:
"Many mistakes."
,
"points"
:
5
},
]
},
]
}
rubric
=
service
.
courses
()
.
courseWork
()
.
rubrics
()
.
create
(
courseId
=
course_id
,
courseWorkId
=
coursework_id
,
body
=
body
)
.
execute
()
print
(
f
"Rubric created with ID
{
rubric
.
get
(
'id'
)
}
"
)
return
rubric
except
HttpError
as
error
:
print
(
f
"An error occurred:
{
error
}
"
)
return
error
Then update and run main.py
to create the example rubric, using your Course
and CourseWork
IDs from earlier:
if
__name__
==
'__main__'
:
service
=
build_authenticated_service
(
YOUR_API_KEY
)
capability
=
service
.
userProfiles
()
.
checkUserCapability
(
userId
=
'me'
,
# Specify the preview version. checkUserCapability is
# supported in V1_20240930_PREVIEW and later.
previewVersion
=
"V1_20240930_PREVIEW"
,
capability
=
"CREATE_RUBRIC"
)
.
execute
()
if
not
capability
.
get
(
'allowed'
):
print
(
'User ineligible for rubrics creation.'
)
# TODO(developer): in a production app, this signal could be used to
# proactively hide any rubrics related features from users or encourage
# them to upgrade to the appropriate license.
else
:
rubric
=
create_rubric
(
service
,
YOUR_COURSE_ID
,
YOUR_COURSEWORK_ID
)
print
(
json
.
dumps
(
rubric
,
indent
=
4
))
Some points about the rubric representation:
- Criterion and level order are reflected in the Classroom UI.
- Scored levels (those with the
pointsproperty), must be sorted by points in either ascending or descending order (they can't be ordered randomly). - Teachers are able to re-sort criteria and scored levels (but not unscored levels) in the UI, and that changes their order in the data.
See limitations for more caveats on rubrics structure.
Back in the UI, you should see the rubric on the assignment.
 Figure 3.View of a sample rubric on a Classroom assignment.
Figure 3.View of a sample rubric on a Classroom assignment.
Read a rubric
Rubrics can be read with the standard list()
and get()
methods.
There can be at most one rubric in an assignment, so list()
may seem
unintuitive, but it is helpful if you don't already have the rubric ID. If there
is no rubric associated with a CourseWork
, the list()
response is empty.
Add the following function to main.py
:
def
get_rubric
(
service
,
course_id
,
coursework_id
):
"""
Get the rubric on a coursework. There can only be at most one.
Returns null if there is no rubric.
"""
try
:
response
=
service
.
courses
()
.
courseWork
()
.
rubrics
()
.
list
(
courseId
=
course_id
,
courseWorkId
=
coursework_id
)
.
execute
()
rubrics
=
response
.
get
(
"rubrics"
,
[])
if
not
rubrics
:
print
(
"No rubric found for this assignment."
)
return
rubric
=
rubrics
[
0
]
return
rubric
except
HttpError
as
error
:
print
(
f
"An error occurred:
{
error
}
"
)
return
error
Update and run main.py
to fetch the rubric you added:
if
__name__
==
'__main__'
:
service
=
build_authenticated_service
(
YOUR_API_KEY
)
rubric
=
get_rubric
(
service
,
YOUR_COURSE_ID
,
YOUR_COURSEWORK_ID
)
print
(
json
.
dumps
(
rubric
,
indent
=
4
))
#TODO(developer): Save the printed rubric ID.
Note the id
property in the rubric for later steps.
Get()
works well when you have the rubric ID. Using get()
in the function
instead might look like:
def
get_rubric
(
service
,
course_id
,
coursework_id
,
rubric_id
):
"""
Get the rubric on a coursework. There can only be at most one.
Returns a 404 if there is no rubric.
"""
try
:
rubric
=
service
.
courses
()
.
courseWork
()
.
rubrics
()
.
get
(
courseId
=
course_id
,
courseWorkId
=
coursework_id
,
id
=
rubric_id
)
.
execute
()
return
rubric
except
HttpError
as
error
:
print
(
f
"An error occurred:
{
error
}
"
)
return
error
This implementation returns a 404 if there is no rubric.
Update a rubric
Updates to a rubric are done with patch()
calls. Due to the complex
structure of a rubric, updates must be done with a read-modify-write pattern,
where the entire criteria
property is replaced.
The update rules are as follows:
- Criteria or levels added without an IDare considered additions.
- Criteria or levels missingfrom before are considered deletions.
- Criteria or levels with an existing ID but modified dataare considered edits. Unmodified properties are left as is.
- Criteria or levels supplied with a new or unknown IDsare considered errors.
- The order of the new criteria and levels is considered the new UI order (with the aforementioned limitations ).
Add a function for updating a rubric:
def
update_rubric
(
service
,
course_id
,
coursework_id
,
rubric_id
,
body
):
"""
Updates the rubric on a coursework.
"""
try
:
rubric
=
service
.
courses
()
.
courseWork
()
.
rubrics
()
.
patch
(
courseId
=
course_id
,
courseWorkId
=
coursework_id
,
id
=
rubric_id
,
body
=
body
,
updateMask
=
'criteria'
)
.
execute
()
return
rubric
except
HttpError
as
error
:
print
(
f
"An error occurred:
{
error
}
"
)
return
error
In this example the criteria
field is specified for modification with an updateMask
.
Then modify main.py
to make a change for each of the aforementioned update
rules:
if
__name__
==
'__main__'
:
service
=
build_authenticated_service
(
YOUR_API_KEY
)
capability
=
service
.
userProfiles
()
.
checkUserCapability
(
userId
=
'me'
,
# Specify the preview version. checkUserCapability is
# supported in V1_20240930_PREVIEW and later.
previewVersion
=
"V1_20240930_PREVIEW"
,
capability
=
"CREATE_RUBRIC"
)
.
execute
()
if
not
capability
.
get
(
'allowed'
):
print
(
'User ineligible for rubrics creation.'
)
# TODO(developer): in a production app, this signal could be used to
# proactively hide any rubrics related features from users or encourage
# them to upgrade to the appropriate license.
else
:
# Get the latest rubric.
rubric
=
get_rubric
(
service
,
YOUR_COURSE_ID
,
YOUR_COURSEWORK_ID
)
criteria
=
rubric
.
get
(
"criteria"
)
"""
The "criteria" property should look like this:
[
{
"id": "NkEyMdMyMzM2Nxkw",
"title": "Argument",
"description": "How well structured your argument is.",
"levels": [
{
"id": "NkEyMdMyMzM2Nxkx",
"title": "Convincing",
"description": "A compelling case is made.",
"points": 30
},
{
"id": "NkEyMdMyMzM2Nxky",
"title": "Passable",
"description": "Missing some evidence.",
"points": 20
},
{
"id": "NkEyMdMyMzM2Nxkz",
"title": "Needs Work",
"description": "Not enough strong evidence..",
"points": 0
}
]
},
{
"id": "NkEyMdMyMzM2Nxk0",
"title": "Spelling",
"description": "How well you spelled all the words.",
"levels": [...]
},
{
"id": "NkEyMdMyMzM2Nxk4",
"title": "Grammar",
"description": "How grammatically correct your sentences are.",
"levels": [...]
}
]
"""
# Make edits. This example will make one of each type of change.
# Add a new level to the first criteria. Levels must remain sorted by
# points.
new_level
=
{
"title"
:
"Profound"
,
"description"
:
"Truly unique insight."
,
"points"
:
50
}
criteria
[
0
][
"levels"
]
.
insert
(
0
,
new_level
)
# Remove the last criteria.
del
criteria
[
-
1
]
# Update the criteria titles with numeric prefixes.
for
index
,
criterion
in
enumerate
(
criteria
):
criterion
[
"title"
]
=
f
"
{
index
}
:
{
criterion
[
'title'
]
}
"
# Resort the levels from descending to ascending points.
for
criterion
in
criteria
:
criterion
[
"levels"
]
.
sort
(
key
=
lambda
level
:
level
[
"points"
])
# Update the rubric with a patch call.
new_rubric
=
update_rubric
(
service
,
YOUR_COURSE_ID
,
YOUR_COURSEWORK_ID
,
YOUR_RUBRIC_ID
,
rubric
)
print
(
json
.
dumps
(
new_rubric
,
indent
=
4
))
The changes should now be reflected for the teacher in Classroom.
 Figure 4.View of the updated rubric.
Figure 4.View of the updated rubric.
View rubric-graded submissions
For now, student submissions can't be graded with a rubric by the API, but you can read rubric grades for submissions that have been graded with a rubric in the Classroom UI.
As a student in the Classroom UI, complete and turn in your sample assignment . Then as the teacher, manually grade the assignment using the rubric .
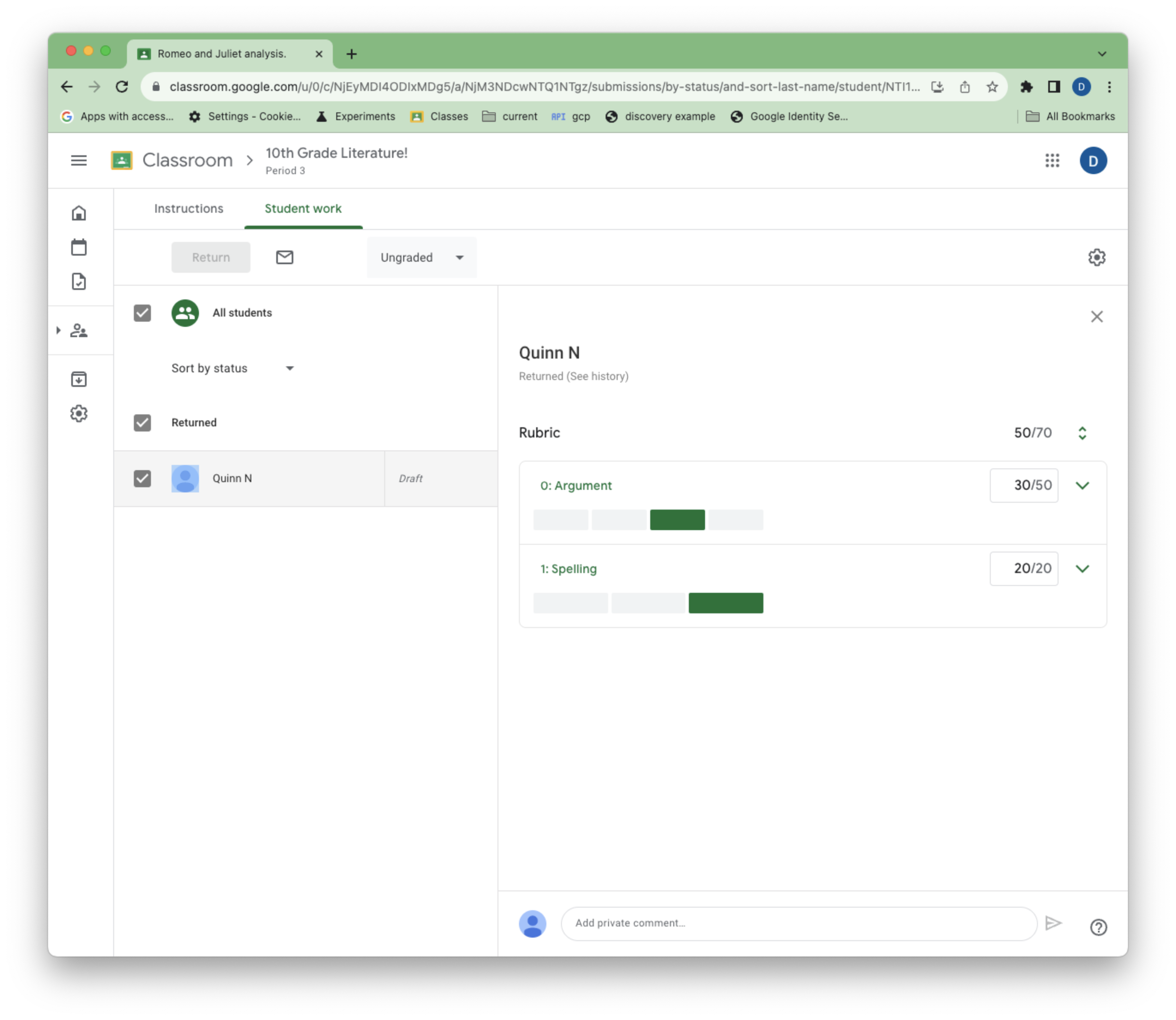 Figure 5.Teacher view of the rubric during grading.
Figure 5.Teacher view of the rubric during grading.
StudentSubmissions
that have been graded with a rubric have two new
properties: draftRubricGrades
and assignedRubricGrades
, representing the
points and levels chosen by the teacher during the draft and assigned grading
states, respectively.
You can use the existing studentSubmissions.get()
and studentSubmissions.list()
methods to view graded submissions.
Add the following function to main.py
to list student submissions:
def
get_latest_submission
(
service
,
course_id
,
coursework_id
):
"""Retrieves the last submission for an assignment."""
try
:
response
=
service
.
courses
()
.
courseWork
()
.
studentSubmissions
()
.
list
(
courseId
=
course_id
,
courseWorkId
=
coursework_id
,
pageSize
=
1
)
.
execute
()
submissions
=
response
.
get
(
"studentSubmissions"
,
[])
if
not
submissions
:
print
(
"""No submissions found. Did you remember to turn in and grade
the assignment in the UI?"""
)
return
submission
=
submissions
[
0
]
return
submission
except
HttpError
as
error
:
print
(
f
"An error occurred:
{
error
}
"
)
return
error
Then update and run main.py
to view the submission grades.
if
__name__
==
'__main__'
:
service
=
build_authenticated_service
(
YOUR_API_KEY
)
submission
=
get_latest_submission
(
service
,
YOUR_COURSE_ID
,
YOUR_COURSEWORK_ID
)
print
(
json
.
dumps
(
submission
,
indent
=
4
))
The draftRubricGrades
and assignedRubricGrades
contain:
- The
criterionIdof the corresponding rubric criteria. - The
pointsthe teacher assigned for each criterion. This could be from the level selected, but the teacher could also have overwritten this. - The
levelIdof the level chosen for each criterion. If the teacher did not choose a level, but still assigned points for the criterion, this field isn't present.
These lists only contain entries for the criteria in which a teacher either
selected a level or set points. For example if a teacher chooses to only
interact with one criterion during grading, the draftRubricGrades
and assignedRubricGrades
would only have one item, even if the rubric has many
criteria.
Delete a rubric
A rubric can be deleted with a standard delete()
request. The following code
shows an example function for completeness, but since grading has already
started, you can't delete the current rubric:
def
delete_rubric
(
service
,
course_id
,
coursework_id
,
rubric_id
):
"""Deletes the rubric on a coursework."""
try
:
service
.
courses
()
.
courseWork
()
.
rubrics
()
.
delete
(
courseId
=
course_id
,
courseWorkId
=
coursework_id
,
id
=
rubric_id
)
.
execute
()
except
HttpError
as
error
:
print
(
f
"An error occurred:
{
error
}
"
)
return
error
Export and import rubrics
Rubrics can be manually exported to Google Spreadsheets for re-use by teachers.
In addition to specifying rubric criteria in code, it's possible to create and
update rubrics from these exported sheets by specifying the sourceSpreadsheetId
in a rubric body instead of criteria
:
def
create_rubric_from_sheet
(
service
,
course_id
,
coursework_id
,
sheet_id
):
"""Creates an example rubric on a coursework."""
try
:
body
=
{
"sourceSpreadsheetId"
:
sheet_id
}
rubric
=
service
.
courses
()
.
courseWork
()
.
rubrics
()
.
create
(
courseId
=
course_id
,
courseWorkId
=
coursework_id
,
body
=
body
)
.
execute
()
print
(
f
"Rubric created with ID
{
rubric
.
get
(
'id'
)
}
"
)
return
rubric
except
HttpError
as
error
:
print
(
f
"An error occurred:
{
error
}
"
)
return
error

